An 80-year-old woman who had undergone aortic valve replacement for aortic valve stenosis was hospitalized for congestive heart failure and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation 4 years prior to the current presentation. At that time, she started receiving oral amiodarone, and she took amiodarone for 4 years. She visited our hospital because dementia had progressed over the previous 2 months, leaving her incapacitated and unable to care for herself. She presented with a blood pressure of 120/48 mmHg, a regular pulse of 52 beats per minute, and a body temperature of 35.6┬░C. Blood tests revealed liver dysfunction and hypothyroidism. Her laboratory findings were as follows: aspartate aminotransferase, 86 IU/L; alanine aminotransferase, 76 IU/L; total bilirubin, 1.82 mg/dL; thyroid-stimulating hormone, 91.29 ╬╝U/mL (reference range, 0.24 to 3.72); free thyroxine level, 0.31 ng/dL (reference range, 0.94 to 1.52); free triiodothyronine level, 0.92 pg/mL (reference range, 2.01 to 3.72); thyroglobulin antibody, < 40 U/mL; and thyroid peroxidase antibody, < 50 U/mL.
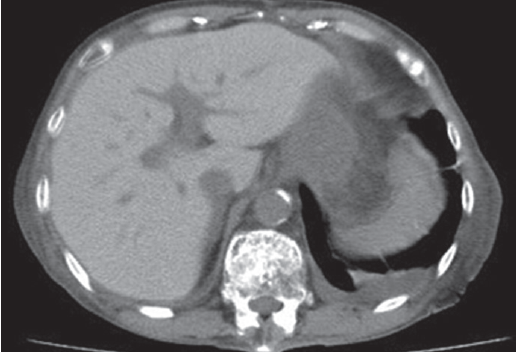
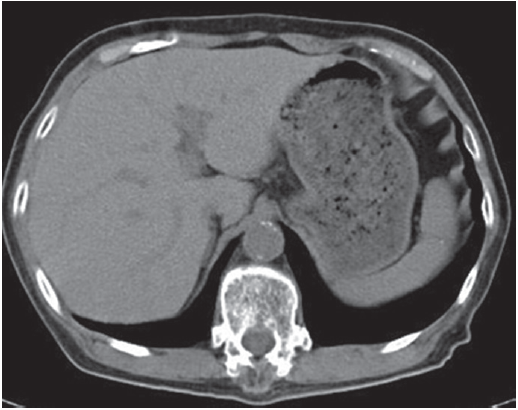
Abdominal plain computed tomography (CT) revealed an increased liver density (Fig. 1). These disorders were determined to be attributable to an overdose of amiodarone, and the drug was discontinued. Thyroid hormone replacement relieved her dementia; the dosage of thyroid hormone preparations was decreased over time and eventually discontinued. Moreover, the liver dysfunction gradually resolved. An abdominal plain CT scan performed 1 year later revealed a decrease in the high liver density (Fig. 2). During this period, no recurrence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation was detected.
In patients receiving long-term oral administration of amiodarone, CT scans may reveal an increased liver density due to iodine deposition in this organ and phospholipidosis caused by disordered metabolism. One report described a correlation between elevated CT values in the liver and desethylamiodarone concentrations in tissue. CT scans and blood tests for liver and thyroid function are useful for monitoring adverse reactions to amiodarone.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





