 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 25(2); 2010 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
To examine the correlation between radiological joint damage and serological parameters in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
This retrospective study reviewed the records of 216 patients diagnosed with RA and classified them according to disease duration: group 1, Ōēż 24 months; group 2, > 24 months; and group 3, all patients combined. The extent of joint damage was assessed from plain radiographs using a modified version of the Larsen method and compared among groups.
Results
The mean radiographic joint damage score was significantly higher in patients who had established RA (10.1 points) compared with those who had early RA. In group 1, the inflammatory parameters, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein were positively correlated with the joint damage score, but rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody were not. A subgroup analysis revealed that the anti-CCP positive patients in groups 1 and 2 had greater joint damage scores than did the anti-CCP negative patients, but no difference in RF was observed between subgroups. Anti-CCP positivity was not significantly correlated with joint damage sores in group 3.
Conclusions
Anti-CCP positivity was significantly correlated with more severe joint damage at diagnosis. A correlation was observed between the radiological joint damage score and inflammatory parameters in early and established RA, indicating that anti-CCP can serve as a diagnostic tool and predict structural joint damage. These findings suggest anti-CCP positive patients should receive aggressive therapeutic intervention.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the joints that affects approximately 0.5% to 1% of the general population [1]. The clinical manifestation and disease progress is heterogeneous. Immunologically mediated inflammation of the synovium causes cartilage destruction and bony erosion that can result in permanent disability. Thus, early diagnosis and treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is necessary to prevent joint destruction and deformity and to preserve function.
Rheumatoid factor (RF) has been the only serologic marker in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) classification criteria for several decades [2]. RF is a valid prognostic indicator, but the antibody's usefulness for early detection of RA is limited by its moderate sensitivity and relatively low specificity [3].
In recent years, the antibody to cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) has been shown to be more specific than and as sensitive as RF for diagnosing RA [3,4].
Anti-CCP belongs to a family of anti-filaggrin antibodies that react with the antigenic determinant that contains citrullinated arginine residues [5].
Studies indicating that anti-CCP is a better diagnostic tool than RF have been reported for several years [6,7]. Anti-CCP has a sensitivity of 40% to 80%, a specificity of 81% to 100% [7], and an excellent positive and negative predictive value for RA diagnosis [6,7]. These features highlight the antibody's value for monitoring the pathogenesis of RA [8]. The presence of anti-CCP is associated with a higher Larsen score at baseline and at follow up, and it predicts radiological joint damage in early RA [4,9-11]. Furthermore, anti-CCP has been shown to predict a change in the Larsen score and poor functional response in patients who were RF negative [12]. These findings suggest that the presence of anti-CCP is as reliable a predictor of future joint damage as is RF.
The present study compared the relationship between joint damage and parameters such as RF and anti-CCP in early RA patients.
This retrospective study reviewed the records of 216 patients who were diagnosed with RA using the ACR criteria [2] and were treated using DMARDs and/or steroids. All patients were over 18 years of age and had been diagnosed with RA for at least 3 months.
The patients were classified into three groups: group 1 had a disease duration Ōēż 24 months, group 2 had a disease duration between 25 and 48 months, and group 3 was the aggregate of all patients.
Several serological markers, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), RF, and anti-CCP measured at the time of diagnosis were examined. RF was measured by immunoturbidimetry using Cobas integra RFII (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and anti-CCP was measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using DIASTATŌäó (Axis-Shield Diagnostics, Dundee, UK).
A radiologist and rheumatologist evaluated joint damage on plain films of the hand or wrist taken at the time of diagnosis using the modified version of the Larsen method [13]. This method reviews plain films of eight proximal interphalangeal joints, two interphalangeal thumb joints, 10 metacarpophalangeal joints, and both wrists. The degree of joint damage was graded as follows: grade 0, normal; grade 1, soft tissue swelling, joint space narrowing, and subchondral osteopenia; grade 2, bone erosion with destruction of < 25% of the joint space; grade 3, 26% to 50% joint space destruction; grade 4, 51% to 75% destruction; and grade 5, > 75% destruction of the joint space. The sum of all scores equaled 110 points. We examined the correlation between the serological parameters and the joint damage score. Scoring reliability was evaluated using the intraclass correlation coefficient 0.96 (95% confidence interval, 0.92 to 0.99).
SPSS version 14.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the statistical analysis. The two-sample t test and chi-squared test were used for between-group comparisons. The correlation between the radiological joint damage score and each serological parameter was evaluated using Pearson's correlation coefficient. All p values < 0.05 were deemed to be statistically significant. The results are expressed as mean and standard deviation.
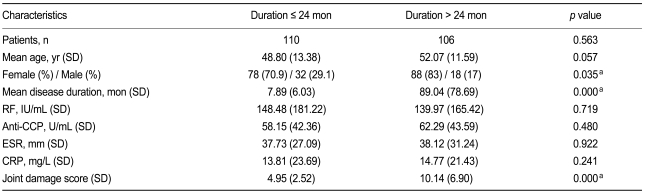
Table 1 shows the patient characteristics. The disease duration and joint damage scores were significantly higher in group 2. Additionally, the number of men in group 1 was significantly higher compared with that in group 2. There was no statistical difference in RF, anti-CCP level, inflammatory parameters between groups.
The joint damage score was correlated with CRP and ESR in all groups, but it was only correlated with disease duration in the established RA and combined groups (Table 2).
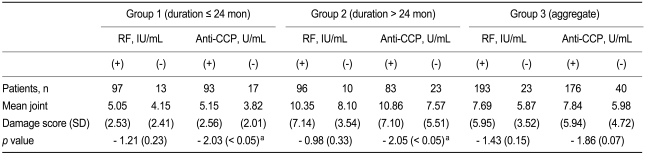
A subgroup analysis of RF and anti-CCP positive and negative patients revealed no difference in the joint damage score between RF positive and negative patients. In contrast, the joint damage score in groups 1 and 2 was significantly higher in the anti-CCP positive patients compared with the anti-CCP negative patients (Table 3) No correlation was found between the joint damage score and the anti-CCP positivity in group 3 (p = 0.07). These results are illustrated in Fig. 1.
RA is characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints that causes structural and functional damage. The disease affects 0.5% to 1% of the general population [1]. The etiology of RA is not fully understood; however, genetic predisposition and environmental factors such as smoking may contribute to the etiopathogenesis [14].
Joint destruction that occurs as the disease progresses decreases the quality of life and increases the socioeconomic burden. Thus, early diagnosis and initiation of a therapeutic intervention is critical for a good prognosis [15,16].
The ACR classification criteria for RA consist primarily of clinical symptoms, and RF is the only serological test [2]. A shortcoming of these criteria is that it is difficult to make a definitive diagnosis until the disease has progressed to the extent that synovial inflammation has caused joint damage.
RF is an autoantibody to the Fc fragment of immunoglobulin G. The effectiveness of the antibody as a diagnostic marker has been questioned because of its unsatisfactory sensitivity and specificity [3,17,18].
Recent reports have suggested that early initiation of therapeutic interventions, including DMARDs, can slow joint damage [19-22]. However, the characteristic clinical features of RA are often not apparent early in the disease process, and therapy is not initiated until considerable time has elapsed and joint damage has appeared. Despite this, RF is included in the diagnostic criteria because it is an indicator of joint damage and level of disability and can be easily tested.
Antiperinuclear factor and anti-keratin antibody are anti-filaggrin antibodies that have a high specificity for RA, but they are not used to diagnose the disease because of difficult technical requirements [23-25].
Recently, anti-CCP has been used to diagnose RA. Arginine residues are converted to citrulline by peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD), and the autoantibody, anti-CCP, reacts with the substrate [26].
Avouac et al. [7] reported that anti-CCP has a diagnostic sensitivity of 39% to 94% and a specificity of 81% to 100% for RA. The autoantibody is closely related to the evolution of RA from undifferentiated arthritis and has a higher sensitivity than does RF for predicting the development of RA in normal healthy controls.
This high specificity suggests that anti-CCP is related to the etiopathogenesis of RA. Suzuki et al. [8] suggested that one haplotype of PAD, type 4, is found more often in people who have RA than in the normal population, suggesting that proteins in RA patients are readily citrullinated and that these proteins cause an autoimmune reaction in the joint cavity. Caspi et al. [27] reported finding higher levels of anti-CCP in the synovial fluid of patients who had RA than in patients who had osteoarthritis or psoriatic arthritis.
Forslind et al. [4] reported that anti-CCP was correlated with a high baseline and 2-year Larsen score in a 2-year follow up of 397 early RA patients who had a disease duration < 1 year.
In the present study, the joint damage score was significantly higher in the anti-CCP positive group than it was in the RF positive group (Table 3). We did not determine the correlation between anti-CCP and the joint damage score; however, the degree of erosive joint damage was significantly higher in patients positive for anti-CCP compared with anti-CCP negative patients in early and established RA. A prospective study is required to determine the prognostic power of anti-CCP.
Group 1 (disease duration Ōēż 24 months) had a significantly higher number of men than did group 2. It is unclear whether the clinical manifestations of RA, such as joint erosion, occur earlier in men, leading to an earlier diagnosis, or if this finding is a result of sampling bias.
Contrary to our expectations, we found no correlation between the joint damage score and anti-CCP positivity (p = 0.065) in group 3. However, this may change in future studies with a larger patient population.
The major limitation of the present study is bias as a result of treatment strategy. A prospective study would allow investigation and manipulation of treatment modalities such as DMARDs, anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy, and systemic glucocorticoids that are confounding factors for disease outcome.
The findings of the present study suggest that the inclusion of anti-CCP in the diagnostic criteria would promote earlier detection of inflammatory arthritis and allow the initiation of more aggressive treatment to prevent joint damage. Our results are consistent with those of others recommending that anti-CCP be included in the RA diagnostic criteria and be used as a marker of the severity of the disease [28-30].
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank professor Im-Hee Shin in the Department of Medical Statistics for supervising the statistical analysis.
References
1. Kvien TK. Epidemiology and burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 2004;22(Suppl 1):1ŌĆō12PMID : 15157000.

2. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:315ŌĆō324PMID : 3358796.


3. De Rycke L, Peene I, Hoffman IE, et al. Rheumatoid factor and anticitrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic value, associations with radiological progression rate, and extra-articular manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63:1587ŌĆō1593PMID : 15547083.



4. Forslind K, Ahlmen M, Eberhardt K, Hafstr├Čm I, Svensson B. BARFOT Study Group. Prediction of radiological outcome in early rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: role of antibodies to citrullinated peptides (anti-CCP). Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63:1090ŌĆō1095PMID : 15308518.



5. Shmerling RH. Testing for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies: is it time to set this genie free? Arch Intern Med 2009;169:9ŌĆō14PMID : 19139318.


6. Ates A, Karaaslan Y, Aksaray S. Predictive value of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide in patients with early arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 2007;26:499ŌĆō504PMID : 16670828.


7. Avouac J, Gossec L, Dougados M. Diagnostic and predictive value of anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Ann Rheum Dis 2006;65:845ŌĆō851PMID : 16606649.



8. Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, et al. Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 2003;34:395ŌĆō402PMID : 12833157.


9. Lindqvist E, Eberhardt K, Bendtzen K, Heinegard D, Saxne T. Prognostic laboratory markers of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:196ŌĆō201PMID : 15458956.



10. Meyer O, Nicaise-Roland P, Santos MD, et al. Serial determination of cyclic citrullinated peptide autoantibodies predicted five-year radiological outcomes in a prospective cohort of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2006;8:R40. PMID : 16469118.



11. Bongi SM, Manetti R, Melchiorre D, et al. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies are highly associated with severe bone lesions in rheumatoid arthritis anti-CCP and bone damage in RA. Autoimmunity 2004;37:495ŌĆō501PMID : 15621577.


12. Quinn MA, Gough AK, Green MJ, et al. Anti-CCP antibodies measured at disease onset help identify seronegative rheumatoid arthritis and predict radiological and functional outcome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:478ŌĆō480PMID : 16287917.


13. Rau R, Herborn G. A modified version of Larsen's scoring method to assess radiologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1995;22:1976ŌĆō1982PMID : 8992004.

14. Padyukov L, Silva C, Stolt P, Alfredsson L, Klareskog L. A gene-environment interaction between smoking and shared epitope genes in HLA-DR provides a high risk of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:3085ŌĆō3092PMID : 15476204.


15. Emery P. The Roche Rheumatology Prize Lecture. The optimal management of early rheumatoid disease: the key to preventing disability. Br J Rheumatol 1994;33:765ŌĆō768PMID : 8055205.


16. van der Heide A, Jacobs JW, Bijlsma JW, et al. The effectiveness of early treatment with "second-line" antirheumatic drugs: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 1996;124:699ŌĆō707PMID : 8633829.


17. Lee DM, Schur PH. Clinical utility of the anti-CCP assay in patients with rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 2003;62:870ŌĆō874PMID : 12922961.



18. Hoffman IE, Peene I, Pottel H, et al. Diagnostic performance and predictive value of rheumatoid factor, anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies, and the HLA shared epitope for diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem 2005;51:261ŌĆō263PMID : 15388633.


19. Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, Stamm TA, Uffimann M, Smolen JS. Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004;43:906ŌĆō914PMID : 15113999.


20. O'Dell JR. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2591ŌĆō2602PMID : 15201416.


21. van Aken J, Lard LR, le Cessie S, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, Huizinga TW. Radiological outcome after four years of early versus delayed treatment strategy in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63:274ŌĆō279PMID : 14962962.



22. Nell VP, Machold KP, Stamm TA, et al. Autoantibody profiling as early diagnostic and prognostic tool for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:1731ŌĆō1736PMID : 15878904.



23. Nienhuis RL, Mandema E. A new serum factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; the antiperinuclear factor. Ann Rheum Dis 1964;23:302ŌĆō305PMID : 14178016.



24. Young BJ, Mallya RK, Leslie RD, Clark CJ, Hambin TJ. Anti-keratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J 1979;2:97ŌĆō99PMID : 111762.



25. Vincent C, de Keyser F, Masson-Bessiere C, Sebbag M, Veys EM, Serre G. Anti-perinuclear factor compared with the so called "antikeratin" antibodies and antibodies to human epidermis filaggrin, in the diagnosis of arthritides. Ann Rheum Dis 1999;58:42ŌĆō48PMID : 10343539.



26. Schellekens GA, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, van de Putte LB, van Venrooij WJ. Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritisspecific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest 1998;101:273ŌĆō281PMID : 9421490.



27. Caspi D, Anouk M, Golan I, et al. Synovial fluid levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and IgA rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006;55:53ŌĆō56PMID : 16463412.


28. Liao KP, Batra KL, Chibnik L, Schur PH, Costenbader KH. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:1557ŌĆō1561PMID : 18234714.



Figure┬Ā1
Comparison of the mean joint damage score in anti-CCP positive and negative patients (A) and RF positive and negative patients (B). Both the open circles and asterisks indicate values beyond 2 standard deviation of the mean value. Anti-CCP, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide; RF, rheumatoid factor.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



