 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 28(1); 2013 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
This study determined the prevalence and determinants of seropositivity for rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody, and anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin (anti-MCV) antibody in unaffected first-degree relatives (FDRs) of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
Methods
A total of 337 subjects (135 with RA and 202 FDRs) were enrolled in this case-control study. Serum RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody were assayed. Subjects in multicase families (≥ 2 affected FDRs within the same family) were identified. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk factors associated with RA-related autoantibodies.
Results
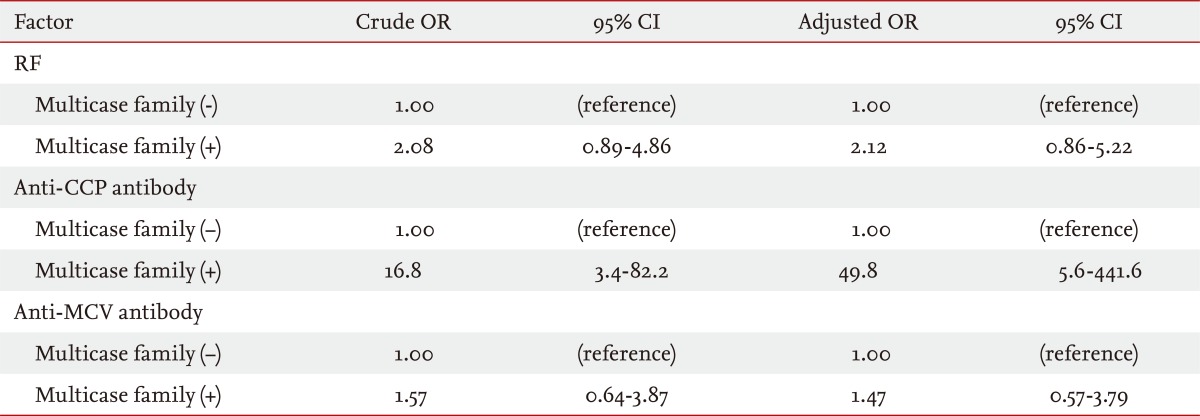
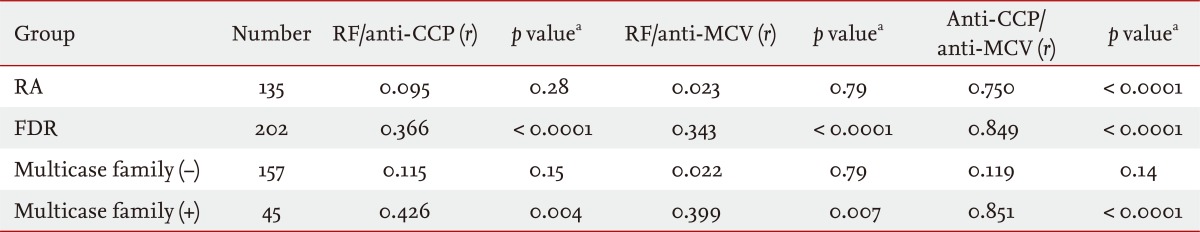
Seropositivity for RF, anti-CCP antibody, or anti-MCV antibody was detected in 14.4%, 5.0%, or 13.4% of unaffected FDRs, respectively. Anti-CCP antibody seropositivity was more prevalent in FDRs in multicase families (17.8%) than in those not in multicase families (1.3%, p < 0.0001). Significant correlations between RA-associated autoantibodies were detected in the FDR group (between RF and anti-CCP antibody: r = 0.366, p < 0.0001; between RF and anti-MCV antibody: r = 0.343, p < 0.0001; and between anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody: r = 0.849, p < 0.0001). After adjustment for age and sex, anti-CCP antibody seropositivity in FDRs was significantly associated with being in a multicase family (odds ratio, 49.8; 95% confidence interval, 5.6 to 441.6).
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by the proliferation of synovial lining cells, angiogenesis, and infiltration of mononuclear cells, resulting in joint destruction and functional disability [1,2]. Although the pathogenesis of RA has not been clearly determined, it is now accepted that the development of RA is closely associated with diverse genetic factors such as the human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR alleles encoding the "shared epitope" and polymorphisms in potent genes, including those for protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 22 (PTPN22), signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4), and 6q23, as well as environmental factors such as coffee consumption and smoking [3-7]. In addition, familial and twin studies have suggested that the occurrence of RA has strong familial aggregation [8-10].
Kolfenbach et al. [11] suggested a model for the development of RA in three serial phases: 1) an initial genetic risk phase, 2) pre-clinical autoimmunity, and 3) clinical disease. Interactions between environmental factors and genetic risks lead to asymptomatic and pre-clinical autoimmunity characterized by early detection of RA-related autoantibodies, including rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (anti-CCP antibody), and markedly increased levels of pro-inflammatory markers in susceptible individuals. Some investigations have indicated that the presence of RF and anti-CCP antibody may precede clinically apparent RA by two decades [12-14]. More prevalent expression of autoantibodies such as RF, RA-associated nuclear antigen, and anti-CCP antibody has been reported to occur in unaffected relatives in multicase RA families [11,15-17]. To our knowledge, no data exist regarding the frequency of anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin antibody (anti-MCV antibody) in unaffected relatives of RA patients. Anti-MCV antibody has been detected in recent-onset RA and very early synovitis [18,19], which suggests its presence prior to clinically established RA.
There is no information regarding the clinical significance of RA-related autoantibodies, including RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody, or the associated risk for development of RA in unaffected first-degree relatives (FDRs) of Korean individuals with RA. In this study, we investigated the prevalence of RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody in unaffected FDRs of RA patients and identified autoantibody seropositivity risk factors in FDRs.
We recruited a total of 337 subjects (135 RA patients and 202 FDRs from 135 RA families). Enrolled RA patients fulfilled the 1987 revised criteria for the classification of RA issued by the American College of Rheumatology [20]. FDRs who did not complain of any signs or symptoms indicative of inflammatory joint disease were identified using a questionnaire and through a physical examination performed by a rheumatologist. The spectrum of FDRs in our study included parents and offspring of RA patients. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Daegu Catholic University Medical Center. All subjects participating in this study gave written informed consent.
Data, including age, sex, and smoking status, were obtained from FDRs and RA patients participating in this study through individual interviews at the time of enrollment. In addition, disease duration and age at diagnosis for RA patients were identified through reviews of medical records and individual interviews. Multicase families were defined by the presence of relatives treated for or diagnosed with RA among siblings or parents of enrolled RA patients. Multicase family positivity for an unaffected FDR means the existence of at least two RA patients among family members and blood relatives of the FDR.
We measured the serum concentrations of RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody in RA patients and their FDRs. Blood samples were collected from veins and stored at -70℃ prior to the measurement of serum titers of the target antibodies. RF serum titers were measured by immunoturbidometry using the Cobas Integra RFII assay (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). Normal RF values are < 10 IU/mL. Anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Diasta, Axis-Shield Diagnostics, Dundee, UK and ORGENTEC, Diagnostica GmbH, Maiz, Germany, respectively). Cut-off values for anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody were 5 and 20 U/mL, respectively.
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables and as a frequency and percentage for categorical variables. Student's t test was used to compare the mean age between pairs of groups. Differences in proportions between pairs of groups were assessed by Fisher's exact test or the chi-squared test. Mean differences in RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody titers between RA patients and matched controls were assessed by analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), after adjustment for age (categorized as < 30, 30 to 39, 40 to 49, and ≥ 50 years), sex, and smoking status (ever-smoker versus never-smoker). Relationships between RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody titers in RA patients and unaffected FDRs were determined by Pearson's correlation analysis. Correlations between RA-related autoantibodies were also assessed by Pearson's correlation analysis. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify predictors of RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody seropositivity among FDRs of RA patients. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated after adjustment for age and sex. Statistical significance was evaluated with a two-sided significance level of 0.05 (p ≥ 0.05 and < 0.10 were considered marginally significant). All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 19.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA).
Demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1. Age, sex, and smoking status differed significantly between the RA and FDR groups (p < 0.0001 for all parameters). Enrolled RA patients were all female, whereas 49 FDRs were male (24.3%). Of the FDRs, 45 (22.3%) were members of multicase families. The mean disease duration of RA patients was 10.9 years (SD, 8.4). Compared with FDRs, RA patients showed significantly higher serum titers and frequencies of seropositivity for RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody (p < 0.0001 for all parameters) (Table 2). Among the FDRs, 14.4% and 13.4% were seropositive for RF and anti-MCV antibody, respectively, and the prevalence of anti-CCP antibody seropositivity (n = 10, 5.0%) was much lower than that of the other antibodies.
The prevalence of each autoantibody in FDRs (n = 202) according to whether they were (n = 45) or were not (n = 157) in multicase families is illustrated in Fig. 1. The proportion of FDRs in multicase families who were positive for anti-CCP antibody (8/45, 17.8%) was significantly different from that of FDRs not in multicase families (2/157, 1.3%; p < 0.0001). The differences for RF (p = 0.09) and anti-MCV antibody (p = 0.32) seropositivity were not statistically significant.
Pearson's correlation analysis revealed significant positive correlations between RF and anti-CCP antibody (correlation coefficient [r] = 0.366, p < 0.0001), between RF and anti-MCV antibody (r = 0.343, p < 0.0001), and between anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody (r = 0.849, p < 0.0001) in the FDRs (Table 3). Furthermore, these correlations were significant in FDRs in multicase families, but not in FDRs not in multicase families. The r for the relationship between anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody in the FDR group was higher than those for the relationships between RF and anti-CCP antibody and between RF and anti-MCV antibody. In RA patients, only anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody were significantly correlated (r = 0.750, p < 0.0001).
The RF titer differed significantly according to age (p = 0.004) and sex (p = 0.01) (Table 4). In addition, the prevalence of anti-CCP antibody seropositivity differed significantly between the two age groups (< 20 years vs. ≥ 20 years, p = 0.03). There was a marginal difference in RF titer between FDRs in multicase families versus those not in multicase families (p = 0.06). After adjustment for age and sex, logistic regression analysis of RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody seropositivity in FDRs (n = 202) in multicase families revealed that the presence of anti-CCP antibody, but not RF or anti-MCV antibody, was closely associated with being in a multicase RA family (OR, 49.8; 95% CI, 5.6 to 441.6) (Table 5).
Familial clustering results increased incidence of RA in unaffected FDRs of RA patients and may provide clues to the mechanism of RA pathogenesis [8-10]. Some investigations have demonstrated a significantly higher prevalence of seropositivity for RA-related autoantibodies in unaffected FDRs, suggesting that aberrant RA-related autoimmunity is relevant to the development of RA [11,15-17].
There are no data for the Korean population regarding pre-clinical autoimmunity, including RA-related autoantibody seropositivity in FDRs of established RA patients prior to the development of RA. This study was initially designed to determine the prevalences of RA-related RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody, and to identify risk factors associated with seropositivity in asymptomatic FDRs of RA patients. Among FDRs, 14.4% were seropositive for RF; 5.0%, for anti-CCP antibody; and 13.4%, for anti-MCV antibody. In addition, anti-CCP antibody was detected more frequently in unaffected FDRs in multicase families than in those not in multicase families, although a definite link between familial genetic and environmental backgrounds remains to be elucidated.
RF and anti-CCP antibody were detected in 14.7% (42) and 1.3% (3) of 286 healthy Korean controls [21]. In a literature review, Vossenaar and van Venrooij [22] reported 0% anti-CCP antibody seropositivity and 11% RF positivity in healthy controls. The prevalence of anti-CCP antibody seropositivity in unaffected FDRs of RA patients in our study is higher than those reported for unrelated healthy controls in two previous studies [21,22]. The higher frequency of anti-CCP antibody seropositivity in our FDRs is also consistent with data from a recent family study [17]. The prevalence of RF seropositivity in our FDR subjects does not differ from that in the healthy controls in two previous studies [21,22]. In a family study of unaffected members of multicase families in northern Sweden, Arlestig et al. [17] reported significantly higher prevalences and serum titers of both RF and anti-CCP antibody in FDRs and RA patients compared with unrelated healthy controls. In the present study, the frequencies and serum titers of RF and anti-CCP antibody differed significantly between RA patients and their FDRs. Earlier and higher expression of RA-related antibodies, especially anti-CCP antibody, may be related to increased risk for RA in the unaffected FDRs of RA patients.
Vimentin, an abundant intermediate filament protein, was first described as the Sa antigen when it was detected on immunoblots of placenta and spleen extracts; it is known to play a role in supporting cytoskeleton structures and cell migration/proliferation [23]. Vimentin is highly expressed in mesenchymal cells, macrophages, and fibroblast-like synoviocytes [24]. The anti-MCV antibody assay has better diagnostic sensitivity (82%) and comparable specificity (98%) compared with the anti-CCP2 antibody assay (72% and 96%, respectively) [25]. Recent clinical studies have revealed that the anti-MCV antibody assay also has higher diagnostic sensitivity [26] and can detect anti-MCV antibody sooner in early RA or synovitis patients [18,19]. Another study has suggested that anti-MCV antibody is comparable to anti-CCP antibody for the diagnosis of RA [27].
To date, there are not sufficient data regarding the presence of anti-MCV antibody in relatives of RA patients. In the present study, the prevalences of anti-MCV antibody in RA patients and their unaffected FDRs were 94.8% and 13.4%, respectively. Nicaise Roland et al. [28] found 10% anti-MCV antibody seropositivity in healthy controls, using a cut-off value of 20 U/mL. Similar anti-MCV antibody prevalences have also been reported in non-RA rheumatic diseases, including psoriatic arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, and ankylosing spondylitis. However, the prevalence of anti-MCV antibody seropositivity in FDRs in our study (13.4%) is much higher than that in 50 Korean osteoarthritis patients (4%, n = 2) [29]. In addition, another study of the diagnostic value of anti-MCV antibody in RA patients did not detect anti-MCV antibody in healthy blood donors [30]. Further studies are needed to clarify the potential clinical value of anti-MCV antibody in unaffected FDRs of RA patients.
There is some evidence suggesting a close correlation among RA-related autoantibodies. Poulsom and Charles [30] found a moderate correlation between quantitative measurements of anti-MCV antibody and anti-CCP antibody (r = 0.6049). They identified correlations between anti-MCV antibody and both anti-CCP antibody (r = 0.596, p < 0.001) and IgM RF (r = 0.301, p = 0.038), but not between anti-CCP antibody and RF. The present study showed a significant correlation only between anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody in RA patients. There was also a closer correlation between anti-CCP antibody and anti-MCV antibody than between the other RA-related autoantibody pairs in FDRs, suggesting that citrullinated processing or increased production of citrullinated peptides may be a crucial determinant of RA pathogenesis.
A primary objective of this study was to identify the clinical risk related to the presence of RA-related antibodies in unaffected FDRs of RA patients. FDRs in multicase families were more likely to be seropositive for anti-CCP antibody in the present study, and several studies have detected RA-related autoantibodies, including anti-CCP antibody, RF, and anti-MCV antibody, in the preclinical phase of RA [12-14].
Our study has some limitations. First, the genetic markers responsible for 50% to 60% of the increased susceptibility to RA, including HLA-DR alleles, PTPN22, STAT4, and the 6q23 locus, were not assessed. These factors may explain the increased familial clustering within FDRs. Second, as this study was initially designed as a cross-sectional study, it provides insufficient data for the incidence of RA development and serial changes in RA-related autoantibodies. A prospective family study is needed to assess the potential associations between RA development and autoantibody seropositivity in unaffected FDRs. Third, all of the enrolled established RA patients were female, and 75.7% of the enrolled FDRs were female. Environmental factors such as coffee consumption and smoking are closely associated with increased susceptibility to RA [6,7] and are thought to play an essential role in the development of RA in subjects with increased genetic susceptibility to RA. A skewed distribution of these factors with respect to sex might have influenced our results.
The detection of RA-related autoantibodies, including RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody, could enhance our understanding of familial clustering in the development of RA, although some debate exists regarding the significance of the frequent detection of these RA-related autoantibodies in FDRs. Our study suggests that anti-CCP antibody may be a serological marker predicting the transition from an asymptomatic preclinical condition to clinical disease in FDRs. Further study is needed to clarify the relationship between serial changes in these biological markers and the development of RA in unaffected FDRs.
1. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis could be affected by genetic and environmental factors.
2. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody might be a potent predictor for overt clinical disease in first-degree relatives of rheumatoid arthritis.
3. The risk of rheumatoid factor and anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin antibody for first-degree relatives of rheumatoid arthritis should be determined in larger population.
References
1. Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 2010;233:233–255PMID : 20193003.



2. Imboden JB. The immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Pathol 2009;4:417–434PMID : 18954286.


3. Lee HS, Lee AT, Criswell LA, et al. Several regions in the major histocompatibility complex confer risk for anti-CCP-antibody positive rheumatoid arthritis, independent of the DRB1 locus. Mol Med 2008;14:293–300PMID : 18309376.



4. Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, et al. STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 2007;357:977–986PMID : 17804842.



5. Thomson W, Barton A, Ke X, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis association at 6q23. Nat Genet 2007;39:1431–1433PMID : 17982455.



6. Baka Z, Buzas E, Nagy G. Rheumatoid arthritis and smoking: putting the pieces together. Arthritis Res Ther 2009;11:238. PMID : 19678909.



7. Mikuls TR, Cerhan JR, Criswell LA, et al. Coffee, tea, and caffeine consumption and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Iowa Women's Health Study. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:83–91PMID : 11817612.


8. Silman AJ, Hennessy E, Ollier B. Incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in a genetically predisposed population. Br J Rheumatol 1992;31:365–368PMID : 1596697.


9. Silman AJ, MacGregor AJ, Thomson W, et al. Twin concordance rates for rheumatoid arthritis: results from a nationwide study. Br J Rheumatol 1993;32:903–907PMID : 8402000.


10. MacGregor AJ, Snieder H, Rigby AS, et al. Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheum 2000;43:30–37PMID : 10643697.


11. Kolfenbach JR, Deane KD, Derber LA, et al. A prospective approach to investigating the natural history of preclinical rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using first-degree relatives of probands with RA. Arthritis Rheum 2009;61:1735–1742PMID : 19950324.



12. Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, et al. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:2741–2749PMID : 14558078.


13. Nielen MM, van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, et al. Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: a study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:380–386PMID : 14872479.


14. Jorgensen KT, Wiik A, Pedersen M, et al. Cytokines, autoantibodies and viral antibodies in premorbid and postdiagnostic sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: case-control study nested in a cohort of Norwegian blood donors. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:860–866PMID : 17644543.


15. Silman AJ, Ollier B, Mageed RA. Rheumatoid factor detection in the unaffected first degree relatives in families with multicase rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1991;18:512–515PMID : 2066941.

16. Hazelton RA, Cross SM, Robert G, Strachan N. A family study of the prevalence of antibodies to the rheumatoid arthritis associated nuclear antigen (RANA). Br J Rheumatol 1986;25:349–352PMID : 3490894.


17. Arlestig L, Mullazehi M, Kokkonen H, Rocklov J, Ronnelid J, Dahlqvist SR. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides of IgG, IgA and IgM isotype and rheumatoid factor of IgM and IgA isotype are increased in unaffected members of multicase rheumatoid arthritis families from northern Sweden. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:825–829PMID : 22128080.



18. Goldbach-Mansky R, Lee J, McCoy A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis associated autoantibodies in patients with synovitis of recent onset. Arthritis Res 2000;2:236–243PMID : 11056669.



19. Raza K, Mathsson L, Buckley CD, Filer A, Ronnelid J. Anti-modified citrullinated vimentin (MCV) antibodies in patients with very early synovitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:627–628PMID : 19846408.


20. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:315–324PMID : 3358796.


21. Choi SW, Lim MK, Shin DH, Park JJ, Shim SC. Diagnostic performances of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides antibody and antifilaggrin antibody in Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Med Sci 2005;20:473–478PMID : 15953872.



22. Vossenaar ER, van Venrooij WJ. Anti-CCP antibodies, a highly specific marker for (early) rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Appl Immunol Rev 2004;4:239–262.

23. Despres N, Boire G, Lopez-Longo FJ, Menard HA. The Sa system: a novel antigen-antibody system specific for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1994;21:1027–1033PMID : 7932409.

24. Tilleman K, Van Steendam K, Cantaert T, De Keyser F, Elewaut D, Deforce D. Synovial detection and autoantibody reactivity of processed citrullinated isoforms of vimentin in inflammatory arthritides. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:597–604PMID : 18326534.


25. Bang H, Egerer K, Gauliard A, et al. Mutation and citrullination modifies vimentin to a novel autoantigen for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56:2503–2511PMID : 17665451.


26. Svard A, Kastbom A, Soderlin MK, Reckner-Olsson A, Skogh T. A comparison between IgG- and IgA-class antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides and to modified citrullinated vimentin in early rheumatoid arthritis and very early arthritis. J Rheumatol 2011;38:1265–1272PMID : 21459947.


27. Dejaco C, Klotz W, Larcher H, Duftner C, Schirmer M, Herold M. Diagnostic value of antibodies against a modified citrullinated vimentin in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2006;8:R119. PMID : 16859519.



28. Nicaise Roland P, Grootenboer Mignot S, Bruns A, et al. Antibodies to mutated citrullinated vimentin for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in anti-CCP-negative patients and for monitoring infliximab therapy. Arthritis Res Ther 2008;10:R142. PMID : 19077182.



Figure 1
Percentage of first-degree relatives (FDRs) who were seropositive for each autoantibody according to whether they were in multicase families. The frequency of seropositivity for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibody was higher in FDRs in multicase families (8/45, 17.8%) compared with FDRs not in multicase families (2/157, 1.3%) (p < 0.0001). There was no statistically signif icant difference in the frequency of seropositivity for rheumatoid factor (RF) (p = 0.09) or anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin (MCV) antibody (p = 0.32) between the two groups. ap > 0.05, bp < 0.0001.
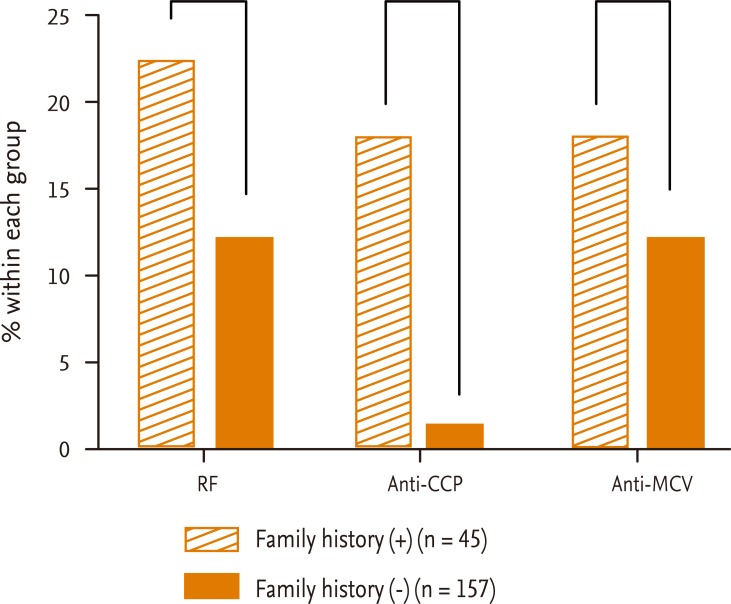
Table 1
Demographic and clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis patients (n = 135) and unaffected first-degree relatives (n = 202)

Table 2
Comparison of serum titers and prevalence of RF (IU/mL), anti-CCP antibody (U/mL), and anti-MCV antibody (U/mL) seropositivity between rheumatoid arthritis patients (n = 135) and first-degree relatives (n = 202)

Values are presented as mean ± SD or number (%).
RF, rheumatoid factor; CCP, cyclic citrullinated peptide; MCV, mutated citrullinated vimentin; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; FDR, first-degree relative.
aCalculated by analysis of covariance, after adjustment for age, sex, and smoking status.
bCalculated by chi-squared test.
Table 4
Comparison of RF (IU/mL), anti-CCP antibody (U/mL), and anti-MCV antibody (U/mL) titers in first-degree relatives (n = 202) according to demographic and clinical characteristics
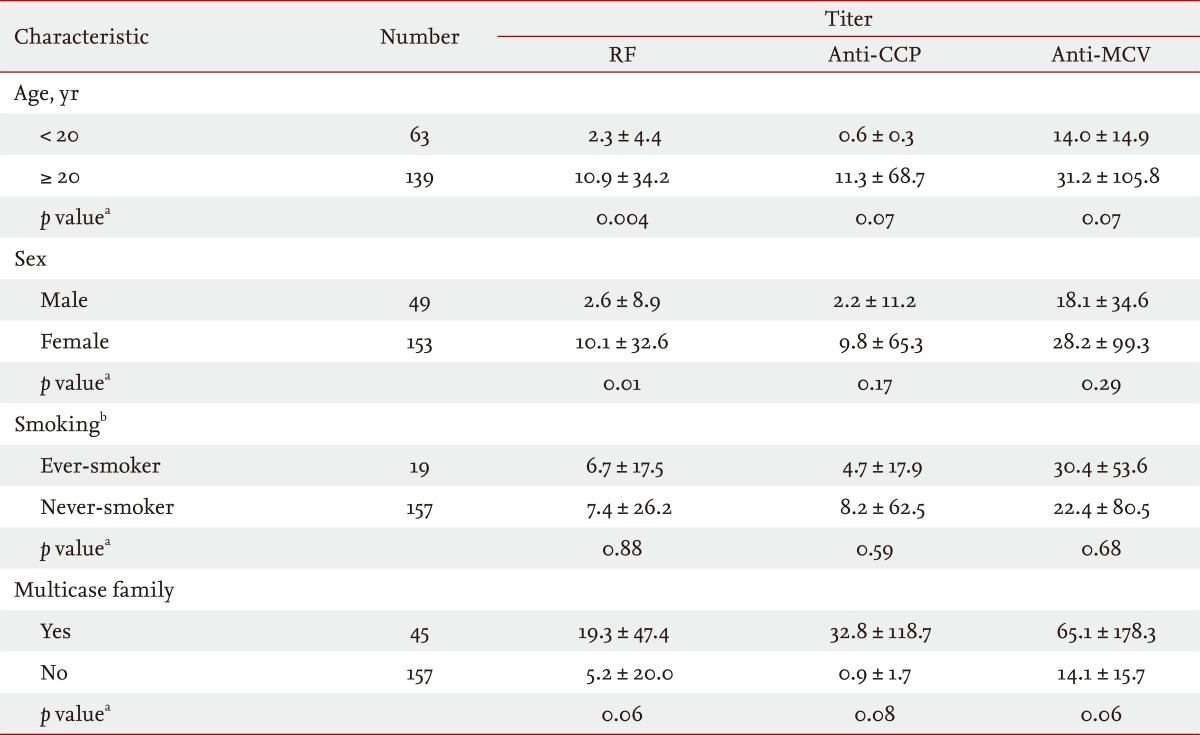
Table 5
Logistic regression analysis of RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody seropositivity in first-degree relatives (n = 202) according to whether they were in a multicase familya
RF, rheumatoid factor; CCP, cyclic citrullinated peptide; MCV, mutated citrullinated vimentin; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
aLogistic regression models were used to calculate ORs and 95% CIs for RF, anti-CCP antibody, and anti-MCV antibody seropositivity, after adjustment for age and sex.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



