 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 41(1); 2026 > Article |
|
Abstract
Sepsis continues to be a serious global health concern with increasing mortality rates owing to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) have emerged as critical tools for optimizing antibiotic use and reducing AMR. This review examines the applications of ASPs in sepsis treatment, highlights their role in improving patient outcomes, and addresses the challenges posed by multidrug-resistant organisms. The review begins by exploring the global AMR crisis and its implications for sepsis therapy and then evaluates the Surviving Sepsis Campaign’s guidelines and their limitations in the context of growing AMR. The core principles of ASPs in sepsis treatment are also discussed. Data from international and Korean studies indicate that effective ASPs may improve patient outcomes; reduce the length of hospital stay; and reduce the incidence of antibiotic-associated adverse events, healthcare costs, and AMR. However, diagnostic delays, staffing shortages, and inconsistent ASP implementation remain significant barriers. Furthermore, robust evidence supporting the effectiveness of ASPs in various patient populations with sepsis is required. This review concludes with the future directions for integrating rapid diagnostics, individualized treatment planning, and informatics. To ensure responsible antibiotic use in sepsis care in increasing resistance, investment in and engagement with ASPs must be increased.
Sepsis continues to cause substantial mortality worldwide, with an estimated 5.3 million deaths annually [1]. Sepsis is a leading cause of in-hospital mortality and contributes substantially to overall inpatient deaths [2,3]. This challenge is expected to worsen as antimicrobial resistance (AMR) continues to rise. The spread of resistant bacteria diminishes the effectiveness of available treatments and impairs timely clinical intervention in patients with sepsis [4,5]. The increasing prevalence of AMR, coupled with high mortality associated with sepsis, presents a looming crisis. If AMR is not addressed urgently, a resurgence in sepsis-related deaths and major setbacks in global infectious disease control efforts are imminent [4].
Notably, recent Korean national cohort data indicate that, although the incidence of sepsis has increased in Korea over the past decade, in-hospital mortality rates have gradually declined with improvements in care; however, the burden remains substantial [6]. This trend aligns with growing concerns regarding AMR in Korea, as studies have shown increasing rates of multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens complicating sepsis treatment, particularly in long-term care and hospital-acquired settings [7]. Korean pediatric data also note rising resistance rates, underscoring the urgency of stewardship among vulnerable populations [8,9]. Given the increasing complexity of sepsis management in the context of AMR, both the recent advancements and ongoing challenges in sepsis treatment should be assessed.
Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) are systematic, multidisciplinary strategies designed to optimize the use of antimicrobial agents, ensuring that patients receive the appropriate antibiotic at the correct time, dose, route, and duration, based on evidence and local epidemiology. The overarching goals of ASPs are twofold: (1) to improve individual patient outcomes, such as survival, adverse event reduction, and timely infection resolution; and (2) to combat the wider threat of AMR by minimizing unnecessary or inappropriate antibiotic exposure at the healthcare system level [10–15]. ASPs incorporate prospective audits, prescriber feedback, formulary restrictions, and protocolized guidance, all supervised by core teams that typically include infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and clinical microbiologists, are supported by hospital leadership [11,13]. The significance of ASPs is increasingly recognized globally, given the escalation of AMR and lag in the development of new antibiotic agents; thus, stewardship is now considered an essential component of modern infectious disease management and a pillar of patient safety and quality improvement initiatives [10,16].
This review addresses the global threat of AMR, focusing on its impact on clinical management and patient outcomes. It discusses the principles of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign while acknowledging its limitations in addressing the evolving challenges posed by AMR. The core principles of ASPs in sepsis, emphasizing timely antibiotic initiation, the importance of de-escalation, and the vital role of infectious disease specialists in optimizing therapy, have also been explored. This review also evaluated the effect of ASPs on sepsis outcomes, underscoring their role in improving patient care and curbing the spread of resistant pathogens. The review concludes by discussing the limitations of the current ASP strategies for sepsis treatment and highlighting future opportunities for strengthening stewardship practices in response to the AMR crisis.
The global threat posed by AMR has reached unprecedented levels, fundamentally challenging effective management of sepsis across healthcare systems. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, AMR was among the most serious global public health concerns, undermining the use of existing antibiotics and contributing to increased mortality, extended hospitalization, and increased healthcare expenditures for patients [5,11,17]. The pandemic has further complicated this picture: although some initial infection prevention measures (e.g., improved hand hygiene and reduced interpersonal contact) may have temporarily curbed certain transmission pathways, disruptions in standard care and the widespread empirical use of antibiotics for viral illnesses with low rates of bacterial co-infection, such as COVID-19, have accelerated the overuse and misuse of antimicrobials [17–20]. This surge in inappropriate prescriptions is now widely recognized as a driver of the emergence and dissemination of MDR pathogens in critical care and hospital settings [5,17,18,21].
Decades of evidence have established a clear and direct relationship between indiscriminate antibiotic use, including overuse (unnecessary initiation or prolonged duration) and misuse (suboptimal selection or dosing), and the development of resistance. In intensive care units (ICUs), where sepsis often requires immediate empiric therapy, the frequent administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics in the absence of adequate diagnostic procedures paradoxically increases the selection pressure for resistant organisms [5,21,22]. This dynamic is further exacerbated when delays in pathogen identification prompt clinicians to extend or escalate antimicrobial coverage [5,22]. As AMR rates increase, clinicians are forced into a cycle of escalating empirical regimens, which further promotes resistance and reduces the future effectiveness of first-line agents [5,11,21]. Multicenter data from Korea have demonstrated that the prevalence of MDR organisms in sepsis is particularly high in long-term care hospitals and nursing home-acquired sepsis cases, even exceeding that in hospital-acquired cases. Drug-bug mismatches in empiric antibiotics are common, highlighting the pressing need for stewardship in these settings [7].
Recognizing this destructive cycle, ASPs have become a cornerstone strategy for curbing resistance, particularly in resource-intensive environments such as sepsis treatment [11,21,22]. ASPs employ multifaceted interventions, including prescriber education, formulary restrictions, protocolized therapy, and audit feedback mechanisms, to ensure that antibiotics are used only when clinically indicated, promptly de-escalated based on microbiological data, and optimized for both spectrum and duration [11,21–25]. In Korea, national surveys of ASPs have revealed an increasing adoption of stewardship practices but have continued limitations in specialist personnel and programmatic focus, with a substantial dependency on pre-authorization measures and ongoing opportunities for improvement [24,26]. Despite these limitations, the stepwise implementation of core stewardship elements at a Korean tertiary hospital has been associated with reductions in antibiotic consumption and more favorable trends in resistance rates than nationwide patterns, underscoring the potential of long-term, multidisciplinary stewardship measures to positively affect AMR burdens, even in resource-limited settings [25].
Recent studies have shown that effective stewardship programming improves patient outcomes and reduces the incidence of healthcare-associated infections caused by MDR organisms [18,22]. Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, the integration of stewardship strategies, such as biomarker- guided discontinuation and rapid diagnostic pathways, has limited unnecessary antibiotic exposure and mitigated the long-term risk of resistance amplification [17,18]. When ASPs are embedded in sepsis protocols and actively supported by infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, clinical microbiologists, and microbiology laboratories, they represent the most effective defense against the relentless progression of AMR in the context of both pandemic and endemic infectious threats [11,21–23,25,27].
In recent years, the Surviving Sepsis Campaign and other international guidelines have underscored the importance of early initiation of antimicrobial therapy in patients with suspected sepsis, emphasizing that delays in antibiotic administration can significantly increase mortality risk, particularly in cases of severe sepsis and septic shock [18,21,22,28]. Multiple large-scale studies and performance improvement programs have demonstrated a clear and near-linear association, in which each hour of delay in administering appropriate empiric antibiotics after the recognition of sepsis correlates with measurable increases in in-hospital mortality, with the effect being most pronounced in patients with severe conditions, including shock and multi-organ failure [29–31]. For instance, a retrospective study of more than 28,000 patients with severe sepsis or septic shock found that mortality increased steadily with every hourly delay in the first antibiotic administration, even after adjusting for sepsis severity and other confounders [29]. Similar findings were observed in emergency department settings, where each hourly delay in antibiotic administration corresponded to increased odds of in-hospital mortality, particularly among those with septic shock [30,31]. Data from Korean studies support these findings. A nationwide analysis from 2007 to 2016 showed that while the incidence of sepsis increased, improved management, including prompt antibiotic initiation, was associated with decreased in-hospital mortality, hospital stay, and ICU admissions for patients with sepsis [6].
Beyond timing, the adequacy of empiric antibiotic therapy, which is the extent to which the initially chosen regimen is active against the identified or suspected pathogen( s), plays a critical role in patient outcomes. Inadequate empiric therapy was significantly associated with increased mortality among patients with sepsis, even after adjusting for comorbidities and illness severity. One meta-analysis of 70 prospective studies quantified this relationship, demonstrating a pooled adjusted odds ratio (OR) for mortality of 1.60 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.37–1.86) for inappropriate empiric antibiotics compared with appropriate ones; this effect was particularly strong in patients with septic shock [32]. Furthermore, delays in the administration of appropriate antibiotics were independently associated with prolonged ICU and length of hospital stays in patients with sepsis, highlighting the importance of early and appropriate therapy selection [33]. Multicenter studies in Korea have emphasized that the risk of drug-bug mismatch is highest in patients with long-term care hospital-acquired sepsis, and careful initial antibiotic selection tailored to the onset location is recommended [7].
However, the strong push for immediate broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage in all suspected sepsis cases has prompted a significant debate, particularly concerning the potential risks of indiscriminate antibiotic use. Broad-spectrum agents are frequently employed empirically to ensure early and adequate coverage in the face of increasing rates of MDR organisms and evolving resistance patterns [5,34]. Although this strategy may improve survival in cases of true infections, it also carries the risk of promoting AMR, increased drug-associated toxicity, development of Clostridioides difficile infections, and unnecessary selective pressure on local microbial ecology [5,34]. Empirical overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics is of particular concern in patient populations with a low risk of MDR, particularly in settings where rapid diagnostics or validated risk stratification tools are available to support targeted therapy [5].
Indeed, the current research underscores the need for individualized risk assessment and stewardship. Kalin et al. have highlighted that identifying MDR risk factors and using rapid molecular diagnostics may facilitate targeted therapy, reduce unnecessary broad-spectrum use, and mitigate collateral damage [5]. Additionally, large real-world analyses of the most recent Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines advocate a risk- and probability-stratified approach to antibiotic timing [35]. Specifically, immediate antibiotic therapy within 1 h is recommended primarily for septic shock or strongly probable infection, whereas a 3-hour window is recommended for patients with possible but less likely infections and no shock [35]. This stratification aligns with real-world data: the mortality benefit of rapid antibiotics is substantial in patients with shock or high-probability sepsis but marginal in those without shock and with only a possible infection, for whom undue haste may more often result in overtreatment than enhanced survival [35,36].
Moreover, critical analyses of the evidence on universal “time-to-antibiotic” performance targets highlight significant methodological heterogeneity and bias in the literature [36,37]. Weinberger et al. have argued that the majority of supporting studies have been observational, have frequently focused on patients in extremely severe conditions (e.g., those with shock or requiring ICU care), and have failed to fully adjust for confounding factors such as presenting symptoms, comorbidities, or illness trajectories [36]. Because many patients with suspected sepsis ultimately have non-infectious or self-limiting etiologies, routine administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics in rigid timeframes risks exposing these individuals to unnecessary harm without a clear survival advantage [36]. Some studies have indicated that the mortality differences between immediate and early antibiotic administration (within 3 h) may not be statistically significant in a broader population of patients with sepsis without shock [38].
Therefore, these insights have shaped consensus on the latest practice recommendations. Although early empirical antibiotics are undeniably lifesaving for high-risk patient groups (notably those with shock, high severity scores, or definitive infection), the indiscriminate or unrefined application of broad-spectrum therapy for all suspected cases carries substantial risks to individual and public health. Accumulated evidence strongly supports a balanced, patient-specific approach that incorporates infection probability, severity, local resistance patterns, and the growing threat of MDR pathogens to maximize survival benefits while minimizing antimicrobial overuse and its repercussions [5,34–36].
ASPs are fundamental for optimizing sepsis treatment in an era marked by an increase in AMR and MDR pathogens, both of which threaten the effectiveness of standard therapeutic approaches. In sepsis treatment, the core principles of ASPs involve a multifaceted strategy that balances the need for timely and effective empirical therapy by minimizing unnecessary antibiotic exposure and subsequent resistance selection.
Timely administration of appropriate empirical antimicrobials is associated with reduced mortality and improved clinical outcomes in patients with sepsis; however, the selection of initial therapy should be guided by local resistance patterns, individual patient risk factors (e.g., previous antimicrobial exposure or healthcare-associated infection), and the suspected site of infection [5,29,30,32–34,39,40]. For critically ill patients, particularly those with septic shock or severe organ dysfunction, immediate broad-spectrum coverage is often warranted; however, the empirical use of broad-spectrum agents should not be indiscriminate; instead, therapy should be targeted to those with a high likelihood of MDR infections based on individual risk stratification and local resistance data [5,34,40].
Rapid initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is essential for the management of sepsis. Rapid diagnostic assays help overcome the time constraints of conventional cultures and strengthen the ability of ASPs to guide timely and appropriate treatment [41]. The advancement and integration of point-of-care testing and rapid molecular diagnostics facilitate earlier and more precise identification of pathogens and resistance mechanisms, thus facilitating the de-escalation and optimized selection of antimicrobial therapy [5,34,42]. Diagnostic stewardship, which ensures the appropriate, timely, and judicious use of these technologies, supports ASPs by directing microbiological testing and antibiotic decisions toward clinically appropriate cases, thus reducing diagnostic delays and overtreatment [42].
However, rapid diagnostic methods have inherent limitations. Indiscriminate use, particularly in patients with a low pre-test probability, may lead to the detection of colonization rather than active infection, resulting in unnecessary antimicrobial therapy [43,44]. Their effectiveness is maximized when interpreted in an appropriate clinical context and implemented in conjunction with active ASPs [45].
Once microbiological data or clinical stabilization have been observed, ASPs emphasize the rapid narrowing (“de-escalation”) of antimicrobial regimens. This approach involves discontinuing redundant or overly broad-spectrum agents in favor of the most targeted, least toxic, and narrowest effective regimen to minimize collateral damage, reduce selective pressure, and curb future AMR [5,40]. Early discontinuation or de-escalation is particularly critical when initial broad-spectrum coverage is empirically selected for high-risk or shock patients but is no longer justified by culture or clinical information.
ASPs also include individualized optimization of antibiotic dosing based on patient-specific factors, such as the severity of illness, organ function, pharmacokinetic variability, and pathogen minimum inhibitory concentrations. Advanced strategies include therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), continuous infusion of time-dependent antibiotics, and combination therapy in selected scenarios to enhance efficacy and prevent the emergence of resistance [5,34].
In the context of sepsis, excessive or unnecessary extension of antibiotic therapy duration (or unwarranted initial use) promotes the selection of MDR organisms, increases the incidence of adverse drug events, and increases healthcare costs [5,34,40]. Stewardship efforts support strict adherence to the daily assessment of ongoing antibiotic therapy, with a low threshold for discontinuation in non-infectious or non-septic cases, and adherence to evidence-based duration guidelines.
Robust ASPs are grounded in the surveillance of local AMR patterns and antibiotic consumption, with regular feedback to clinical teams. This approach facilitates updated empirical therapy recommendations and supports behavioral changes that align with resistance trends [5,34]. In sepsis care, stewardship frameworks emphasize the use of local microbiological and resistance data to guide early empirical choices and support timely review, de-escalation, and discontinuation once diagnostic data become available [28,46,47].
In a Korean study, the implementation of a prospective audit-and-feedback program in a surgical ICU reduced unnecessary use of anti-pseudomonal β-lactams, increased appropriate de-escalation, and improved adjusted ICU mortality [48].
The implementation of ASPs in sepsis treatment requires active collaboration among infectious disease specialists, critical care physicians, clinical microbiologists, pharmacists, and nursing staff to ensure that antimicrobial decisions are context- and patient-specific and rapidly responsive to emerging data [5,42]. Thus, in sepsis treatment, ASPs are not merely about restricting antibiotic use but also about intelligently integrating timely and effective therapy with careful selection, rapid adjustment, and ongoing monitoring, striving for a balance between immediate clinical need and the long-term imperative to preserve antibiotic efficacy [5,34,42].
Appropriate empirical antibiotic therapy for sepsis is defined as the timely initiation of one or more agents that reliably cover the most likely causative pathogens, selected in accordance with local epidemiology and patient-specific factors, such as previous exposure, comorbidities, and infection source [5,49]. Its importance has been heightened by the increasing prevalence of MDR organisms, with inadequate initial coverage being associated with increased mortality and adverse outcomes in multiple large-scale studies and systematic reviews [29,30,32,33,39,50]. Multicenter cohort data from Korea indicate that the likelihood of drug-bug mismatch varies substantially with the onset location of sepsis, with the lowest match rates in long-term care hospital-acquired cases, underscoring the need for risk-based and epidemiology-informed initial selection [7].
Despite the known benefits of early broad-spectrum therapy, its indiscriminate and prolonged use may cause AMR and increase the risk of adverse events [5,34,51]. De-escalation refers to the practice of systematically narrowing the antimicrobial spectrum or discontinuing unnecessary agents after clinical reassessment and when microbiological data become available. This strategy aims to balance the need for timely and appropriate initial coverage guided by local epidemiological data to minimize unnecessary antibiotic exposure, thereby preserving antibiotic efficacy for future patients and reducing the risk of MDR pathogens [5,51].
Evidence from ICU and sepsis settings indicate that de-escalation is feasible and generally safe, with observational studies showing no increase in negative outcomes, even though limited randomized data caution about possible higher reinfection rates without a clear effect on mortality [51]. A retrospective study conducted in a Korean surgical ICU demonstrated that a comprehensive ASP led by an infectious disease physician and pharmacist significantly improved outcomes in patients with sepsis by reducing the use of anti-pseudomonal β-lactams, facilitating timely de-escalation, and most notably, reducing ICU mortality [48].
Importantly, the success of de-escalation relies heavily on the adequacy of the initial empirical regimen, with coverage selected to achieve timely activity against possible pathogens, while avoiding unnecessary breadth; if the initial regimen does not adequately cover probable pathogens based on clinical and epidemiological factors, opportunities for safe spectrum narrowing may be missed or delayed, potentially compromising patient outcomes [32,51]. Korean multicenter cohort data underscore that de-escalation and appropriate strategies should be tailored according to the local epidemiology and healthcare setting because MDR risk and pathogen profiles differ by onset location [7].
Implementing appropriate empirical therapy is increasingly challenging owing to evolving MDR patterns and imperfect predictive tools [5,34]. Empirically selected regimens may be inappropriate because of patient-level risk factors (e.g., previous antibiotic exposure, previous hospitalizations, or residence in long-term care), variable pathogen prevalence, and the time required to obtain definitive microbiological identification [5,40,49]. Even with rapid diagnostics, coverage cannot always be precisely tailored at the outset, making an ongoing risk-benefit evaluation essential [42,52].
De-escalation itself faces institutional and cognitive barriers, and clinicians may be reluctant to narrow the therapy because of the fear of missing uncommon pathogens or unexpected deterioration, particularly in critically ill or immunocompromised patients [34,51]. There is also heterogeneity in definitions and implementation across centers, and some studies report lower real-world adoption of de-escalation (< 60%) [51]. In Korea, the use of procalcitonin assays for sepsis and pneumonia has been approved and incorporated into stewardship strategies to guide the safe reduction of unnecessary antibiotic use and support shorter treatment durations without increasing adverse outcomes [53]. However, although biomarkers such as procalcitonin can support decisions to taper or stop antibiotics, they remain imperfect and require clinical correlation [52,54].
Given these complexities, the involvement of infectious disease specialists and pharmacists is crucial to promote antibiotic appropriateness and judicious spectrum reduction. Infectious disease specialists have expertise in pathogen risk stratification, MDR epidemiology, and diagnostic interpretation, which directly contribute to the tailored selection of empiric regimens and decisive patient-specific de-escalation decisions [5,34,49]. Pharmacists play key roles in dose optimization, drug monitoring (e.g., TDM for dose adjustment), drug-drug interaction management, stewardship policy implementation, and education [5].
Their collaborative efforts are central to ASPs, which have been shown to facilitate the timely initiation of appropriate therapies, exploit new rapid diagnostics for early pathogen identification, and implement de-escalation without compromising safety or outcomes [5,42,51]. ASP teams can conduct periodic reviews and audits, offer feedback and targeted interventions, and provide evidence-based guidance for clinical practice [5,42,55,56]. As MDR sepsis becomes more prevalent and its management becomes increasingly complex, expertise is essential to ensure immediate clinical success and long-term preservation of antibiotic efficacy [5,34,42].
ASPs have emerged as essential frameworks for sepsis management. The aim of ASPs is to achieve a balance between aggressive early empiric treatment and avoid antibiotic overuse, which has profound repercussions across the clinical, economic, and public health spectra. The following sections elaborate on the effects of ASPs on various sepsis outcomes, with supporting evidence (Table 1, Fig. 1).
Prompt and appropriate antimicrobial therapy is a key determinant of the survival of patients with sepsis. In the MONARCS trial (n = 2,634), the crude mortality rate was 33% among patients receiving adequate therapy and 43% among those receiving inadequate therapy [57]. A meta-analysis of 70 prospective studies reported a pooled adjusted OR for mortality of 1.60 (95% CI, 1.37–1.86) associated with inappropriate empiric antibiotics [32].
Recent studies have shown that interventions to improve the antimicrobial therapy for sepsis can reduce mortality. In a Brazilian ICU, a quality improvement initiative emphasizing early and appropriate antimicrobial therapy for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock was associated with increased bundle compliance and a decline in inpatient mortality [58]. Although a formal ASP was not adopted, this result was consistent with the findings of stewardship-led programs. A 10-year Japanese cohort study reported a sustained reduction in 30-day mortality in sepsis after the ASP-supported optimization of empiric and definitive therapies [59]. In bloodstream infection-associated sepsis, the integration of rapid molecular diagnostics with real-time ASP guidance shortens the time to appropriate therapy and reduces the 28-day mortality in critically ill patients [60]. These observations indicated that stewardship interventions could improve the survival of patients with sepsis. However, well-designed prospective studies are limited, and most of the available data are from single-center or retrospective analyses.
Stewardship programs can reduce hospital LOS by facilitating timely and appropriate therapy and reducing unnecessary antibiotic exposure. High-resolution data showed that each hour of delay in delivering appropriate antibiotics increased hospital LOS by 0.134 days, independent of severity or comorbidity [34]. Recent intervention studies demonstrate that structured ASP activities, such as weekend pharmacist-driven audit [61], prescriber acceptance of ASP recommendations [62], and targeted interventions promoting intravenous-to-oral conversion of fluoroquinolones [55], are associated with significant reductions in hospital LOS. In addition to mitigating delays and curbing the effect of MDR infections [5], ASPs help relieve bed pressure and improve care efficiency.
A cornerstone of stewardship is the reduction of unnecessary and prolonged antibiotic exposure, which directly translates to lower rates of drug-related toxicity, including nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and C. difficile infection. In a randomized trial of patients with sepsis, a procalcitonin-guided stewardship strategy reduced the composite incidence of infection-associated adverse events, including new C. difficile infection, MDR organism infection, or related mortality (7.2% vs. 15.3%; hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.20–0.98) without increasing mortality or relapse [63]. In broader hospitalized populations that include many patients with sepsis, ASP implementation has been associated with reduced vancomycin-related nephrotoxicity [64] and a lower incidence of antimicrobial-related adverse events, such as allergic reactions, hematologic toxicity, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea [56]. Meta-analysis has shown that hospital ASPs significantly decrease the incidence of C. difficile infections [65]. These findings support the role of ASPs in improving safety outcomes and their effects on antimicrobial optimization.
ASPs have been associated with a reduction in AMR and the emergence of MDR organisms in populations, including patients with sepsis. In an Italian pre–post quasi-experimental study of Gram-negative bloodstream infections, involvement of a multidisciplinary stewardship team reduced new MDR organism acquisition from 36.6% to 8.3% (OR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.05–0.67), with shorter antibiotic treatment durations, high rates of appropriate empirical therapy, and decreased microbiological failure but without differences in 30-day mortality [66]. The implementation of a prospective audit-and-feedback ASP in two ICUs led to a significant reduction in overall antibiotic consumption and the incidence of bloodstream infections caused by MDR Gram-negative organisms without affecting mortality or LOS [47]. A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that ASP implementation was associated with reduced incidence of resistant Gram-negative bacteria, extended-spectrum β-lactamase–producing Enterobacterales, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection [65]. In Korea, the stepwise expansion of ASPs in tertiary care hospitals has significantly reduced the overall antibiotic use and contributed to the stabilization or decline in resistance rates for major nosocomial pathogens, despite increments in national resistance trends [25]. These data suggest that ASPs can help limit the resistance and spread of MDR organisms, although well-designed studies focusing specifically on sepsis are limited.
The economic burden of sepsis is immense, estimated at $38 billion annually in the US alone, aggravated by MDR sepsis and protracted hospital stays [34]. ASPs reduce these costs substantially by minimizing unnecessary broad-spectrum use, decreasing hospital LOS, reducing adverse events and readmission rates, and blunting the economic fallout of AMR emergence. Although well-designed studies remain limited, several investigations have demonstrated the cost-effectiveness and cost-benefit of ASPs that employ persuasive and structural interventions; reported estimates range from $415 per patient to $19,287.54 per averted death in 30 days, depending on the type of intervention evaluated [67]. A recent systematic review found that stewardship-facilitated rapid molecular diagnostics consistently yielded better cost-effectiveness than standard practice, not only by accelerating care but also by controlling the downstream cascade of complications and resistance [68].
Several limitations in the systemic, operational, and cultural domains hinder the consistent application of ASPs in sepsis treatment. Systemic barriers include a global surge in MDR pathogens and complicated empirical therapy selection for adult and pediatric sepsis, leading to diagnostic delays and increased reliance on broad-spectrum agents [5,17,69]. These trends propagate a cycle of antibiotic overuse and further resistance, particularly when diagnostic uncertainty dominates or patient stratification tools are lacking [5,10]. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has intensified these problems, and the disruption of standard healthcare pathways and increased empirical antibiotic use for viral infections have fueled AMR escalation, challenging the ASP efficacy [10,17]. In Korea, a national survey revealed that most hospitals had ASPs on paper but suffered from a scarcity of human resources and programs that relied heavily on pre-authorization rather than comprehensive, multidisciplinary review [24–26]. These factors undermine the breadth and responsiveness of stewardship actions, particularly in cases of complex sepsis. The lack of uniform access to multidisciplinary stewardship teams, including infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and clinical microbiologists, limits the reach and consistency of stewardship efforts, particularly in resource-limited settings [11,22,23,70].
Operational constraints include slow and uneven integration of advanced microbiological diagnostics and rapid molecular assays in clinical pathways for sepsis [5,23,42,71]. Although these tools have the potential to drive early targeted therapy, the translation of rapid laboratory results into real-time clinical action remains inconsistent, often because of limited infrastructure or weak associations between the microbiology laboratory and prescribers [23,42]. Stewardship often falls short of timely antibiotic de-escalation and individualized therapy. Empiric antibiotic regimens are commonly maintained for longer than necessary, particularly when laboratory data are delayed or ambiguous, leading to overtreatment and increased risk of AMR [5,21,22]. Although pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic optimization tools, such as TDM and continuous infusions, offer promise for personalized dosing in sepsis, their implementation and evidence bases across diverse patient populations remain limited [5,21]. In pediatrics, contextual adaptation and tailored ASP strategies are further impeded by the lack of standardized metrics and the need to involve caregivers in stewardship decisions [69].
Culture and behavior, including variable prescriber attitudes and institutional prescribing habits, act as barriers to guideline adherence and stewardship uptake [21,27,70]. Gaps in education, accountability, and feedback mechanisms undermine ASP sustainability even in high-resource settings [11,27,70].
One major obstacle to demonstrating the clinical benefits of ASPs in this context is the broad and evolving definition of sepsis, which includes a heterogeneous spectrum of infection-related syndromes. This heterogeneity often leads to inconsistent findings across clinical studies, reduces the statistical power of trials, and complicates the efforts to establish clear causal associations between stewardship interventions and patient outcomes during sepsis treatment [72–74]. Moreover, conducting prospective randomized controlled trials in real-world sepsis populations remains inherently difficult owing to the acute and variable nature of the condition, ethical considerations, and logistical constraints pertaining to critically ill patients. To address these challenges and generate robust evidence, well-designed and methodologically rigorous studies are essential for clarifying the effects of ASPs on sepsis outcomes.
The effectiveness of ASPs for the treatment of sepsis depends on several strategic advancements. The integration of rapid diagnostics with stewardship practices is poised to revolutionize patient management, enabling clinicians to move beyond empiricism to pathogen-directed therapy within hours instead of days [5,23,42,69,71]. Effective collaboration between diagnostic and antimicrobial stewardships is essential for designing protocols that ensure appropriate and timely test utilization and direct and swift clinical responses [42,71,75]. A recent quasi-experimental study by Albin et al. [76], which evaluated a bundled diagnostic stewardship intervention for ventilator-associated pneumonia, found that integrating diagnostic and antimicrobial stewardship could safely reduce unnecessary respiratory cultures and broad-spectrum antibiotic use in ICU patients. This study highlights the tangible effects of coordinated diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in improving antimicrobial practices in critical care settings.
Biomarker-guided stewardship, particularly using procalcitonin algorithms, holds promise for optimizing antibiotic duration and facilitating earlier safe discontinuation, which reduces overall exposure and secondary MDR complications [18]. Although procalcitonin is the best-studied biomarker, future studies on other biomarkers and novel panels may further refine therapies for sepsis and related syndromes [18,69]. Artificial intelligence and advanced informatics platforms can further support risk stratification, real-time decision-making, and predictive analytics to guide stewardship interventions at the point of care [69].
System-wide engagement and scalable models that address variability in resources, institutional capacity, and prescriber behavior are required [11,70]. Multidisciplinary collaboration, including infectious diseases, microbiology, intensive care, pharmacy, infection control, and information technology teams, should be hardwired into stewardship frameworks [22,70]. Moreover, public health policies should incentivize investment in diagnostic and stewardship infrastructure, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, and foster the pragmatic adaptation of ASP principles to various local contexts [10,11,70]. In pediatrics, the integration of parent and caregiver education, context-specific outcome measures, and cost-effectiveness analyses are key research priorities [69].
In November 2024, the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea launched a 3-year pilot initiative on ASPs that targeted hospitals with bed capacities exceeding 300. This program aimed to elevate institutional awareness of antimicrobial use and encouraged evidence-based selection and administration of antibiotics in clinical care. This initiative seeks to establish a standardized and sustainable ASP infrastructure across healthcare facilities and promote its systematic implementation. Considering the fragmented implementation of ASPs in Korean hospitals, this policy is a significant step forward. In the long term, it is expected to improve antimicrobial prescription practices and enhance the clinical outcomes of sepsis treatment.
In summary, the persistent global threat of sepsis, compounded by the proliferation of MDR organisms, demands a multifaceted and forward-thinking approach to antimicrobial therapy. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign provides a crucial framework for the early recognition and management of sepsis. However, limitations persist, particularly regarding the balance between prompt empirical therapy and appropriate antimicrobial selection in this era of increasing resistance. This review underscores the core tenets of ASPs, appropriate empirical antibiotic use, timely de-escalation, and active involvement of infectious disease experts, which are indispensable for optimizing clinical outcomes and preserving antimicrobial efficacy. Evidence shows that ASPs reduce mortality, hospital LOS, and the incidence of adverse events while curbing the development of resistance and associated costs in sepsis treatment. Nevertheless, significant challenges remain, including delays in diagnosis, gaps in rapid resistance detection, pharmacokinetic variability in critical illnesses, human resource limitations, and the inconsistent global adoption of stewardship strategies. The integration of rapid molecular diagnostics, individualized dosing approaches, and robust interdisciplinary collaboration holds significant promise for further refinement of stewardship efforts. Sustained investment in human resources, infrastructure, and capacity-building for ASPs, as well as support for innovation and research, is essential. In parallel, high-quality evidence from well-designed studies is urgently needed to strengthen the foundation for effective implementation of ASPs in sepsis treatment. These efforts are critical for bridging the current gaps and ensuring optimal outcomes in patients with sepsis amid the evolving threat of AMR.
Notes
Figure 1
ASP intervention pathway and its impact on sepsis outcomes and antimicrobial resistance. ASP, antimicrobial stewardship program; SSC, Surviving Sepsis Campaign.
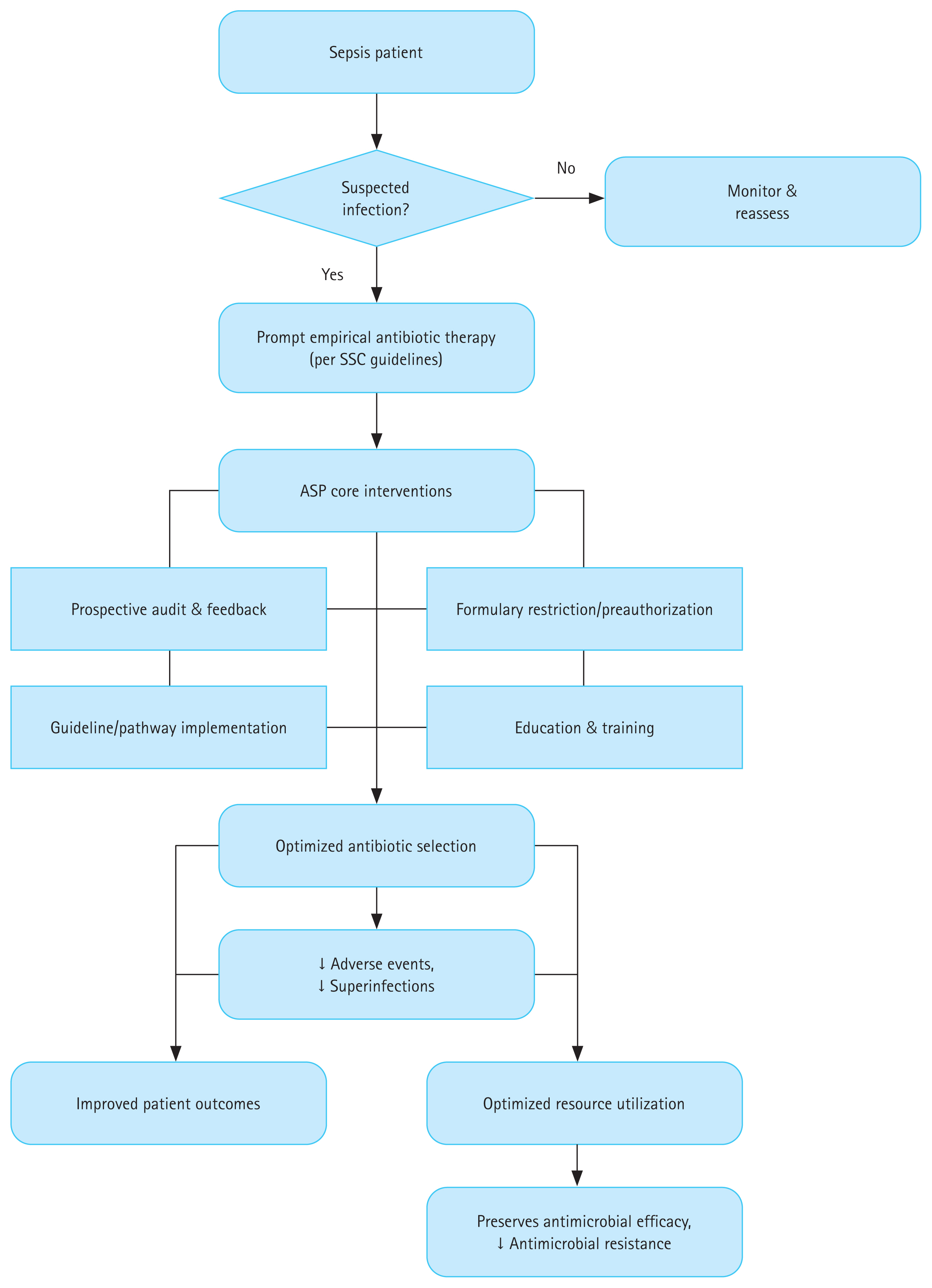
Table 1
Summary of proven and potential effects of ASPs on sepsis outcomes
| Outcome domain | ASP-driven intervention(s) | Key findings & supporting evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Mortality | Optimization of empiric/definitive therapy; rapid diagnostics with ASP guidance | ASP-supported optimization lowered 30-day mortality [59]; rapid diagnostics plus ASP guidance reduced 28-day mortality [60]. |
| Hospital LOS | Pharmacist-driven audit; acceptance of ASP advice; IV-to-oral conversion | ASP interventions reduced LOS via pharmacist audit [61], prescriber acceptance [62], and IV-to-oral fluoroquinolone conversion [55]. |
| Antibiotic adverse events and toxicity | Antibiotic duration reduction; biomarker-guided ASP; pharmacist involvement | PCT-guided ASP lowered infection-associated adverse events [63]; ASPs reduced vancomycin nephrotoxicity [64] and antibiotic-related ADEs [56]; meta-analysis confirmed reduction in Clostridioides difficile infection [65]. |
| AMR & MDR organism burden | Multidisciplinary ASP teams; prospective audit and feedback; stepwise ASP expansion | Multidisciplinary ASP reduced new MDR organism acquisition [66]; ICU ASP reduced MDR Gram-negative BSI [47]; meta-analysis showed reductions in resistant GNB, ESBL, and MRSA [65]; Stepwise ASP expansion reduced antibiotic use and stabilized resistance [25]. |
| Healthcare cost and resource utilization | Structural ASP interventions; integration of rapid diagnostics | Cost-effectiveness studies of ASPs show savings per patient and per averted death [67]; stewardship-facilitated rapid diagnostics improved cost-effectiveness [68]. |
ASP, antimicrobial stewardship program; LOS, length of stay; PCT, procalcitonin; ADE, adverse drug event; AMR, antimicrobial resistance; MDR, multidrug-resistance; ICU, intensive care unit; BSI, bloodstream infection; GNB, gram negative bacilli; ESBL, extended spectrum β-lactamase; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
REFERENCES
1. Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, et al. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016;193:259–272.


2. Knoop ST, Skrede S, Langeland N, Flaatten HK. Epidemiology and impact on all-cause mortality of sepsis in Norwegian hospitals: a national retrospective study. PLoS One 2017;12:e0187990.



3. Rhee C, Jones TM, Hamad Y, et al. Prevalence, underlying causes, and preventability of sepsis-associated mortality in US acute care hospitals. JAMA Netw Open 2019;2:e187571.



4. GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024;404:1199–1226.


5. Kalın G, Alp E, Chouaikhi A, Roger C. Antimicrobial multidrug resistance: clinical implications for infection management in critically Ill patients. Microorganisms 2023;11:2575.



6. Oh SY, Cho S, Kim GH, et al. Incidence and outcomes of sepsis in Korea: a nationwide cohort study from 2007 to 2016. Crit Care Med 2019;47:e993–e998.


7. Kim HJ, Oh DK, Lim SY, et al. Antibiogram of multidrug-resistant bacteria based on sepsis onset location in Korea: a multicenter cohort study. J Korean Med Sci 2023;38:e75.




8. Seo JH, Jun JS, Yeom JS, et al. Changing pattern of antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in children during 20 years in Jinju, South Korea. Pediatr Int 2013;55:332–336.

9. Park CH, Seo JH, Lim JY, Woo HO, Youn HS. Changing trend of neonatal infection: experience at a newly established regional medical center in Korea. Pediatr Int 2007;49:24–30.


10. Majumder MAA, Rahman S, Cohall D, et al. Antimicrobial stewardship: fighting antimicrobial resistance and protecting global public health. Infect Drug Resist 2020;13:4713–4738.




11. MacDougall C, Polk RE. Antimicrobial stewardship programs in health care systems. Clin Microbiol Rev 2005;18:638–656.




12. Majumder MAA, Singh K, Hilaire MG, Rahman S, Sa B, Haque M. Tackling antimicrobial resistance by promoting antimicrobial stewardship in medical and allied health professional curricula. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2020;18:1245–1258.


13. Ohl CA, Luther VP. Antimicrobial stewardship for inpatient facilities. J Hosp Med 2011;6:Suppl 1. S4–S15.



15. Griffith M, Postelnick M, Scheetz M. Antimicrobial stewardship programs: methods of operation and suggested outcomes. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2012;10:63–73.


16. McGregor JC, Fitzpatrick MA, Suda KJ. Expanding antimicrobial stewardship through quality improvement. JAMA Netw Open 2021;4:e211072.


17. Knight GM, Glover RE, McQuaid CF, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and COVID-19: Intersections and implications. Elife 2021;10:e64139.




18. Kyriazopoulou E, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ. Antimicrobial stewardship using biomarkers: accumulating evidence for the critically Ill. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022;11:367.



19. Shin DH, Kang M, Song KH, Jung J, Kim ES, Kim HB. A call for antimicrobial stewardship in patients with COVID-19: a nationwide cohort study in Korea. Clin Microbiol Infect 2021;27:653–655.



20. Choi Y, Kang M, Shin DH, et al. Antibiotic prescription in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: analysis of National Health Insurance System data in the Republic of Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2023;38:e189.




22. Murphy CV, Reed EE, Herman DD, Magrum B, Beatty JJ, Stevenson KB. Antimicrobial stewardship in the ICU. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2022;43:131–140.


23. Morency-Potvin P, Schwartz DN, Weinstein RA. Antimicrobial stewardship: how the microbiology laboratory can right the ship. Clin Microbiol Rev 2016;30:381–407.




24. Kim B, Kim J, Kim SW, Pai H. A survey of antimicrobial stewardship programs in Korea, 2015. J Korean Med Sci 2016;31:1553–1559.




25. Shin DH, Kim HS, Heo E, et al. Stepwise expansion of antimicrobial stewardship programs and its impact on antibiotic use and resistance rates at a tertiary care hospital in Korea. Microbiol Spectr 2022;10:e0033522.




26. Park SY, Chang HH, Kim B, et al. Human resources required for antimicrobial stewardship activities for hospitalized patients in Korea. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2020;41:1429–1435.


27. Tamma PD, Holmes A, Ashley ED. Antimicrobial stewardship: another focus for patient safety? Curr Opin Infect Dis 2014;27:348–355.

28. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med 2021;49:e1063–e1143.

29. Ferrer R, Martin-Loeches I, Phillips G, et al. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med 2014;42:1749–1755.

30. Liu VX, Fielding-Singh V, Greene JD, et al. The timing of early antibiotics and hospital mortality in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017;196:856–863.



31. Seymour CW, Kahn JM, Martin-Gill C, et al. Delays from first medical contact to antibiotic administration for sepsis. Crit Care Med 2017;45:759–765.



32. Paul M, Shani V, Muchtar E, Kariv G, Robenshtok E, Leibovici L. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of appropriate empiric antibiotic therapy for sepsis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2010;54:4851–4863.




33. Zhang D, Micek ST, Kollef MH. Time to appropriate antibiotic therapy is an independent determinant of postinfection ICU and hospital lengths of stay in patients with sepsis. Crit Care Med 2015;43:2133–2140.


34. Kumar NR, Balraj TA, Kempegowda SN, Prashant A. Multidrug- resistant sepsis: a critical healthcare challenge. Antibiotics (Basel) 2024;13:46.



35. Taylor SP, Kowalkowski MA, Skewes S, Chou SH. Real-world implications of updated surviving sepsis campaign antibiotic timing recommendations. Crit Care Med 2024;52:1002–1006.


36. Weinberger J, Rhee C, Klompas M. A critical analysis of the literature on time-to-antibiotics in suspected sepsis. J Infect Dis 2020;222(Suppl 2):S110–S118.



37. Seok H, Jeon JH, Park DW. Antimicrobial therapy and antimicrobial stewardship in sepsis. Infect Chemother 2020;52:19–30.




38. Althunayyan SM, Aljanoubi MA, Alghadeer SM, et al. The impact of emergency antibiotic administration time on patients with sepsis. Saudi Med J 2021;42:1002–1008.



39. Garnacho-Montero J, Garcia-Garmendia JL, Barrero-Almodovar A, Jimenez-Jimenez FJ, Perez-Paredes C, Ortiz-Leyba C. Impact of adequate empirical antibiotic therapy on the outcome of patients admitted to the intensive care unit with sepsis. Crit Care Med 2003;31:2742–2751.


40. Johnson MT, Reichley R, Hoppe-Bauer J, Dunne WM, Micek S, Kollef M. Impact of previous antibiotic therapy on outcome of Gram-negative severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 2011;39:1859–1865.


41. Eubank TA, Long SW, Perez KK. Role of rapid diagnostics in diagnosis and management of patients with sepsis. J Infect Dis 2020;222(Suppl 2):S103–S109.



42. Messacar K, Parker SK, Todd JK, Dominguez SR. Implementation of rapid molecular infectious disease diagnostics: the role of diagnostic and antimicrobial stewardship. J Clin Microbiol 2017;55:715–723.




43. Dangerfield B, Chung A, Webb B, Seville MT. Predictive value of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) nasal swab PCR assay for MRSA pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014;58:859–864.




44. Polage CR, Gyorke CE, Kennedy MA, et al. Overdiagnosis of Clostridium difficile Infection in the molecular test era. JAMA Intern Med 2015;175:1792–1801.



45. Peri AM, Chatfield MD, Ling W, Furuya-Kanamori L, Harris PNA, Paterson DL. Rapid diagnostic tests and antimicrobial stewardship programs for the management of bloodstream infection: what is their relative contribution to improving clinical outcomes? A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 2024;79:502–515.




46. Cortegiani A, Antonelli M, Falcone M, et al. Rationale and clinical application of antimicrobial stewardship principles in the intensive care unit: a multidisciplinary statement. J Anesth Analg Crit Care 2023;3:11.




47. Onorato L, Macera M, Calò F, et al. The effect of an antimicrobial stewardship programme in two intensive care units of a teaching hospital: an interrupted time series analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect 2020;26:782.e1–782.e6.


48. Kim SH, Yoon JG, Park HJ, et al. Effects of a comprehensive antimicrobial stewardship program in a surgical intensive care unit. Int J Infect Dis 2021;108:237–243.


49. Bochud PY, Bonten M, Marchetti O, Calandra T. Antimicrobial therapy for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: an evidence-based review. Crit Care Med 2004;32(11 Suppl):S495–S512.


50. Vazquez-Guillamet C, Scolari M, Zilberberg MD, Shorr AF, Micek ST, Kollef M. Using the number needed to treat to assess appropriate antimicrobial therapy as a determinant of outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med 2014;42:2342–2349.


51. Garnacho-Montero J, Escoresca-Ortega A, Fernández-Delgado E. Antibiotic de-escalation in the ICU: how is it best done? Curr Opin Infect Dis 2015;28:193–198.

52. Schuetz P, Raad I, Amin DN. Using procalcitonin-guided algorithms to improve antimicrobial therapy in ICU patients with respiratory infections and sepsis. Curr Opin Crit Care 2013;19:453–460.


53. Kim JH. Clinical utility of procalcitonin on antibiotic stewardship: a narrative review. Infect Chemother 2022;54:610–620.




54. Kim CJ. Current status of antibiotic stewardship and the role of biomarkers in antibiotic stewardship programs. Infect Chemother 2022;54:674–698.




55. Park SM, Kim HS, Jeong YM, et al. Impact of intervention by an antimicrobial stewardship team on conversion from intravenous to oral fluoroquinolones. Infect Chemother 2017;49:31–37.




56. Suh Y, Ah YM, Chun HJ, et al. Potential impact of the involvement of clinical pharmacists in antimicrobial stewardship programs on the incidence of antimicrobial-related adverse events in hospitalized patients: a multicenter retrospective study. Antibiotics (Basel) 2021;10:853.



57. MacArthur RD, Miller M, Albertson T, et al. Adequacy of early empiric antibiotic treatment and survival in severe sepsis: experience from the MONARCS trial. Clin Infect Dis 2004;38:284–288.


58. Yokota PK, Marra AR, Martino MD, et al. Impact of appropriate antimicrobial therapy for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock--a quality improvement study. PLoS One 2014;9:e104475.



59. Saito N, Tsuchiya J, Itoga M, et al. Multiple blood culture sampling, proper antimicrobial choice, and adequate dose in definitive therapy supported by the antimicrobial stewardship team could decrease 30-day sepsis mortality rates. Infect Drug Resist 2024;17:207–219.




60. Tseng HY, Chen CL, Chen WC, et al. Reduced mortality with antimicrobial stewardship guided by BioFire FilmArray Blood Culture Identification 2 panel in critically ill patients with bloodstream infection: a retrospective propensity score-matched study. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2024;64:107300.


61. Elrefaei H, El Nekidy WS, Nasef R, et al. The impact of clinical pharmacist-driven weekend antimicrobial stewardship coverage at a quaternary hospital. Antibiotics (Basel) 2024;13:974.



62. Hurtado D, Varela M, Juarez A, Nguyen YN, Nhean S. Impact of antimicrobial stewardship program intervention acceptance on hospital length of stay. Hosp Pharm 2023;58:491–495.




63. Kyriazopoulou E, Liaskou-Antoniou L, Adamis G, et al. Procalcitonin to reduce long-term infection-associated adverse events in sepsis. A randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2021;203:202–210.



64. Fodero KE, Horey AL, Krajewski MP, Ruh CA, Sellick JA Jr, Mergenhagen KA. Impact of an antimicrobial stewardship program on patient safety in veterans prescribed vancomycin. Clin Ther 2016;38:494–502.


65. Baur D, Gladstone BP, Burkert F, et al. Effect of antibiotic stewardship on the incidence of infection and colonisation with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2017;17:990–1001.


66. Rinaldi M, Gatti M, Tonetti T, et al. Impact of a multidisciplinary management team on clinical outcome in ICU patients affected by Gram-negative bloodstream infections: a pre-post quasi-experimental study. Ann Intensive Care 2024;14:36.




67. Naylor NR, Zhu N, Hulscher M, Holmes A, Ahmad R, Robotham JV. Is antimicrobial stewardship cost-effective? A narrative review of the evidence. Clin Microbiol Infect 2017;23:806–811.


68. Rojas-Garcia P, van der Pol S, van Asselt ADI, et al. Diagnostic testing for sepsis: a systematic review of economic evaluations. Antibiotics (Basel) 2021;11:27.



69. Donà D, Barbieri E, Brigadoi G, et al. State of the art of antimicrobial and diagnostic stewardship in pediatric setting. Antibiotics (Basel) 2025;14:132.



70. Charani E, Holmes AH. Antimicrobial stewardship programmes: the need for wider engagement. BMJ Qual Saf 2013;22:885–887.


71. Curren EJ, Lutgring JD, Kabbani S, et al. Advancing diagnostic stewardship for healthcare-associated infections, antibiotic resistance, and sepsis. Clin Infect Dis 2022;74:723–728.



72. Verdonk F, Blet A, Mebazaa A. The new sepsis definition: limitations and contribution to research and diagnosis of sepsis. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2017;30:200–204.

73. Lyle NH, Pena OM, Boyd JH, Hancock RE. Barriers to the effective treatment of sepsis: antimicrobial agents, sepsis definitions, and host-directed therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2014;1323:101–114.


74. Yu SC, Betthauser KD, Gupta A, et al. Comparison of sepsis definitions as automated criteria. Crit Care Med 2021;49:e433–e443.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



