 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 33(3); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
For patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), golimumab has consistent efficacy in controlling disease activity over 5 years but its benefit in preventing radiographic progression was less clear at 4 years. To predict radiographic progression, we analyzed the baseline characteristics of AS patients in a Korean population.
Methods
Sixty-eight Korean patients with AS participated in the phase 3, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial (GO-RAISE) which has previously been described. Baseline modified stoke AS spine score (mSASSS) and change in mSASSS from baseline (ΔmSASSS) until week 208 were analyzed in the Korean patients enrolled in the GO-RAISE study.
Results
Although Korean patients had lower baseline mSASSS compared to non-Korean patients and received active management, radiographic progression was not prevented. Korean patients who did not undergo radiographic progression of spinal lesions of AS were younger and had shorter symptomatic duration, lower Bath AS functional and metrology indices, better chest expansion, and lower baseline mSASSS. The baseline mSASSS and ΔmSASSS were positively correlated in Korean AS patients (p < 0.001). Radiographic progression was more prevalent (80.0%) when baseline mSASSS > 10 and less common (13.0%) with baseline mSASSS = 0.
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic rheumatic disease associated with spinal inflammation and bony fusion of the spine that leads to functional impairment [1]. Radiographic damage of the spine can be quantified by the modified stoke AS spine score (mSASSS) [2]. Although tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) blockade has been shown to reduce active inflammation in AS patients, the previous clinical trials of TNF-α blockade showed discordant results in preventing radiologic progression as measured by mSASSS [3-7]. Golimumab, a human monoclonal anti-TNF-α antibody, was evaluated successfully by the randomized controlled trial GO-RAISE (multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial), which demonstrated the consistent efficacy of golimumab over 5 years in terms of function, disease activity, and spinal mobility [8]. However, the benefit of golimumab over placebo in preventing radiographic progression was unclear at 4 years because the patients in the placebo group crossed over to the golimumab 50 mg group at week 24 due to ethical concerns.
After following the patients with AS who received golimumab for more than 3-and-a-half to 4 years in Korea, we had a clinical impression that our patients could be divided into two groups based on radiographic progression. Indeed, in infliximab users, radiographic damage at baseline was suggested as a predictor for radiographic progression [3]. In the Korean population, several factors, including baseline mSASSS and peripheral joint disease, were proposed to be associated with radiographic progression in previous studies [9,10]. However, these retrospective studies were not able to draw definite conclusions about the factors predictive for radiographic progression.
To investigate the reason for these outcomes, we tried to analyze baseline characteristics and to suggest factors predictive for radiographic progression in Korean patients with AS who were enrolled in the GO-RAISE trial.
In Korea, 72 patients were enrolled initially in the phase 3, GO-RAISE trial investigating the clinical efficacy of golimumab, as previously described [7,8]. Of these, 66 remained on trial through 5 years and 68 Korean patients who had radiographic data were included in this analysis. According to the study protocol, all patients gave informed consent. The clinical study was conducted in six centers in Korea and approved by the local Ethics Committees of each participating center.
Among the 68 patients, 15, 24, and 29 of them were initially assigned to receive subcutaneous doses of placebo, golimumab 50 mg, or golimumab 100 mg, respectively, at baseline and every 4 weeks thereafter. All 15 patients initially assigned to the placebo group crossed over at week 24 to the 50 mg golimumab group. After unblinding at week 104, patients receiving golimumab 50 mg could increase the dose to 100 mg every 4 weeks. A dose decrease from 100 to 50 mg was also allowed. Radiographic evaluations were performed at baseline, week 104, and week 208. Therefore, all 68 patients received golimumab for at least 3-and-a-half years before week 208.
The mSASSS scorings for radiographic assessment of the spinal lesions for all the GO-RAISE trial patients were performed by two independent readers who were blinded to treatment information and radiographic sequence.
After analyzing the baseline characteristics that might predict radiographic progression in Korean patients, we compared baseline mSASSS and change in mSASSS from baseline (ΔmSASSS) at week 208 among the Korean patients and those of other countries (Canada, USA, Germany, Belgium, Taiwan, Finland, France, and the Netherlands). Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) partial remission rate was also compared. We carried out a more detailed analysis on the pattern of the relationship between baseline mSASSS and ΔmSASSS. The trial is registered as a clinical trial at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00265083) (registration date: December 12, 2005).
Based on whether any progression of radiographic lesion(s) existed, we divided the patients into two groups: one group was ‘progressors’ who had relatively aggressive exacerbation over time and the other was ‘non-progressors’ who remained in an indolent status. Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were compared between patients with radiographic progression at week 208 (ΔmSASSS > 0 vs. ΔmSASSS ≤ 0) using an independent t test. The correlation between baseline mSASSS and ΔmSASSS was calculated using Spearman’s rho and the Freeman-Halton extension of the Fisher exact probability test. All statistical tests were performed with two-sided alternatives and with a type I error of 0.05 by SAS version 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
The patients who did not undergo radiographic progression of the spinal lesion(s) of AS had the following characteristics: (1) relatively younger age; (2) shorter symptom duration; (3) lower Bath AS Functional Index; (4) lower Bath AS Metrology Index; (5) greater chest expansion; and (6) lower baseline mSASSS (Table 1). As the mean ΔmSASSS of ‘ΔmSASSS ≤ 0’ group was −0.56 ± 1.39 and ‘ΔmSASSS > 0’ group was 7.22 ± 6.62 in Korean patients, ΔmSASSS = 0 could be a useful parameter for separating non-progressors from progressors. Sex, human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B27, smoking, baseline level of C-reactive protein, disease duration before diagnosis, Bath AS disease activity index, and patients’ general assessment of back pain and disease activity were not significantly different between progressors and non-progressors. After logistic regression analysis by the parameters with statistical significance or clinical importance, baseline mSASSS was the only variable predicting radiographic progression at week 208 (Table 2).
Of the 271 patients who had radiographic data in GORAISE trial, there were 68 Korean patients (25.1%), the third largest population by country. Baseline mSASSS was lower in Korean than non-Korean patients with statistical significance (Fig. 1). In addition, Korean patients were consistently more treatment-compliant (Korean 91.7%, non-Korean 66.4%, p < 0.001) and had a higher ASAS partial remission rate (Korean 44.4%, non-Korean 31.3%, p = 0.036) until week 256 (Fig. 2). However, ΔmSASSS was higher in Korean patients when evaluated at week 104 (Korean 1.72 ± 4.14, non-Korean 0.97 ± 3.62, p = 0.143) and week 208 (Korean 2.87 ± 5.93, non-Korean 1.66 ± 4.42, p = 0.393) but this was without statistical significance (Fig. 1).
There was a positive correlation between baseline mSASSS and ΔmSASSS at week 208 in Korean AS patients (Spearman’s rho = 0.487, p < 0.001) (Fig. 3). The trend was more evident when the patients were stratified into subgroups based on the baseline mSASSS. Radiographic progression was more prevalent (80.0%) in the patients who had a baseline mSASSS > 10 and less common (13.0%) in the group without baseline radiographic damage (mSASSS = 0) (Fig. 3).
According to our analysis, radiographic progression in Korean patients with AS showed particular features. In spite of favorable radiographic status at baseline and the clinical course during the trial, radiographic progression was not prevented as a result of treatment with golimumab. Ironically, the baseline characteristic with the highest predictive value was baseline mSASSS. Most of the progressors (ΔmSASSS > 0) had a higher baseline mSASSS (> 10) and most of the non-progressors (ΔmSASSS ≤ 0) had no radiographic damage initially. This ‘all-or-none’ phenomenon could be explained by the hypothesis that early spinal lesions may resolve completely after effective suppression of inflammation with TNF-α blockade [11,12].
Previous studies considered two units or more of mSASSS change (ΔmSASSS ≥ 2) as significant change [7,13]. In light of our results, the criteria we set (baseline mSASSS = 0, ΔmSASSS > 0) were more meaningful for predicting progression because a single bone lesion on X-ray could indicate the existence of other reversible spinal lesions, not detectable by X-ray but which could be detected by magnetic resonance imaging [12]. Our findings also support previous results that showed early initiation and longer use of TNF-α blockade was effective in preventing radiographic progression [14].
As a Korean population is relatively homogeneous in ethnicity, subgroup study can be valuable. Indeed, the predominant subtype of HLA-B27 of Korean AS patients was HLA-B*2705, unlike other Asians [15]. The previous retrospective studies on the clinical characteristics of Korean patients with AS focused mainly on the higher prevalence of juvenile onset AS and peripheral arthritis and the association between the presence of peripheral arthritis and slow radiographic progression [9,10,16,17]. Younger age was shown to be a favorable factor for radiographic progression, but the influence of peripheral arthritis was still controversial [18].
Our study provided the first prospective data for an analysis of the clinical features of AS regarding radiographic progression in Korean patients receiving TNF-α blockade, but the study did have a few limitations. (1) Although Koreans have homogeneous Asian ethnicity, some patients from other countries such as Taiwan were included. Therefore, the results of this study cannot be generalized to Asian ethnicity. (2) Because of the smaller size of the study population the statistical power was weaker than for the original study. However, a consistent tendency was noted when comparing baseline mSASSS and ΔmSASSS in Korean and non-Korean populations. (3) The natural course of disease in Korean AS patients could be different from that in golimumab users. In addition, as in the original study, the true effect of golimumab itself was uncertain because all the patients initially belonging to the placebo group (22% of the total study population) crossed over to golimumab groups during the study [8]. Therefore, the results of this study should be interpreted with caution, recognizing these limitations related to the study population.
In conclusion, Korean patients with AS involved in the randomized controlled trial receiving golimumab for up to 4 years had distinctive patterns of spinal lesion progression detected by simple radiographs at week 208. This distinctive pattern of progression could be predicted reliably by the initial severity of the spinal lesion(s). Despite several shortcomings, this study confirmed the value of early and active biological treatment for AS before the appearance of overt spinal damage.
Figure 1.
(A) Means of baseline modified stoke ankylosing spondylitis (AS) spine score (mSASSS) and (B) means of change in mSASSS from baseline (ΔmSASSS) at week 104 and 208.
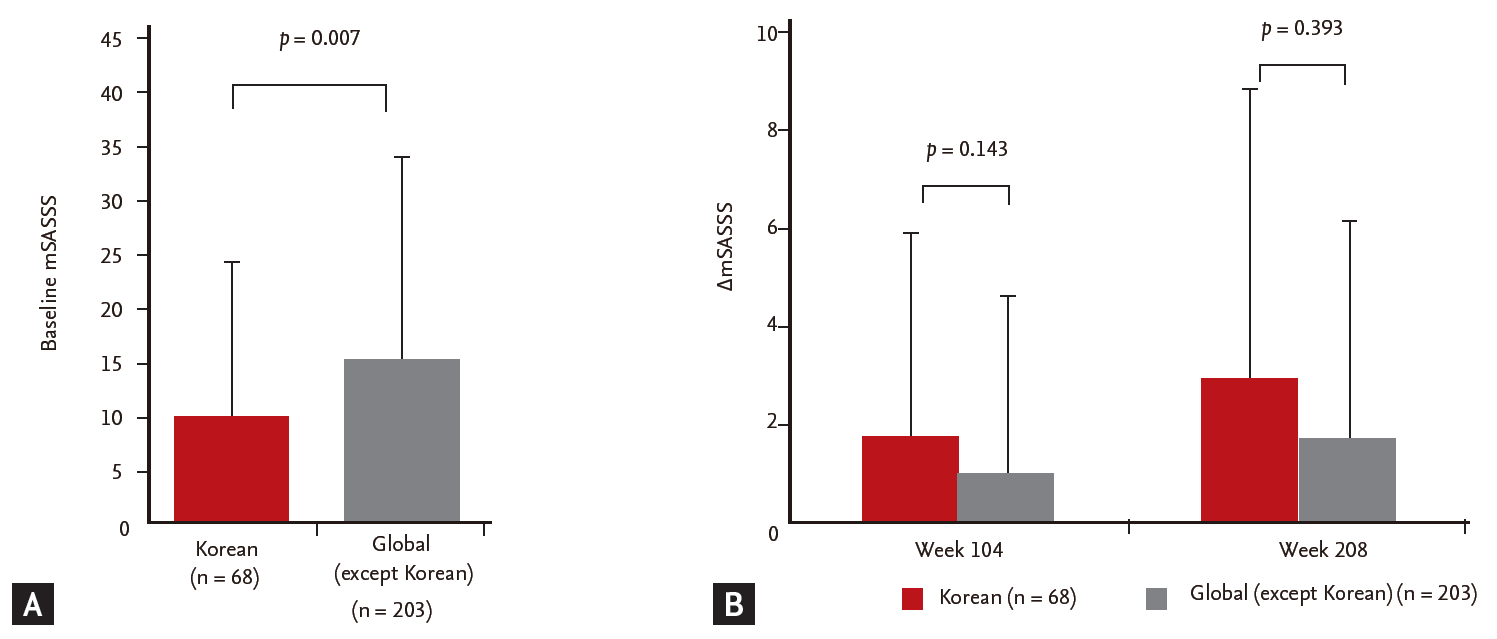
Figure 2.
Comparison of ASAS (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society) partial remission rate in Korean and non-Korean ankylosing spondylitis patients using golimumab till week 256. ap < 0.05.

Figure 3.
(A) Correlation between baseline modified stoke ankylosing spondylitis (AS) spine score (mSASSS) and change in mSASSS from baseline (ΔmSASSS) at week 208 (Spearman’s rho). (B) Population distribution stratified by baseline mSASSS and ΔmSASSS at week 208 analyzed by the Freeman-Halton extension of the Fisher exact probability test.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics associated with radiographic progression over 4 years in Korean ankylosing spondylitis patients
| Characteristic | ΔmSASSS ≤ 0 (n = 38) | ΔmSASSS > 0 (n = 30) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yra | 27.79 ± 7.14 | 33.10 ± 7.36 | 0.003 |
| Male sex, % | 86.8 | 90.0 | 0.688 |
| HLA-B27 (positive), % | 92.1 | 93.3 | 0.847 |
| Smoking (yes), % | 36.8 | 46.7 | 0.414 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL | 2.18 ± 2.37 | 2.70 ± 2.30 | 0.438 |
| Disease duration, yr | 4.30 ± 4.41 | 5.96 ± 4.71 | 0.059 |
| Duration of SpA symptoms, yra | 5.24 ± 4.49 | 7.93 ± 5.92 | 0.037 |
| Duration of inflammatory back pain, yra | 5.32 ± 4.59 | 8.57 ± 6.09 | 0.015 |
| BASDAI score | 6.48 ± 1.34 | 7.00 ± 1.23 | 0.093 |
| BASFI scorea | 2.33 ± 1.69 | 4.07 ± 2.54 | 0.002 |
| BASMI scorea | 2.29 ± 1.41 | 4.20 ± 2.38 | < 0.001 |
| Chest expansion, cma | 3.82 ± 1.66 | 2.51 ± 1.23 | < 0.001 |
| mSASSSa | 2.74 ± 4.85 | 18.80 ± 17.26 | < 0.001 |
| Patients’ general assessment of total back pain (VAS, 0–10) | 6.74 ± 1.61 | 7.49 ± 1.63 | 0.055 |
| Patients’ general assessment of disease activity (VAS, 0–10) | 6.62 ± 1.84 | 7.03 ± 1.99 | 0.336 |
Values are presented as mean ± SD.
mSASSS, modified stoke ankylosing spondylitis (AS) spine score; ΔmSASSS, change in mSASSS from baseline; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; SpA, spondyloarthropathy; BASDAI, Bath AS Disease Activity Index; BASFI, Bath AS Functional Index; BASMI, Bath AS Metrology Index; VAS, visual analog scale.
Table 2.
Logistic-regression analysis to identify predictors of radiographic progression at week 208 in Korean ankylosing spondylitis patients
| Response variable | Independent variable | Coefficient | p value | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔmSASSS ≤ 0 (Y/N) | Age, yr | −0.08 | 0.139 | 0.92 (0.83–1.03) |
| Smoking (yes), % | −0.07 | 0.856 | 0.86 (0.18–4.23) | |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL | 0.06 | 0.736 | 1.06 (0.77–1.46) | |
| Disease duration, yr | 0.12 | 0.216 | 1.13 (0.93–1.37) | |
| Duration of SpA symptoms, yr | −0.00 | 0.999 | 1.00 (0.77–1.30) | |
| Duration of inflammatory back pain, yr | −0.10 | 0.430 | 0.90 (0.70–1.16) | |
| BASFI score | −0.35 | 0.170 | 0.71 (0.43–1.16) | |
| BASMI score | 0.09 | 0.748 | 1.10 (0.62–1.94) | |
| Chest expansion, cm | 0.29 | 0.329 | 1.34 (0.75–2.39) | |
| mSASSSa | −0.15 | 0.032 | 0.86 (0.74–0.99) |
REFERENCES
1. Landewe R, Dougados M, Mielants H, van der Tempel H, van der Heijde D. Physical function in ankylosing spondylitis is independently determined by both disease activity and radiographic damage of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:863–867.


2. Creemers MC, Franssen MJ, van’t Hof MA, Gribnau FW, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Assessment of outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: an extended radiographic scoring system. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:127–129.



3. Baraliakos X, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, Brandt J, Sieper J, Braun J. Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 2 years of treatment with the tumour necrosis factor alpha antibody infliximab. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:1462–1466.



4. Baraliakos X, Listing J, Brandt J, et al. Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 4 yrs of treatment with the anti-TNF-alpha antibody infliximab. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2007;46:1450–1453.



5. van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Einstein S, et al. Radiographic progression of ankylosing spondylitis after up to two years of treatment with etanercept. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:1324–1331.


6. van der Heijde D, Salonen D, Weissman BN, et al. Assessment of radiographic progression in the spines of patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with adalimumab for up to 2 years. Arthritis Res Ther 2009;11:R127.



7. Braun J, Baraliakos X, Hermann KG, et al. The effect of two golimumab doses on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis: results through 4 years of the GO-RAISE trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1107–1113.



8. Deodhar A, Braun J, Inman RD, et al. Golimumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in ankylosing spondylitis: 5-year results of the GO-RAISE study. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:757–761.



9. Baek HJ, Shin KC, Lee YJ, et al. Clinical features of adult-onset ankylosing spondylitis in Korean patients: patients with peripheral joint disease (PJD) have less severe spinal disease course than those without PJD. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004;43:1526–1531.


10. Kim TJ, Lee S, Joo KB, et al. The presence of peripheral arthritis delays spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis: Observation Study of the Korean Spondyloarthropathy Registry. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2014;53:1404–1408.



11. Maksymowych WP. Spondyloarthritis in 2012: advances in pathogenesis through animal models and imaging. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2013;9:72–74.



12. Maksymowych WP, Morency N, Conner-Spady B, Lambert RG. Suppression of inflammation and effects on new bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis: evidence for a window of opportunity in disease modification. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:23–28.


13. Baraliakos X, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, et al. Progression of radiographic damage in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: defining the central role of syndesmophytes. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:910–915.



14. Haroon N, Inman RD, Learch TJ, et al. The impact of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 2013;65:2645–2654.



15. Lee SH, Choi IA, Lee YA, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-B*2705 is the predominant subtype in the Korean population with ankylosing spondylitis, unlike in other Asians. Rheumatol Int 2008;29:43–46.


16. Kim TJ, Kim TH. Clinical spectrum of ankylosing spondylitis in Korea. Joint Bone Spine 2010;77:235–240.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



