INTRODUCTION
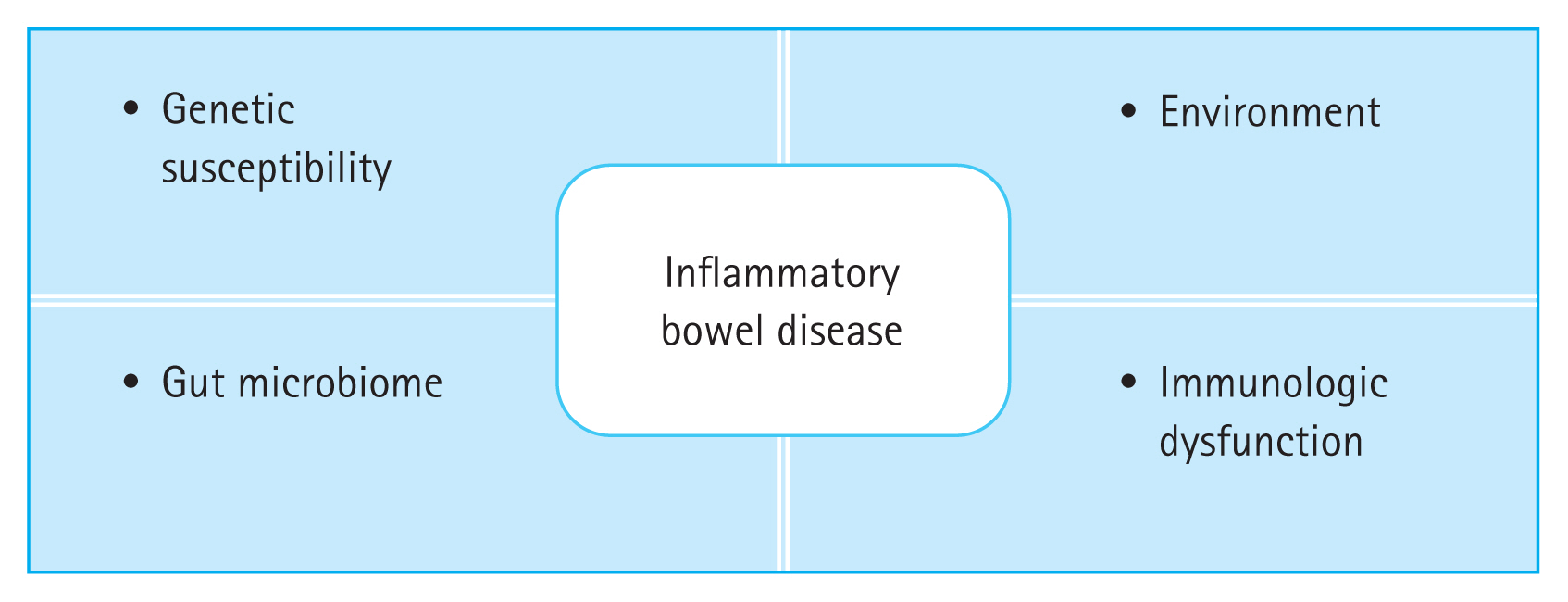
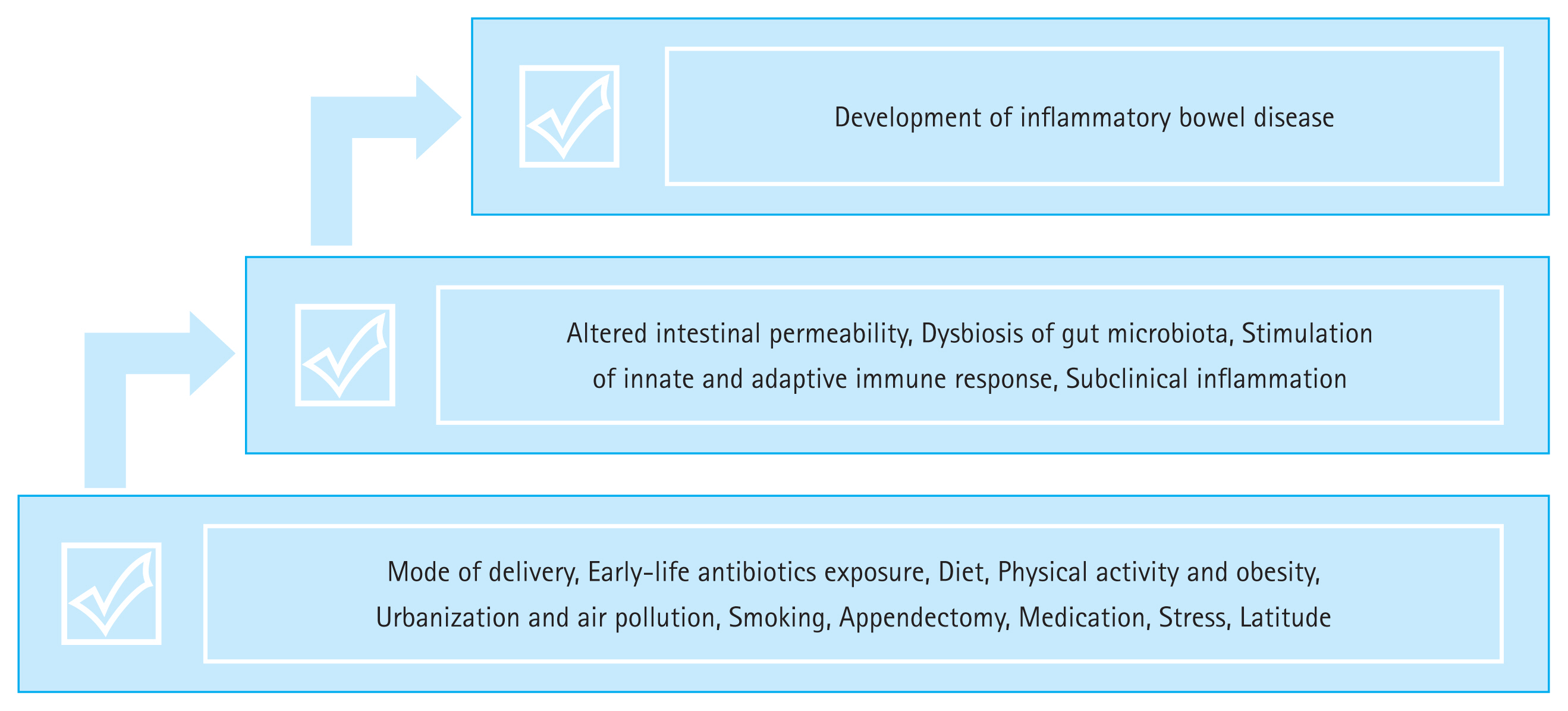
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis (UC) and CrohnŌĆÖs disease (CD), is a lifelong disease characterized by chronic refractory immune-mediated inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The pathogenesis of IBD is complex and multifactorial, and its etiology remains largely unknown [1]. The most widely held hypothesis on IBD pathogenesis is that it involves a complex interaction among genetics, environment, microbiota, and immune responses (Fig. 1) [2,3]. Recent genome-wide association studies have identified many genetic loci associated with IBD. Furthermore, technological advances, such as single cell RNA sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, and single-cell-level mass cytometry, have the potential to identify new specific cell subtypes related to IBD [4ŌĆō6]. Although host genetic factors may significantly influence the development of IBD, they do not change over just a few decades. Therefore, environmental factors may explain the recent rapid increase in IBD epidemiology. Although still lower than that in Western countries, from 1990 to 2019, the incidence and prevalence of IBD in East Asia have shown a rapid rise in recent epidemiologic studies [7,8]. Additionally, many epidemiological studies on Asian migrants who migrated from low-to high-incidence regions have found an increased prevalence of IBD, particularly in first-generation children. This result supports the hypothesis that exposure to a high-risk environment rather than actual ethnic and genetic factors may play a role in increasing IBD risk [9]. Additionally, in a large European study, the concordant CD rate in monozygotic twins raised in the same environment was between 20% and 50%, whereas in dizygotic twins, the rate was less than 10%. The difference in rates reflects a genetic component in the development of IBD, whereas the low concordance rate among the twins highlights environmental influences [10ŌĆō12]. In this review, we describe the current understanding of the environmental factors that underpin the increased risk of developing IBD (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
EARLY-LIFE INFLUENCES
Infancy is a critical period for establishing the gut microbiome, which is important for the immunological and metabolic development of an individualŌĆÖs future health. The hygiene hypothesis proposes that diminished exposure to microbial antigens associated with improved hygiene in early life may increase the risk of immune-mediated diseases, including IBD [13,14].
Mode of delivery
According to the delivery mode, cesarean section could cause slow colonization of the gut microbiota in neonates compared to vaginal delivery and affect the development of the immune system [15,16]. From a Danish cohort from 1973 to 2008, the overall incidence rate ratio (IRR) of IBD associated with cesarean section compared to vaginal delivery was 1.14 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.06ŌĆō1.22), and age-specific IRRs were higher in the age groups 0ŌĆō4, 5ŌĆō9, and 10ŌĆō14 years (1.37, 1.30, and 1.25, respectively) and lower in the age groups 15ŌĆō19, 20ŌĆō24, 25ŌĆō29, and 30ŌĆō35 years (1.05, 1.19, 1.01, and 1.12, respectively) [17]. Recent evidence suggests that this altered microbial colonization early in life, related to the mode of delivery, does not influence the diagnosis of IBD later in life [18ŌĆō20].
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding provides essential nutrients, rich oligosaccharides, and high amounts of immunoglobulin A, which affect early gut microbial structure and immunological function more profoundly than formula feeding [21]. Although there are many conflicting studies on the relationship between breastfeeding and the development of IBD, most have shown that breastfeeding plays a protective role against the risk and severity of IBD [22]. In a recent systematic review with meta-analysis, breastfeeding was associated with a lower risk of CD (odds ratio [OR]: 0.71, 95% CI: 0.59ŌĆō0.85) and UC (OR: 0.78, 95% CI: 0.67ŌĆō0.91). Moreover, longer duration of breastfeeding (Ōēź 12 months) decreases the risk of IBD compared to 3 or 6 months [23].
Early-life antibiotics exposure
The use of antibiotics in early life can imprint immunological and microbial changes that may predispose individuals to IBD in later life. In a recent Sweden and Norway cohort study, the use of antibiotics in the first year was associated with IBD (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.33, 95% CI: 1.01ŌĆō1.76) [24]. In a large prospective case-control study in Sweden, antibiotic exposure was associated with an increased risk of UC (OR: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.64ŌĆō1.85) and CD (OR: 2.27, 95% CI: 2.06ŌĆō2.49) compared with no antibiotic use [25]. In a recent meta-analysis, the risk of IBD increased with cumulative antibiotic exposure (Ōēź 3 dispensations: OR: 2.02, 95% CI: 1.49ŌĆō2.74; 2 dispensations: OR: 1.36, 95% CI: 1.03ŌĆō1.78; 1 dispensation: OR: 0.96, 95% CI: 0.72ŌĆō1.26) [26,27].
DIET, FOOD, AND NUTRITIONAL EXPOSURES
Diet, food, and nutritional exposures play a dominant role in shaping the microbial ecology and regulating the immune response in the gut. The Western diet is high in fat, sugar, and refined carbohydrates and low in fiber and fruits. Western dietary patterns in developed countries may be a major driver of the growing incidence of IBD [28].
Since 1978, high intakes of fruits, vegetables, and dietary fiber have been found to be strongly associated with a reduced incidence of IBD [29,30]. Dietary fibers, called micro-biota-accessible carbohydrates, have been suggested to be important in the prevention of IBD by providing energy for the intestinal microbiota. Moreover, their products, short-chain fatty acids, could reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines by gut microbiota modulation and barrier maintenance [31]. In contrast, Western dietary patterns and fast food consumption are associated with an increased incidence of IBD [29]. Long-term high intake of fat and sucrose in artificial sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs), cakes, cookies, and chocolates could alter the gut microbiota composition and IBD predisposition status in animal studies [32ŌĆō34]. However, a large comparative study did not find an association between total carbohydrate, sugar, and starch intake and the incidence of IBD [35]. A recent meta-analysis found that dietary intake of carbohydrates and SSBs is not significantly associated with an increased risk of IBD, whereas sugar intake is associated with an increased risk [36]. Regarding the high-fat diet, particularly saturated fat, it disrupts the intestinal barrier, decreases mucus production, and activates inflammatory pathways in animal studies [37,38]. In humans, although high saturated fat, high n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), and low n-3 PUFA levels have been associated with an increased risk of IBD, some prospective studies have not identified such an association [39ŌĆō41]. Regarding protein intake, no association between other protein sources such as fish, shellfish, eggs, and poultry and IBD was observed. However, total meat consumption is associated with a higher risk of IBD in a dose-dependent manner [42]. Each 100 g/day increment in dietary total meat consumption is associated with a 38% greater risk of IBD incidence [43].
In conclusion, because ingested food, host microbiome, and immune function interact in a complex manner, it is difficult to determine whether a single food component is a direct cause of IBD. Nevertheless, based on various research results, it can be concluded that a high intake of fruits, vegetables, and fiber may lower the risk of IBD, whereas a Western diet, excessive intake of fat and sucrose, and excessive intake of protein may increase the risk of IBD.
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND OBESITY
In line with the worldwide trend of increasing obesity, the number of patients with IBD is also reported to be increasing among patients with obesity [44]. In a large, prospective cohort of United States women from 1991 to 2008, women with obesity were positively associated with the development of CD compared to women with normal body mass index (HR: 2.3, 95% CI: 1.15ŌĆō4.69) [45]. In contrast, no association between obesity and the development of IBD in the data from a European prospective cohort study [46]. Although clinical results are conflicting, studies on its pathogenesis have shown that obesity may be a risk factor for the development of IBD. In patients with obesity and high levels of subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissues, adipokines and inflammatory cytokines may be increased, inducing immune responses, altering the composition of the gut microbiota, and maintaining a low-grade preclinical inflammatory state [24,44,47].
In contrast to obesity, regular physical activity contributes to the prevention of various chronic diseases through gastrointestinal anti-inflammatory effects and autophagy activation in animal models. Interest in this area has recently increased [48,49]. Although there have been many contradictory clinical results, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that physical activity is associated with a lower risk of developing CD and UC [50].
URBANIZATION AND AIR POLLUTION
IBD is a worldwide disease, from an epidemiological perspective. Moreover, it has stratified stages: emergence, acceleration in incidence, compounding prevalence, and prevalence equilibrium stages [51]. Western countries are in the compounding prevalence or prevalence equilibrium stage, newly industrialized countries are in the acceleration in incidence stage, and developing countries are in the emergence stage [51]. Urbanization brings about many lifestyle changes, including poor housing, diets with contaminated water, improper food storage, exposure to air pollution, and challenges to global health [52]. No studies have investigated the relationship between the rural versus urban gut microbiomes and development of IBD. Several studies have been conducted in healthy populations; bacterial diversity is lower in rural residents than in urban residents, which is consistent with the reduced bacterial richness and diversity observed in IBD pathogenesis [53]. In the Asia-Pacific CrohnŌĆÖs and Colitis Epidemiologic Study, the incidence of IBD in highly urbanized regions was higher than that in rural regions [54]. Similarly, a systematic review and meta-analysis suggested that urban regions have a higher incidence rate of UC (IRR: 1.17, 95% CI: 1.03ŌĆō1.32) and CD (IRR: 1.42, 95% CI: 1.26ŌĆō1.60) than rural regions [55,56]. However, some studies have contradictory results, showing no difference in the prevalence of IBD between rural and urban areas of India and South Korea [57].
Exposure to air pollution accompanied by urbanization is expected to have a harmful effect on human health. Particles inhaled from the lungs through the gutŌĆōlung axis into the intestine, airborne particles entering the intestine, or airborne particles in food can affect the gut microbiota and metabolic and immune systems [58]. A recent meta-analysis suggested that although preclinical studies have suggested a link between air pollution exposure and the development of IBD, clinical studies have reported conflicting and inconsistent results depending on air particle size and type [59]. Air pollutants (higher levels of PM2.5), industrial chemicals (Pb, Cu, Fe), and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances have been reported to increase the risk of the development of IBD [59].
SMOKING
In 1984, smoking was suggested as an independent risk factor for the development of CD (RR: 3.5, 95% CI: 1.8ŌĆō6.6) [60]. Smoking induces many carcinogenic and mutagenic compounds such as aldehydes, quinones, peroxides, nicotine, and nitrosamines. These compounds alter the composition of the gut microbiota and immune system and affect the occurrence and poor disease course of CD [61,62]. Smoking cessation for > 1 year in an intervention study could make the disease course more benign compared to continuing smoking [63].
Conversely, smoking is known to reduce the risk of developing UC compared to non-smokers (OR: 0.58, 95% CI: 0.45ŌĆō0.75) since the 1980s [64,65]. Additionally, some studies have suggested a protective effect on the clinical course of UC, such as colectomy, relapse, and hospitalization rates, in smokers compared to non-smokers [66]. The reason for the opposing effects of smoking on UC and CD is largely unknown, but many studies have investigated the role of nicotine in the colonic mucosal layer, dendritic cells, and cytokines [67ŌĆō69]. In summary, smoking could increase the risk and worsen the disease course of CD but decrease the risk and alleviate the disease course of UC.
Recent studies on the etiology of smoking in IBD have suggested that nicotine induces epigenetic changes [70]. Through epigenetic mechanisms, environmental factors can change genomic activity without changing DNA structure, contributing to the pathogenesis of IBD [70]. For example, in a mouse colitis model, nicotine was shown to increase the expression of microRNA124 and regulate the Th1/Th2 balance, which explains the dual role of smoking in IBDs [71].
APPENDECTOMY
The appendix contains rich lymphoid follicles that resemble PeyerŌĆÖs patches and act as gut-associated lymphoid tissue, an important part of the immune system, through immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin A production and microbial reservoirs [72,73]. From this perspective, appendectomy status was found to be associated with the development of CD compared with non-appendectomy status (IRR: 2.11, 95% CI: 1.21ŌĆō3.79) [74]. Moreover, a recent meta-analysis found that the risk of developing CD increases after appendectomy (RR: 2.28, 95% CI: 1.66ŌĆō3.14), which persists 5 years postoperatively (RR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.12ŌĆō1.36) [75].
In contrast to CD, previous appendectomy status is an independent protective factor against developing UC compared with non-appendectomy status (OR: 0.44, 95% CI: 0.30ŌĆō0.64) [76]. Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis suggested that previous appendectomy status is an independent protective factor for future colectomy in patients with UC (OR: 0.76, 95% CI: 0.65ŌĆō0.89) [77]. However, the therapeutic role of appendectomy after UC diagnosis has not yet been investigated [78]. Many hypotheses have been proposed to explain the association between appendectomy and UC [79]. One hypothesis states that pathogenic bacteria associated with the pathogenesis of UC are removed by appendectomy, thereby protecting against UC [79]. This also explains why changes in mucosal immune responses and microbiota because of appendectomy negatively impact the development of UC [79].
MEDICATIONS
Oral contraceptives
Oral contraceptives are widely used in women aged 15ŌĆō44 years. A recent meta-analysis has found that exposure to oral contraceptives is an independent risk factor for UC (OR: 1.30, 95% CI: 1.13ŌĆō1.49) and CD (OR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.09ŌĆō1.40) [80]. The most common oral contraceptive type is combined oral contraceptive pills (COCPs) that release both estrogen and progesterone. Both second-generation COCPs (CD: OR: 2.12, 95% CI: 1.83ŌĆō2.44; UC: OR: 1.27, 95% CI: 1.12ŌĆō1.44) and newer COCPs (CD: OR: 1.64, 95% CI: 1.33ŌĆō2.01; UC: OR: 1.38, 95% CI: 1.14ŌĆō1.67) are associated with the development of IBD. However, the use of progesterone-only pills and parenteral contraceptives is not associated with the development of IBD [81]. The exact mechanism has not been established. However, some studies have suggested that oral contraceptives modify intestinal permeability, alter T cell-mediated immune responses, and influence gut microbiota composition, which can lead to the development of IBD [82].
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are among the most commonly prescribed medications for pain and inflammation; however, they can cause gastrointestinal toxicity, including gastrointestinal erosions and ulcers [83]. It is well known that frequent use of NSAIDs is associated with the worsening of IBD; therefore, caution is recommended in clinical practice [84]. In three studies that investigated the association between NSAIDs and the development of IBD, the use of NSAIDs was associated with the development of IBD (OR: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.19ŌĆō1.92) [85ŌĆō87]. NSAID administration causes a decrease in prostaglandin levels through the inhibition of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme, which contributes to the inflammatory response and may contribute to the development of IBD [83]. COX-2 is upregulated by inflammatory cytokines in the gastrointestinal tract of patients with IBD; however, the role of selective COX-2 inhibitors is controversial [88]. Selective COX-2 inhibitors have fewer gastrointestinal side effects; however, there are conflicting results regarding their effectiveness in treating IBD in animal colitis studies [89].
Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, a retinoid derivative of vitamin A, is the most effective prescription medication for treating severe acne [90]. Although there have been no randomized controlled trials, some case reports have suggested an association between isotretinoin exposure and the development of IBD [91]. A case report was published of a 29-year-old male patient with acne who was diagnosed with UC in 2007 after 8 months of taking isotretinoin 20 mg twice daily [92]. In a case-control study using large insurance claims data, the study population consisted of 8,189 patients with IBD and 21,832 controls, of whom a total of 60 patients (24 patients with IBD and 36 controls) were exposed to isotretinoin. The study has found that UC is strongly associated with previous isotretinoin exposure (OR: 4.36, 95% CI: 1.97ŌĆō9.66) [93]. However, a recent retrospective study found that the incidence of crude IBD was 0.08% (21/27,230) in patients with acne exposed to isotretinoin and 0.04% (254/631,089) in patients with acne not exposed to isotretinoin [94]. Therefore, the relationship between the development of IBD and isotretinoin, an acne treatment, remains controversial and requires further investigation.
PSYCHOLOGICAL STRESS AND SLEEP
Psychological stress, anxiety, and depression
Psychological stress can trigger a cascade of the hypothalamic- pituitary-adrenal axis and sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic nervous systems [95]. These systems interact with the enteric nervous system, which is the gutŌĆÖs own autonomous nervous system comprised of 200ŌĆō600 million neurons, leading to gut inflammation [96]. Chronic psychological stress can induce the dysfunction of innate and adaptive immune pathways and activate intestinal mucosal mast cells, which increase intestinal permeability, alter macrophage function and autophagy, affect helper/regulatory T cell differentiation, and change microbiota composition [97]. Psychological disorders, such as anxiety or depression, can stimulate the brainŌĆōgut axis and may lead to gastrointestinal symptoms [98]. Psychological disorders are more likely to be associated with disease progression or relapse than with IBD onset [99].
Sleep
Sleep disorders are associated with an increase in the sympathetic nervous system and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 [100]. Chronic sleep disruption in patients with obstructive sleep apnea can alter the composition of the gut microbiota and induce systemic inflammation [101]. Melatonin is a neurotransmitter produced in the pineal gland in the brain that increases at night and decreases during the day. It not only regulates circadian sleep patterns but is also linked to intestinal inflammation [102]. Therefore, sleep quality may affect subclinical inflammation in IBD development and prognosis [103,104].
LATITUDE AND GEOGRAPHY
From 1991 to 1993, the overall incidence of IBD was higher in Northern Europe than in Southern Europe [105]. Similarly, the overall incidence of IBD was higher in the northern parts of the United States than in the southern parts [106]. A study conducted in Scotland from 1981 to 1995 found no variation in UC incidence between the south and the north, but higher incidence rates (2.8 ├Ś 105 persons per year) of CD in the north than in the south (1.8 ├Ś 105 persons per year) [107]. In addition, a study conducted in France from 2000 to 2002 found no variation in UC incidence between the south and north, but higher incidence rates of CD in the north than in the south [108]. The etiology of the northŌĆōsouth gradient in IBD, particularly CD, is unclear but is believed to be the result of a combination of climate, diet, economic wealth, and genetic susceptibility. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is generally greater at southern latitudes because they are closer to the equator; UV radiation from the sun is the best natural source of vitamin D and induces regulatory T cells [109,110].
Additionally, exposure to hypoxia during air or high-altitude travel is reportedly associated with various gastrointestinal symptoms and may influence the pathogenesis and course of IBD [111]. Hypoxia could activate hypoxia-inducible factors and induce transcription of numerous genes such as nuclear factor-╬║B and toll-like receptors [112].
CONCLUSION
Environmental factors play a key role in the development and progression of IBD. Some environmental factors such as diet, air pollution, smoking, medication, psychological stress, and sleep are modifiable lifestyle factors. It is important to understand and control modifiable risk factors, especially in high-risk groups for IBD, such as the family members of patients with IBD. Host genomic predisposition can be aggravated by various environmental factors, leading to gut microbiota dysbiosis, immune pathway activation, and epigenetic modulation via chromatin modifications [70]. Nevertheless, the interaction between environmental factors and the development of IBD is very complex, and the mechanisms underlying these relationships are not well understood. Various longitudinal studies in humans and specific molecular pathway studies in animal or in vitro settings are warranted to demonstrate the potential causeŌĆōeffect relationship.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





