 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 35(6); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Global incidence of hypertension is estimated to be, in excess of, one billion people, and given the efficacy of soluble dietary fibers, in particular, Psyllium, to positively impact blood pressure in patients with hypertension, it is of clinical importance that consensus on its supplementation be established. Therefore, the aim of the study was systematically review and meta-analyze the effect of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure of hypertensive patients in randomized controlled trials.
Methods
We searched six universal databases including; Pubmed/Medline, Ovid, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, Embase, and Scopus until November 2018. Both combined and stratified analyzes were conducted. A fixed-effects or random- effects model was used to assess the mean effect sizes.
Results
An eventual 11 trials with 592 participants were considered as eligible for inclusion in the present meta-analysis. The meta-analysis revealed a significant reduction of 2.04 mmHg in systolic blood pressure (weighted mean difference, –2.04; 95% confidence interval, –2.82 to –1.63; p < 0.001). Whilst meta-regression highlighted that the hypotensive effect of psyllium was stronger in subjects with higher baseline blood pressure.
Observational and experimental studies suggest dietary fiber intake may confer a beneficial effect on blood pressure, in both normotensive and hypertensive patients [1-3]. Whilst clinical trials of fiber supplementation have shown wide variation in blood pressure response [2]; in trials with purified fiber supplements, reductions in blood pressure are, ostensibly, larger than in trials with fiber-rich foods. This difference in blood pressure response is putatively explained by fiber dose, type of fiber consumed, or better compliance with dietary supplements than with high-fiber diets [2].
It is well known that a dietary approach, adjunct to traditional pharmacotherapy, is a useful tool for the management of the cardiovascular (CV) risk, not only in patients affected by relevant metabolic diseases, such as hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, and hypertension, but also at a broader, population level [4,5]. Moreover, it has been asserted that the intake of dietary fibers either contained in the food or supplemented [6] may be inversely related to blood pressure levels and may conceivably inhibit hypertension development as well [7,8]. Accordingly, an increase in dietary fibers has been recommended by the World Health Organization as a safe and practical approach to CV risk reduction in hypertensive populations [9].
Despite empirical evidence affirming the utility of dietary fibers, no specific suggestion has been provided regarding the most effective fiber to be supplemented. In fact, “dietary fiber” is an umbrella term for a variety of plant substances that are resistant to digestion by human gastrointestinal enzymes [10,11]. Dietary fibers may be dichotomized into two major groups, dependent upon their solubility in water. In humans, the structural or matrix fibers (lignin’s, cellulose, and some hemicelluloses) are insoluble, whereas the natural gel-forming fibers (pectin’s, gums, mucilage’s, and the remainder of the hemicelluloses) are soluble [10,11]. Soluble dietary fibers encompass an extensive array of compounds (primarily of plant origin) with known physiological benefits, including laxation, and improvements in glucose homeostasis and dyslipidemia [12]. Among the most popular, supplmentable, soluble dietary fibers, globally, are the seed husks of psyllium (Plantago spp., in particular P. ovata), also known as ispaghula, which is often used to enrich cereals and other food items. Psyllium husks encompass a mixture of neutral and acid polysaccharides, containing galacturonic acid, with a 70 to 30 ratio of soluble/ insoluble fiber. Psyllium has been administered safely in children, adolescents and adults, and has been shown to improve hypercholesterolemia [13-15].
Furthermore, soluble fiber supplementation, in the form of psyllium, has also been suggested to improve the control of body weight, mainly by slowing the gastric emptying [16], which may further contribute to CV risk reduction, concomitant to a lipid lowering effect. Furthermore, as excess weight, above that of a healthy level, is associated with an increased risk of inhibited blood pressure control [17,18]; it is therefore plausible that fiber intake can exert a hypotensive effect and is strongly manifest in patients with existing hypertension.
Current incidence of hypertension is estimated to be over one billion, globally [19], and given the antecedence of soluble dietary fibers, in particular, Psyllium, to positively effect blood pressure in patients with hypertension, it is of clinical importance that consensus on its supplementation be established. Thus, the aim of the study was systematically review and meta-analyze the effect of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure of hypertensive patients in randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
The present systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted in adherence with the PRISMA guidelines [20] and Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews [21]. We searched six universal databases including Pubmed/Medline, Ovid, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, Embase, and Scopus until November 2018. We systematically searched for RCTs to investigate the efficacy of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure. Additionally, we manually searched to detect additional potentially eligible trials in the reference lists of relevant publications. We used both free-text and MeSH terms as follow: (“psyllium” OR “mucilage” OR “lunelax” OR “Metamucil” OR “ispaghul” OR “plantago” OR “isogel” OR “reguval”) AND (“Blood Pressure” [MeSH] OR “Blood Pressure” OR “Hypertension” [MeSH] OR “Prehypertension” [MeSH] OR “SBP” OR “DBP”).
Study selection were undertaken independently by two authors (E.A. and M.S.), with discrepancies resolved by consensus and discussion with a third investigator (S.J.). E.A. and M.S. independently carried out the initial search. Duplicated were removed, and titles/abstracts of each study were screened. They independently detected each study as excluded or requiring further evaluation. If there were lack of necessary data or the full text of eligible studies were unavailable, we emailed the corresponding author for the comprehensive details. We included the original studies that met the following criteria: (1) RCT study design with psyllium or psyllium rich foods, as the intervention, (2) Studies with either Persian or English languages, (3) Studies with measured systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) at the baseline and end of the trial (mean changes and standard deviations or sufficient data for calculating if they were no available in the text).
We extracted the following items from studies and recorded as the Table 1: the first author, year of publication, location of study, the sample size of intervention and control groups, characteristics of participants (sex and age), design of RCT, baseline dietary/intervention dose of psyllium (gram per day), clinical conditions of participants, duration of study, form of psyllium administration, significant reporting outcomes of trials, baseline SBP and DBP in the intervention and control groups.
The quantitative Jadad scale was used to assess the quality of included trials. The score ranges from 0 to 5, in which higher scores indicating better quality. This includes three main parameters; randomization, blinding and monitoring of subject withdrawals. The Jadad scoring approach is as follows; one point was given for stating random allocation and one additional point if the method was appropriate. One point was given when it was mentioned that the trial was blinded and one extra point if the method of blinding was suitable. One point was withdrawn if the method of randomization or blinding was inappropriate. Reporting of dropouts was given one point if the fate of all participants is known [22].
All analyses were conducted using Review Manager Software (Review Manager 5.3, Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, England) and Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (version 3.2, Biostat).
Mean difference and standard deviation (SD) of both SBP and DBP values in baseline and end of trial in intervention and control groups were extracted or calculated to estimate pooled effect size. SD was estimated by (SD = SEM × sqrt [n]; n = number of subjects) when standard error of mean (SEM) was reported. In the case of missed SD values, we converted the reported median values with confidence intervals or ranges to mean and SD, based on the method of Hozo et al. [23]. Statistical heterogeneity was estimated using I2 statistic test and chi-square on Cochrane’s Q statistic test. Significant inter-study heterogeneity was defined as I2 > 50% or p < 0.05 for heterogeneity. Based on the heterogeneity between included studies, a random or fixed effects model was used in the meta-analysis. However, based on the Cochrane Handbook Guideline, the random effects model is preferable. Due to detect source of possible heterogeneity, stratified analysis was applied. Moreover, we assessed the influence of individual studies on the overall effect size by performing sensitivity analyses according to the Cochrane guidelines [24].
We assessed the potential publication bias using Egger’s weighted regression test, Begg’s rank correlation method and visual inspection of funnel plots, in which an asymmetric shape of funnel-plot can bean indicator of a publication bias. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Fig. 1 presents a detailed flow chart of the study selection and trials included in the present meta-analysis. A total of 218 articles were identified from the initial database search, in which 139 articles were excluded for duplicates. After screening the titles and abstracts of eligible studies, 63 articles were excluded because they were experimental (n = 40) or in vitro (n = 12) studies, non-original research including review, letters, editorials and case reports articles (n = 4), non-English/Persian papers (n = 1) and research with entirely unrelated to the topic (n = 6). The remaining 16 full-text papers were assessed for possible eligibility, in which additional seven studies were excluded because they were not RCTs, or they lacked the necessary data of SBP or DBP for meta-analysis after trying to contact the authors. Several studies including, Burke et al. [25] and Jenkins et al. [26] investigated the effect of psyllium on different groups separated by participants characteristics and according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [27], each arm was considered independently in the evaluation. Finally, nine studies with 11 trials fulfilled the eligibility criteria and included in meta-analysis [25,26,28-34].
Details of the trial characteristics are given in Table 1. The included 11 trials were published between 1988 and 2017. Four of the included trials were carried out in USA [26,28,30], two in Australia [25], two in Pakistan [29,33], two in Italy [31,34], and the other one trial was performed in Iran [32]. One trial included only male participants [28], one trial included only female participants [32] and the remaining nine trials were conducted in both male and female participants [25,26,29-31,33,34]. In total, 11 trials with 592 participants (intervention, n = 300 and placebo, n = 292), were included in the present meta-analysis.
The sample size of included trials ranged from nine to 65 subjects. The age of the participants ranged from 25 to 70 years. The clinical statuses of participants of included trials were as follow: two trials with type 2 diabetes mellitus [32,34], six trials with hypercholesterolemia and/or hyperlipidemia [26,28-30,33], three trials with hypertension [25,31]. Amongst included studies, based on the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) updated guidelines, three trials included normative participants [26,28,30], one trial included elevated blood pressure subjects [32] and the other seven trials were performed in participants with stage 1 or stage 2 hypertensive disorders [25,26,29,31,33,34]. Duration of intervention ranged from 4 weeks to 6 months, and the daily psyllium dosage varied from 3.7 to 15 g. No specific reported side effects were mentioned after psyllium supplementation in the included trials. Nine trials used parallel design [25,28-34], while other two trials were conducted in the cross-over designation [26]. The mean value of baseline SBP and DBP ranged from 117.5 to 146.5 mmHg and 71 to 93.01 mmHg, respectively.
Results of the quality assessment of the included trials based on the Jadad scale are shown in Table 2. Two out of 11 trials clearly described the blinding approach [31,32], four of the included trials (four of 11) showed the appropriate explanation of randomization method [25,31,32]. All trials stated withdrawals and dropouts descriptions [25,26,28-34]. Therefore, based on previous studies, which indicated the trials with Jadad score of more than three as the high quality trials, eight included trials were classified as high-quality trials [25,28-33] and the other 3 trials were categorized as low quality trials [26,34].
From visual inspection of the funnel plots, which is presented in Fig. 2, neither changes in SBP nor changes in DBP showed potential publication bias of psyllium administration on outcomes. Results of the Begg’s rank correlation test were not significant (SBP: Kendall’s Tau with continuity correction: –0.40; z = 1.71; two-tailed p = 0.08; DBP: Kendall’s Tau with continuity correction: 0.00; z = 0.0; two-tailed p = 1.00). Moreover, Egger’s linear regression test confirmed that there were no significant publication biases for both SBP and DBP: SBP (intercept: –0.008; standard error: 0.33; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.76 to 0.75; t = 0.02, df = 9; two-tailed p = 0.98) and DBP (intercept: 0.29; standard error: 0.62; 95% CI, –1.11 to 1.70; t = 0.47, df = 9; two-tailed p = 0.64).
We performed a meta-analysis to examine reported quantitative data of 592 subjects from 11 trials regarding SBP and DBP. The impact of psyllium of SBP and DBP was reported in all included trials. Three [29,31] and one [29] out of the 11 trials included in the present meta- analysis reported a statistically significant improvements in SBP and DBP after psyllium administration, respectively. As shown in Fig. 3, the pooled effect of psyllium supplementation revealed significant reduction of 2.22 mmHg in SBP (weighted mean difference [WMD]: –2.22 mmHg; 95% CI, –2.82 to –1.63, p < 0.001). The meta- analysis of the effect of psyllium supplementation did not show significant improvement on DBP (WMD: –0.72 mmHg; 95% CI, –1.98 to –0.53; p = 0.25). The test for overall heterogeneity effect revealed no significant heterogeneity in the effect of psyllium administration between the included studies according to both chi-square and I2 test, suggesting no possible heterogeneity among trials regarding to SBP (heterogeneity: Tau² = 0.00; Chi² = 7.55, df = 10 [p = 0.67]; I² = 0%). Additionally, meta-analysis did not suggest any heterogeneity between studies concerning DBP (heterogeneity: Tau² = 1.15; Chi² = 14.72, df = 10 [p = 0.26]; I² = 32%). However, we tried to clarify the effect of possible moderators by stratified analysis based on participants’ characteristics.
Stratified analysis was conducted to evaluate the association of effect size on SBP with baseline blood pressure (normotensive, elevated BP and hypertensive subjects), duration of follow-up (cut-off point = 8 weeks), dosage of supplementation (cut-off point = 10.2 g/day) and quality of studies (high vs. low quality) (Table 3). With respect to baseline blood pressure, a statistically significant reduction in SBP was detected in the subset of hypertensive patients. However, normotensive and elevated blood pressure groups did not show any significant beneficial effect of psyllium on SBP. The lowering effect of psyllium on DBP was not significant in each subgroups including normotensive and elevated BP subjects, whereas the supplementation reduced DBP in hypertensive subjects. As far as the duration of follow-up is concerned, a significant reduction of SBP and DBP was detected in subsets of studies divided according to duration of supplementation of ≥ 8 weeks ([SBP WMD = –2.28; 95% CI, –2.88 to –1.68; p < 0.001], [DBP WMD = –1.41; 95% CI, –2.27 to –0.55; p = 0.001]). Subgroup analysis based on dose of psyllium consumption showed significant improvements in lower dose groups regarding both SBP (WMD = –2.14; 95% CI, –2.79 to –1.49; p < 0.001) and DBP (WMD = –1.41; 95% CI, –2.48 to –0.33; p = 0.01) with a SBP-lowering effect of higher dose of psyllium consumption (WMD = –2.68; 95% CI, –4.15 to –1.20; p < 0.001). Notably, subgroup analysis based on quality of studies indicated that psyllium administration significantly reduced both SBP and DBP in subsets of high-quality studies in compared with low quality studies by 2.26 mmHg (95% CI, –2.86 to –1.66; p < 0.001) and 1.32 mmHg (95% CI, –2.19 to –0.45; p < 0.001), respectively (Table 3).
Sensitivity analysis was performed to evaluate the effect of single trials with a high risk of bias on overall estimated pooled effect size. After excluding each trial, the lowering effects of psyllium on SBP did not significantly change the overall pooled effect size. Therefore, the effect of psyllium on SBP remained significant which ranged from –2.11 (95% CI, –2.75 to –1.47) to –2.38 (95% CI, –3.75 to –1.00) in SBP, suggesting that the risk of bias did not considerably influence the final results (Fig. 4).
A meta-regression analysis was conducted to evaluate the effect of potential moderators on the overall estimated effect size. The dosage and duration of supplementation were not associated with SBP-lowering activity (dosage [slope: 0.29; 95% CI, −0.63 to 1.23; p = 0.53]; duration of supplementation [slope: –0.08; 95% CI, −0.21 to 0.05; p = 0.24]) (Fig. 5) and DBP-lowering activity (duration of supplementation [slope: –0.06; 95% CI, −0.17 to 0.05; p = 0.27]) (Fig. 5) of psyllium supplementation. However, meta-regression analysis showed a linear relationship between the baseline blood pressure and effect size of psyllium administration on SBP and DBP, indicating that the hypotensive effect of psyllium on blood pressure became stronger in subjects with higher baseline SBP and DBP ([SBP slope: –0.28; 95% CI, –0.55 to –0.02; p = 0.03]; [DBP slope: –0.17; 95% CI, –0.28 to –0.06; p = 0.002]) (Fig. 5).
The prevention and alleviation of disease is a principal aim of healthcare professionals. With an estimated one billion worldwide cases, hypertension constitutes the number one health risk factor quantified in terms of disability adjusted life years, which are the sum of years of life lost due to premature mortality and years lived with disability [35]. In 2015, 41% of disability adjusted life years were attributed to elevated SBP alone [36]. It is one of the first causes of premature cardiovascular disease and therefore any viable means of combatting such a prevalent problem is warranted. Although traditionally treated with pharmacotherapy, there is an increasing interest in using alternative methods of treatment. Moreover, it has been asserted that the intake of dietary fibers either contained in food or supplemented [6] are inversely related to blood pressure levels and can elicit hypotensive effects in hypertensive patients [3,15]. Therefore, given the antecedence of soluble dietary fibers, and in particular, psyllium, to elicit hypotensive effects in patients with hypertension, it is of clinical importance that consensus on its supplementation be established, or at least further evidenced. Thus, the aim of the study was systematically review and meta-analyze the effect of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure of hypertensive patients in RCTs. In accord with the aforementioned aim, the principal findings of this study were, (1) meta-regression of the data showed that higher baseline DBP leads to higher reductions of blood pressure after Psyllium supplementation, (2) longer duration and high-quality studies yielded a significant reduction in blood pressure, and (3) no heterogeneity was observed in the meta-analysis (for both SBP and DBP); therefore, we can assert veracity in our findings.
Previous randomized clinical trials and meta-analyses have demonstrated the efficacy of soluble fibers, and, in particular, psyllium, as anti-hypercholesterolemic agents in moderately hypercholesterolemic patients and improves glycaemic control in patients with diabetes [37]. Grundy et al. [38] previously observed that a long-term treatment with high doses of soluble fibers could significantly improve parameters related to the insulin-resistance, the pathogenetic basis of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes, whilst the present meta-analysis supported the use of longer duration supplementation for greater improvement in blood pressure. Previously, a small antihypertensive effect of fiber supplementation was reported in Streppel et al. [6]; however, the minimal improvement reported, compared to the present study, can viably be explained by the fact that the meta-analysis included numerous studies that have been carried out on small patient samples, studies with short treatment duration; and low dosed fiber supplementation. Whilst in a meta-analysis carried out by Whelton et al. [39], fiber supplementation was associated with a significant blood pressure decrease in hypertensive subjects, comparable to that observed in our study. Moreover, in the present study, antihypertensive effects occurred to a greater magnitude when supplementation was longer than 8 weeks. Such additional findings in the present study may be attributable to the fact that we incorporated a larger number of studies, with greater sample sizes, respectively, and focused on psyllium supplementation only, thereby reducing potential heterogeneity and abate the influence of uncontrolled moderators; enabling us to affirm veracity in our findings.
Dietary fiber or nonstarch polysaccharide is a collective term for a variety of plant substances that are resistant to digestion by human gastrointestinal enzymes. The structural fibers (cellulose, lignin, and hemicelluloses) are insoluble whereas the natural gel-forming fibers (pectins, gums, and mucilages) are soluble [40]. In the human diet, insoluble fiber is mainly derived from whole-grain products and soluble fiber from fruits, vegetables, pulses, and oats [40]. Little is known about the potential mechanisms through which dietary fiber might lower blood pressure. Dietary fiber reduces the glycaemic index of foods, thereby attenuating insulin response [41]. Insulin may play a role in blood pressure regulation [42] and dietary fiber has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and vascular endothelial function [41,43]. Furthermore, there is putative evidence that fiber, particularly soluble types, improve mineral absorption in the gastrointestinal system [44,45], which may confer an indirect, but favourable effect on blood pressure. Whilst such ostensible benefits of dietary fiber are known, alteration of diets to confer said benefits is much more problematic. Therefore, implementing supplmentable dietary fiber, such as Psyllium, may be beneficial to facilitate adherence to increased dietary fiber intake.
Several physiological mechanisms have been proposed for the antihypertensive effect of soluble fiber such as psyllium. Consumption of viscous fiber increases the viscosity of the digesta, delaying the absorption of nutrients within the gastrointestinal system, which has been purportedly associated with postprandial glucose excursion blunting and improvement of systemic insulin resistance [46]. Insulin resistance, with concurrent, compensatory insulinaemia, is a pivotal pathophysiological mechanism in the development of endothelial dysfunction and hypertension [47]; indeed, numerous accompanying mechanisms are characterized in this respect, including increases in renal sodium reabsorption, sympathetic nervous system activation, transmembrane ion transport alteration, and hypertrophy of resistance vessels, partially mediated by mitogen activated protein kinase pathway activation [48-50]. Intake of viscous fibers, such as psyllium, concomitantly produces a modest effect on weight management/reduction via a satiety linked mechanism, in addition to reductions in blood pressure being linearly correlated with reductions in body mass [51,52]. Moreover, Khan et al. [53] suggested that blood pressure reductions may be dependent on starting body weight, which may conceivably account for the larger reductions observed in hypertensive individuals. However, it is probable that numerous pathways contribute to the observed reduction in blood pressure, and further mechanistic studies are needed to elucidate the putative pathways and mechanism of action.
Whilst Kahn et al. [53] was the first study to report that supplementation of psyllium fiber can significantly lower SBP, the present meta-analysis highlighted a number of novel findings; meta-regression of the data showed that higher baseline DBP leads to higher reductions of blood pressure after psyllium supplementation, which agrees with the subgroup analysis in which hypertensive patients showed significant reductions in blood pressure in comparison to normotensive/ patients with elevated blood pressure, in addition to longer duration and high-quality studies showed a significant reduction of blood pressure. Whilst contrary to Khan et al. [53], who included low quality studies in addition to reporting substantial heterogeneity in the analysis of SBP and DBP, which remained unexplained by sensitivity analyses, we found no heterogeneity in the present meta- analysis (for both SBP and DBP); thereby enabling us to assert our findings as firm evidence for the SBP-lowering effect of psyllium supplementation. A further strength of the present meta-analysis is that the findings are generalizable, given trials included participants that were both healthy and non-healthy (hypertensive). Further strengths in our meta-analysis include that whilst the number of studies included for analyses in previous meta-analyses, specifically regarding Psyllium, has been limited; in the present study, we were able to analyse a large number of studies. Further, the sample sizes included in numerous, previous studies regarding Psyllium was small; contrastingly, the respective sample sizes in our study was large. Moreover, further compounding divergent findings in the literature is the fact that meta- analyses, thus far, have not focused on one, specific fiber, whereas we concentrated on a single dietary fiber to reduce the chance of any possible heterogeneity and decrease the influence of moderators, enabling greater veracity in the results we obtained.
Notwithstanding, the current study has some limitations worth considering. A number of included trials were small in sample size, and it has been asserted by Sterne and Egger [54] that it is probable for studies with small sample sizes to report bigger effect sizes in intervention arms than studies with larger participant pools, nevertheless, this was out of the operational control of the meta-analysis. A further limitation of the present study was the paucity of eligible studies, highlighting the need for more, high-quality RCT’s. It is conceivable that other unexplored sources of heterogeneity may have included differences in supplementation administration (capsule vs. food source), differential or habitual fiber consumption levels at baseline, severity of patient medical conditions and comorbidities, or, indeed, disparity in clinical blood pressure measuring devices such as ambulatory monitoring, sphygmomanometers or auscultation vs oscillation-based tools.
The results of current meta-analysis study support the use of Psyllium supplementation in patients who have hypertension. The present study highlighted, through meta-regression, that higher baseline DBP leads to higher reductions of blood pressure after psyllium supplementation. Moreover, this work elucidated that studies of higher quality, and longer supplementation period yield significant reductions of blood pressure. Finally, through robust analyses, we highlighted no heterogeneity was manifest, for both SBP and DBP, indicating veracity in the observed results. Given the overarching benefits evident, particularly for hypertensive patients, and concomitant lack of reported side effects, health care providers and clinicians should consider the use of psyllium supplementation for the treatment or abatement of hypertension, or hypertensive symptoms.
1. Psyllium supplementation revealed significant reduction of 2.22 mmHg in systolic blood pressure (SBP). The significant reductions in SBP and DBP were detected in the subset of hypertensive patients. However, normotensive and elevated blood pressure groups did not show any significant beneficial effect of psyllium on blood pressure.
2. Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure were reduced in subsets of studies with duration of supplementation of ≥ 8 weeks.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of literature search and article selection. RCT, randomized controlled trial; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
Figure 2.
Funnel plot of included studies detailing publication bias: (A) systolic blood pressure; (B) diastolic blood pressure.
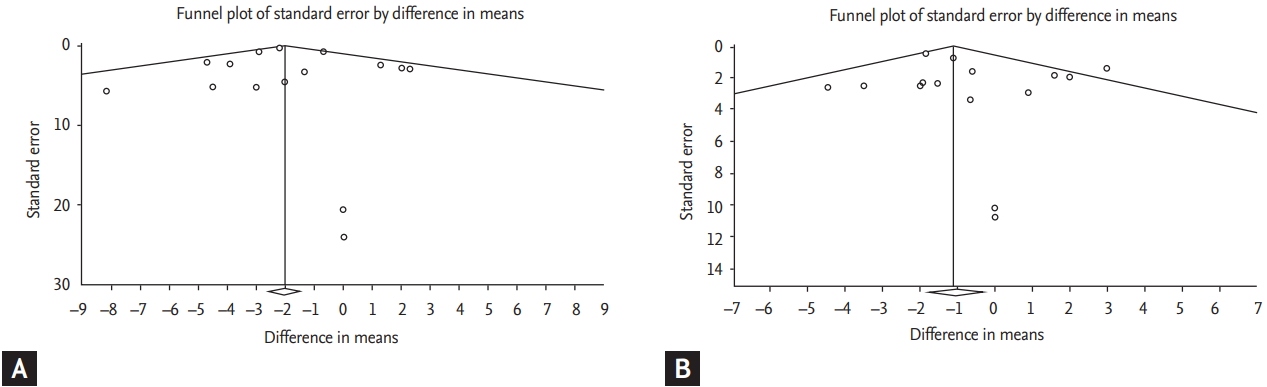
Figure 3.
Forest plot representing the pooled effect of psyllium supplementation on (A) systolic blood pressure, and (B) diastolic blood pressure by using a random effects model. CI, confidence interval.
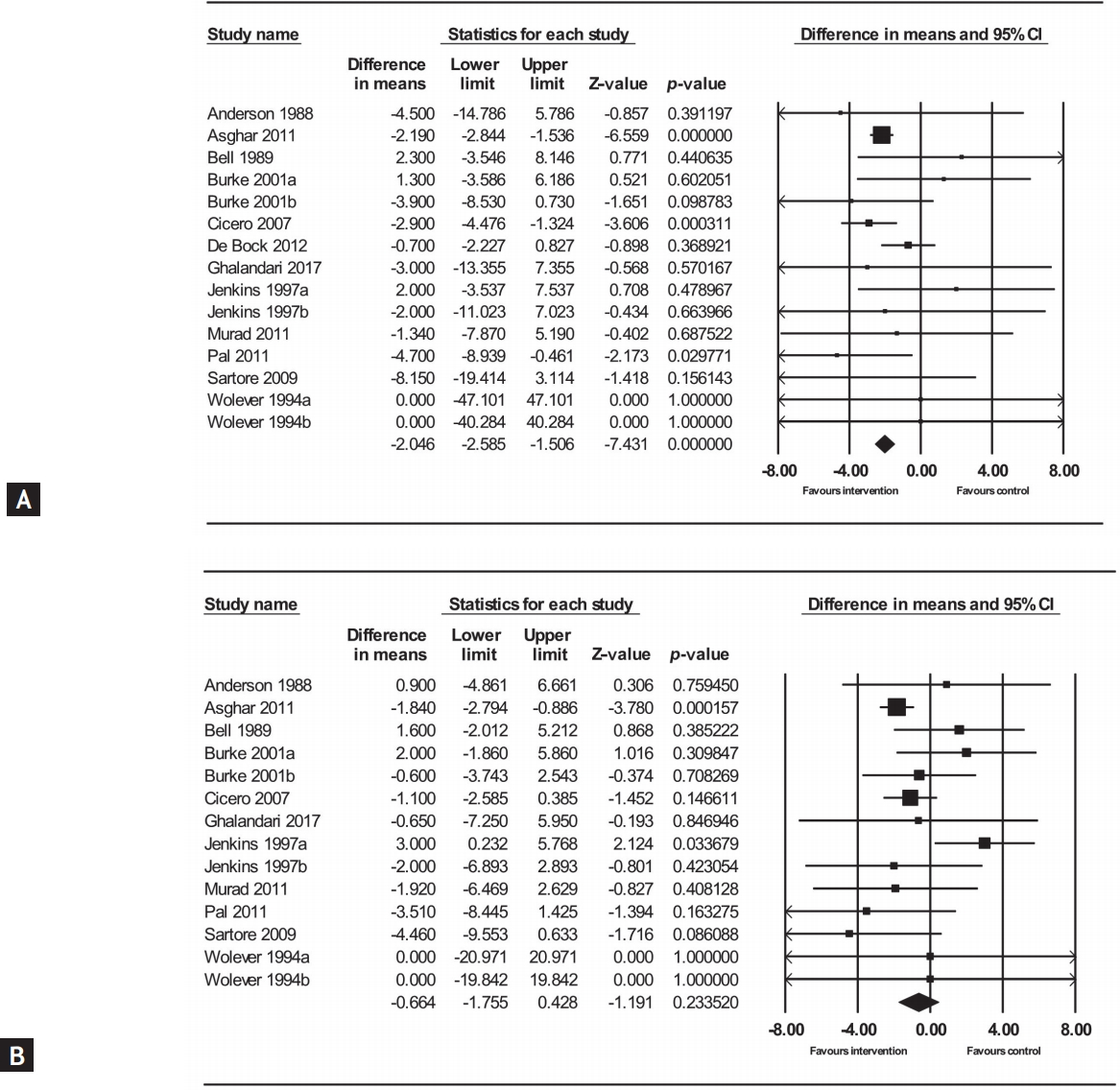
Figure 4.
Sensitivity analysis of the effect of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure. CI, confidence interval.
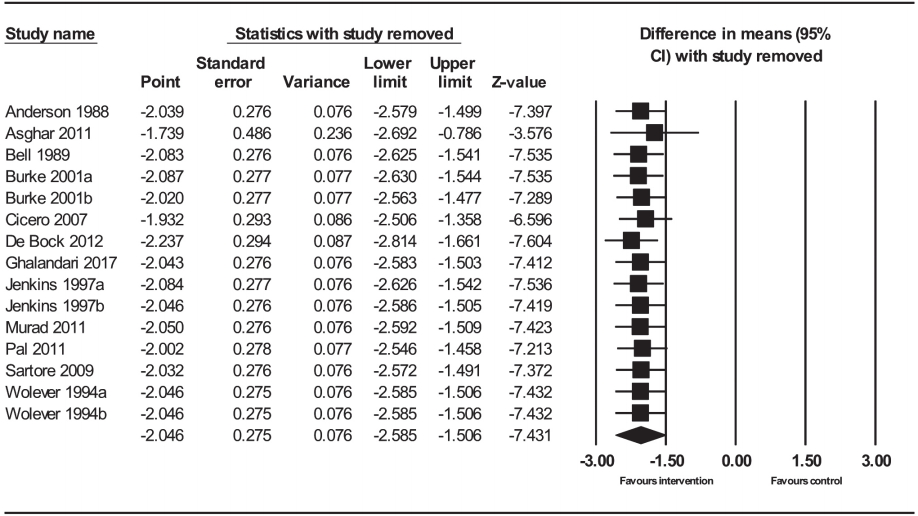
Figure 5.
(A) Meta-regression plot of the association between mean changes in systolic blood pressure (SBP) after psyllium administration with treatment dosage. (B) Meta-regression plot of the association between mean changes in SBP after psyllium administration with duration of intervention. (C) Meta-regression plot of the association between mean changes in diastolic blood pressure (DBP) after psyllium administration with duration of supplementation. (D) Meta-regression plot of the association between mean changes in DBP after psyllium administration with baseline DBP in intervention groups. (E) Meta-regression plot of the association between mean changes in SBP after psyllium administration with baseline SBP in intervention groups.
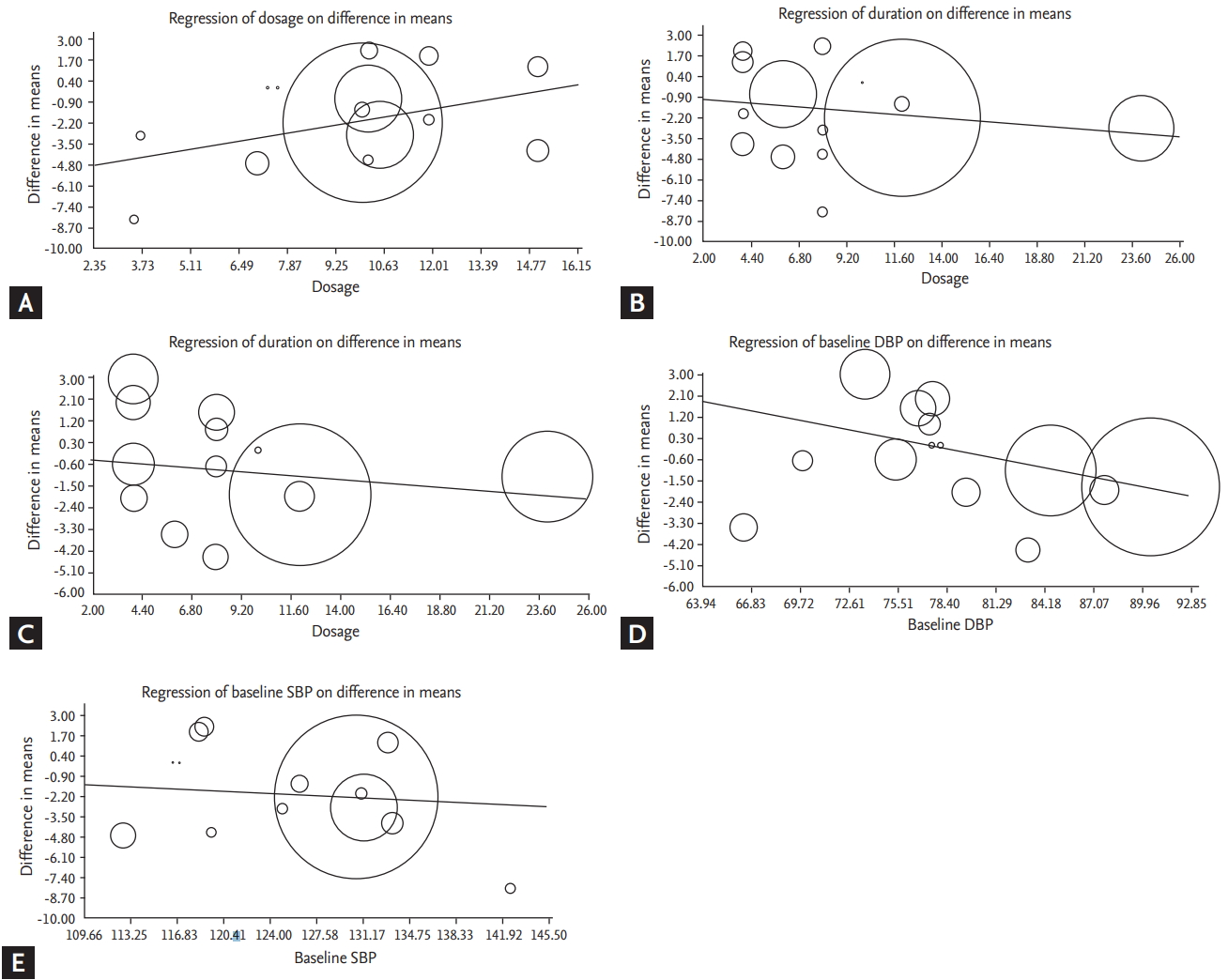
Table 1.
Characteristics of included trials
| Study | Country | Age, mean of intervention group | Sex | Intervention sample size | Placebo sample size | Follow-up duration | Dosage, g/day | Clinical condition | Design | Baseline BP (intervention) | Significant outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anderson et al. (1988) [28] | USA | 47.6 | M | 14 | 14 | 8 wk | 10.2 g/day stirring into 250 mL of water and drinking immediate- ly | Hypercholesteromia | Parallel | 119.3/76.6 | Psyllium reduced serum total cholesterol levels, LDL-C and the ratio of LDL-C to HDL-C relative to baseline values. No significant changes in BP. |
| Asghar et al. (2011) [29] | Pakistan | 25–70 | M/F | 65 | 65 | 3 mon | 10 g/day psyllium husk | Primary hyperlipidemia | Parallel | 131.12/93.01 | Elevation of HDL-C and reduction of LDL-C, TG, SBP, DBP, and body weight |
| Bell et al. (1989) [30] | USA | 46.2 | M/F | 40 | 35 | 8 wk | 10.2 g/day before each meal in 240 mL (8 oz) of water | Mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia | Parallel | 117.5/75.9 | Compared with placebo, psyllium achieved a reduction in total cholesterol level, reduction in LDL-C level, and reduction in apolipoprotein B level |
| Burke (a) et al. (2001) [25] | Australia | 57.3 | M/F | 9 | 9 | 8 wk | 15 g/day taken as a drink mixed with juice or water throughout the day, provided 12.5% of energy from protein | Treated hypertensive | Parallel | 131.6/78.1 | Additive effects to lower 24-hour and awake SBP. The net reduction in 24-hour SBP was 5.9 mmHg with fiber and with protein. |
| Burke (b) et al. (2001) [25] | Australia | 59.3 | M/F | 9 | 9 | 8 wk | 15 g/day taken as a drink mixed with juice or water throughout the day, provided 25% energy as protein | Treated hypertensive | Parallel | 135/74.1 | Additive effects to lower 24-hour and awake SBP. The net reduction in 24-hour SBP was 5.9 mmHg with fiber and with protein. |
| Cicero et al. (2007) [31] | Italy | 58.4 | M/F | 48 | 45 | 6 mon | 10.5 g/day psyllium husk | Hypertensive, overweight | Parallel | 131.4/84.6 | Psyllium supplementation improved significantly BMI, FPG, FPI, HOMA index, HbA1c, LDL-C, and ApoB, plasma TG concentration, SBP and DBP. Psyllium supplementation significantly reduce both SBP and DBP in hypertensive overweight subjects. |
| Ghalandari et al. (2017) [32] | Iran | 55.9 | F | 18 | 16 | 8 wk | 3.7 g/day dissolved in one glass of water in the evening | Type 2 diabetes | Parallel | 126.4/71 | Fasting plasma insulin and HO- MA-IR were significantly lower in the CRHF group. The levels of IL-6 significantly decreased in the CRHF and CRLC groups. TNF-levels were significantly lower only in the CRHF com- pared to the advice group. |
| Jenkins (a) et al. (1997) [26] | USA | 57.5 | M/F | 32 | 32 | 4 wk | 11.9 g/day psyllium breakfast cereals, 20% of energy as fat (6% MUFA diet) | Hypercholesterolemia | Crossover | 118/72 | Psyllium lowered LDL-C and HDL-C at both MUFA intakes. Psyllium resulted in significant reductions in LDL-C, and HDL-C compared with the wheat bran control. |
| Jenkins (b) et al. (1997) [26] | USA | 58 | M/F | 27 | 27 | 4 wk | 11.9 g/day psyllium breakfast cereals, 29% of energy as fat (12% MUFA diet) | Hypercholesterolemia | Crossover | 134/82 | Psyllium lowered LDL-C and HDL-C at both MUFA intakes. Psyllium resulted in significant reductions in LDL-C, and HDL-C compared with the wheat bran control. |
| Murad et al. (2011) [33] | Pakistan | 21–65 | M/F | 18 | 20 | 12 wk | 10 g/day psyllium husk | Primary hyperlipidemia | Parallel | 129.72/91.11 | Reduction of bodyweight, SBP and DBP. Psyllium decreased serum total cholesterol, TG, LDL-C, and increased serum HDL-C in 3 months of treatment. |
| Sartore et al. (2009) [34] | Italy | 61 | M/F | 20 | 20 | 8 | 3.5 g sachet of fiber, followed by 50 mL water to rinse the glass and to drink the mixture before each meal (10.5 g/day) | Type 2 diabetes | Parallel | 146.5/85.5 | BMI, waist circumference, HbA1c and FPG levels had significantly decreased in both groups. TGs were significantly lower in G1, but not in G2. |
BP, blood pressure; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; BMI, body mass index; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; FPI, fasting plasma insulin; HOMA, homeostasis model assessment; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; ApoB, apoprotein B; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; CRHF, calorie-restricted, higher fiber diet; IL, interleukin; CRLC, calorie-restricted, lower carbohydrate diet; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; MUFA, mono-unsaturated fatty acid.
Table 2.
Quality of the included studies based on the Jadad score
| Study | Blinding | Randomization | Withdrawals and dropouts descriptions | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anderson et al. (1988) [29] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Asghar et al. (2011) [30] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Bell et al. (1989) [31] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Burke et al. (2001) [25] | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Cicero et al. (2007) [32] | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| Ghalandari et al. (2017) [34] | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| Jenkins et al. (1997) [26] | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Murad et al. (2011) [35] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Sartore et al. (2009) [37] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Table 3.
Stratified analysis
REFERENCES
1. Beilin LJ. Vegetarian and other complex diets, fats, fiber, and hypertension. Am J Clin Nutr 1994;59:1130S–1135S.



2. He J, Whelton PK. Effect of dietary fiber and protein intake on blood pressure: a review of epidemiologic evidence. Clin Exp Hypertens 1999;21:785–796.


3. Rouse IL, Beilin LJ, Armstrong BK, Vandongen R. Blood-pressure-lowering effect of a vegetarian diet: controlled trial in normotensive subjects. Lancet 1983;1:5–10.


4. Forman D, Bulwer BE. Cardiovascular disease: optimal approaches to risk factor modification of diet and lifestyle. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 2006;8:47–57.



5. Pearson TA, Bazzarre TL, Daniels SR, et al. American Heart Association guide for improving cardiovascular health at the community level: a statement for public health practitioners, healthcare providers, and health policy makers from the American Heart Association Expert Panel on Population and Prevention Science. Circulation 2003;107:645–651.


6. Streppel MT, Arends LR, van ‘t Veer P, Grobbee DE, Geleijnse JM. Dietary fiber and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Arch Intern Med 2005;165:150–156.


7. He J, Klag MJ, Whelton PK, Chen JY, Qian MC, He GQ. Dietary macronutrients and blood pressure in southwestern China. J Hypertens 1995;13:1267–1274.


8. Stamler J, Caggiula A, Grandits G. Relationships of dietary variables to blood-pressure (BP): findings of the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT). Circulation 1992;85:867.
9. Nishida C, Uauy R, Kumanyika S, Shetty P. The joint WHO/FAO expert consultation on diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases: process, product and policy implications. Public Health Nutrm 2004;7:245–250.

10. Brown L, Rosner B, Willett WW, Sacks FM. Cholesterol- lowering effects of dietary fiber: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 1999;69:30–42.



12. Howlett JF, Betteridge VA, Champ M, Craig SA, Meheust A, Jones JM. The definition of dietary fiber: discussions at the Ninth Vahouny Fiber Symposium: building scientific agreement. Food Nutr Res 2010;54.

13. Taneja A, Bhat CM, Arora A, Kaur AP. Effect of incorporation of isabgol husk in a low fibre diet on faecal excretion and serum levels of lipids in adolescent girls. Eur J Clin Nutr 1989;43:197–202.

14. Dennison BA, Levine DM. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-period crossover clinical trial of psyllium fiber in children with hypercholesterolemia. J Pediatr 1993;123:24–29.


15. Glassman M, Spark A, Berezin S, Schwarz S, Medow M, Newman LJ. Treatment of type IIa hyperlipidemia in childhood by a simplified American Heart Association diet and fiber supplementation. Am J Dis Child 1990;144:973–976.


16. Delargy HJ, O’Sullivan KR, Fletcher RJ, Blundell JE. Effects of amount and type of dietary fibre (soluble and insoluble) on short-term control of appetite. Int J Food Sci Nutr 1997;48:67–77.


17. Racette SB, Deusinger SS, Deusinger RH. Obesity: overview of prevalence, etiology, and treatment. Phys Ther 2003;83:276–288.



18. Hense HW. Once at risk--forever at risk? The long-term impact of cardiovascular risk factors on death. Eur J Epidemiol 2004;19:409–410.


19. Sepanlou SG, Parsaeian M, Krohn KJ, et al. Disability-Adjusted Life-Years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE) in Iran and its neighboring countries, 1990-2015: findings from Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Arch Iran Med 2017;20:403–418.

20. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 2009;151:264–269.


21. Green S, Higgins J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2005.
22. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 1996;17:1–12.


23. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 2005;5:13.




24. Gopalakrishnan S, Ganeshkumar P. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis: understanding the best evidence in primary healthcare. J Family Med Prim Care 2013;2:9–14.



25. Burke V, Hodgson JM, Beilin LJ, Giangiulioi N, Rogers P, Puddey IB. Dietary protein and soluble fiber reduce ambulatory blood pressure in treated hypertensives. Hypertension 2013;38:821–826.

26. Jenkins DJ, Wolever TM, Vidgen E, et al. Effect of psyllium in hypercholesterolemia at two monounsaturated fatty acid intakes. Am J Clin Nutr 1997;65:1524–1533.


27. Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Hoboken (NJ): Wiley, 2008.
28. Anderson JW, Zettwoch N, Feldman T, Tietyen-Clark J, Oeltgen P, Bishop CW. Cholesterol-lowering effects of psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid for hypercholesterolemic men. Arch Intern Med 1988;148:292–296.


29. Asghar J, Gill KU, Murad S, Asif S, Bashir A, Mahmood G. Biostatistical analysis of morbidity & mortality due to myocardial infarction and its prevention by hypolipidemic drug regimen. Pak J Med Health Sci 2011;5:445–449.
30. Bell LP, Hectorne K, Reynolds H, Balm TK, Hunninghake DB. Cholesterol-lowering effects of psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid. Adjunct therapy to a prudent diet for patients with mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia. JAMA 1989;261:3419–3423.


31. Cicero AF, Derosa G, Manca M, Bove M, Borghi C, Gaddi AV. Different effect of psyllium and guar dietary supplementation on blood pressure control in hypertensive overweight patients: a six-month, randomized clinical trial. Clin Exp Hypertens 2007;29:383–394.


32. Ghalandari H, Kamalpour M, Alimadadi A, Nasrollahzadeh J. Comparison of two calorie-reduced diets of different carbohydrate and fiber contents and a simple dietary advice aimed to modify carbohydrate intake on glycemic control and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Int J Endocrinol Metab 2017;16:e12089.



33. Murad S, Waseem R, Bashir A, Ashraf HH, Ghurbakhshani AL, Sheikh RA. Keep heart healthy by normalising body weight, blood pressure and weight reduction. Pak J Med Health Sci 2011;5:228–231.
34. Sartore G, Reitano R, Barison A, et al. The effects of psyllium on lipoproteins in type II diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Nutr 2009;63:1269–1271.



35. Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380:2197–2223.


36. GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016;388:1659–1724.


37. Slavin JL, Greenberg NA. Partially hydrolyzed guar gum: clinical nutrition uses. Nutrition 2003;19:549–552.


38. Grundy SM, Hansen B, Smith SC Jr, et al. Clinical management of metabolic syndrome: report of the American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Diabetes Association conference on scientific issues related to management. Circulation 2004;109:551–556.


39. Whelton SP, Hyre AD, Pedersen B, Yi Y, Whelton PK, He J. Effect of dietary fiber intake on blood pressure: a meta- analysis of randomized, controlled clinical trials. J Hypertens 2005;23:475–481.


40. Spiller GA. CRC Handbook of Dietary Fiber in Human Nutrition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC press, 2001.
42. Landsberg L. Insulin-mediated sympathetic stimulation: role in the pathogenesis of obesity-related hypertension (or, how insulin affects blood pressure, and why). J Hypertens 2001;19:523–528.


43. Cleland SJ, Petrie JR, Ueda S, Elliott HL, Connell JM. Insulin as a vascular hormone: implications for the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1998;25:175–184.


44. Coudray C, Demigne C, Rayssiguier Y. Effects of dietary fibers on magnesium absorption in animals and humans. J Nutr 2003;133:1–4.



45. Greger JL. Nondigestible carbohydrates and mineral bio availability. J Nutr 1999;129:1434S–1435S.



46. Wong JM, Jenkins DJ. Carbohydrate digestibility and metabolic effects. J Nutr 2007;137:2539S–2546S.



48. Schulman IH, Zhou MS. Vascular insulin resistance: a potential link between cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Curr Hypertens Rep 2009;11:48–55.



49. Zhou MS, Schulman IH, Raij L. Vascular inflammation, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension: role of nuclear factor kappa B activation. J Hypertens 2010;28:527–535.


50. Landin K, Holm G, Tengborn L, Smith U. Guar gum improves insulin sensitivity, blood lipids, blood pressure, and fibrinolysis in healthy men. Am J Clin Nutr 1992;56:1061–1065.



51. Chutkan R, Fahey G, Wright WL, McRorie J. Viscous versus nonviscous soluble fiber supplements: mechanisms and evidence for fiber-specific health benefits. J Am Acad Nurse Pract 2012;24:476–487.


52. January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;64:e1–e76.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



