 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 40(3); 2025 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. This study aimed to investigate the recent nationwide trends in major dietary risk factors for dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.
Methods
We estimated age-standardized mean intakes of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, whole grains, dietary fiber, and sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs); and mean percentage of energy intake from protein, total fat, saturated fat, and polyunsaturated fat using nationally representative samples from the Korean National Health Examination and Nutrition Survey 2013–2022. To assess overall diet quality, we calculated mean Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI) (range 0–100, higher scores indicating greater diet quality).
Results
In 2013–2022, there were overall decreasing trends in age-standardized mean KHEI score and intakes of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and dietary fiber; and overall increasing trends in mean intakes of SSBs, protein, and dietary fat among both male and female. The KHEI score increased in older adults aged ≥ 60 years, whereas it decreased among younger adults. Throughout the study period, younger adults tended to have lower intakes of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, and whole grains; higher intakes of SSBs, protein, and dietary fat; and lower KHEI score. The mean KHEI score was lower in male (vs. female) and lower (vs. higher) income groups.
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide [1]. Dyslipidemia is one of known risk factors for cardiovascular disease [2]. In South Korea (Korea hereafter), the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia have increased over the past few decades [3]. To prevent dyslipidemia and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis provides the dietary guidelines that recommend increasing intakes of fresh fruits, whole grains, and dietary fiber and decreasing intakes of saturated fat. Studies have demonstrated that a healthy diet, such as high intakes of fresh fruits and vegetables and low intake of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs), is associated with a favorable lipid profile [4–8] and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease [8–10]. A meta-analysis of 81 prospective cohort studies reported that high intakes of fruits and vegetables are associated with a 12% reduced risk of coronary heart disease and an 18% reduced risk of stroke [8]. High intake of dietary fiber, which is abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can reduce serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [11], which is a leading cause of atherosclerosis, and decrease blood pressure [12]. Macronutrient composition may also influence the risk of cardiovascular disease [13]. In randomized controlled trials, replacing the energy intake of saturated fat with polyunsaturated fat decreased the incidence of cardiovascular disease [14,15]. Intake of SSBs, including soft drinks, fruit -juice, and energy drinks that contain added sugars, is another dietary risk factor associated with weight gain [16–18] and cardiovascular disease risk [10,19,20]. When overall diet quality was evaluated using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI), higher KHEI score, indicating greater diet quality, was associated with a favorable cardiometabolic profile (e.g., lower concentrations of triglyceride, lower waist circumference) and reduced risks of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality [21].
To identify national priorities in dietary interventions for dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease prevention, it is necessary to understand the nationwide trends in dietary factors for these diseases and assess whether the population is adequately following the recommended dietary guidelines. Additionally, a comprehensive understanding of these trends by sex, age, and income groups can help identify priority populations for dietary interventions. In this study, the Nutrition Council of the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis provides a Fact Sheet reporting the most recent nationwide trends in major dietary factors (fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, dietary fiber, dietary protein and fat, SSBs, and the KHEI diet quality score) for dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis among Korean adults, using nationally representative survey data from 2013 to 2022. This study also investigated the trends by age, sex, and income groups.
The study population of this study was restricted to Korean adults aged 19 or older. For dietary factors (dietary fiber, protein, and total fat intakes) that were previously reported in the Korea Health Statistics 2022, we extracted the estimates from the report. For other dietary factors (fruits, vegetables, whole grains, saturated fat, polyunsaturated fat, and SSB intakes; and KHEI diet quality score) that were not reported in the Korea Health Statistics 2022, we conducted serial cross-sectional analyses using nationally representative samples from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2013–2022 [22]. The KNHANES is a national cross-sectional survey, designed to assess health and nutritional status of noninstitutionalized Korean population. A multistage clustered probability-based sampling design was used to select the sample units based on sex, age, and geographic region. The KNHANES has been conducted annually since 2007 by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA), collecting comparable data using similar designs and methods. The information on sociodemographic characteristics, including age, sex, and income, were collected during the health interview, which was conducted at mobile examination centers. One week after the health interview, a nutrition survey was conducted by a trained dietitian during the home visit. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before their enrollment in the survey. All procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the KDCA (2013-07CON-03-4C, 2013-12EXP-03-5C, 2015-01-02-6C, 2018-01-03-P-A, 2018-01-03-C-A, 2018-01-03-2C-A, 2018-01-03-5C-A, and 2018-01-03-4C-A).
We used dietary data that were collected via a single-day 24-hour dietary recall. We estimated mean dietary intakes of fresh fruits (excluding fruit juice; g/d), fresh vegetables (excluding kimchi and pickles; g/d), whole grains (g/d), and SSBs (g/d); and mean percentages of energy intake from saturated fat and polyunsaturated fat each year from 2013 to 2022. The estimated intakes of dietary fiber (g/d) and the percentages of energy intake from protein and total dietary fat were obtained from the Korea Health Statistics 2022 [22]. The information on dietary fiber was not available for 2013–2015 and thus we included the estimates only for 2016–2022. To assess the overall diet quality, we calculated the KHEI, which was previously validated and shown to be associated with cardiometabolic profile and mortality risk [21]. The detailed scoring scheme is presented in Supplementary Table 1. Briefly, the KHEI (range, 0–100) was calculated as the sum of 14 component scores (breakfast intake; whole grains; total fruits; fresh fruits; total vegetables; fresh vegetables; protein-rich foods; dairy; sodium; energy from sweets and beverage intake; total energy intake; energy intake from carbohydrates; energy intake from total fat; energy intake from saturated fat) selected based on the national dietary guidelines for Korean adults. The standards for minimum and maximum scores were determined based on the Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015 and the World Health Organization dietary recommendations. For some dietary factors (sodium, total energy intake, energy intake from carbohydrates and fat), the intake levels corresponding to the 15th and 85th percentiles were referenced from the national distributions. A higher KHEI score indicates greater overall adherence to recommended dietary guidelines.
All analyses accounted for complex sampling design using sampling weights.
We estimated the age-standardized mean intakes of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, whole grains, dietary fiber, and SSBs; and mean percentage of energy intake from protein, total fat, saturated fat, and polyunsaturated fat; and mean KHEI using the 2005 Korean Census population as the reference population. We also estimated the mean intakes separately for different age (19–29, 30–39, 40–49, 50–59, 60–69, ≥ 70 yr), sex (male/female), and income groups (low, middle-low, middle, middle-high, high).
All analyses were performed using Stata statistical software (StataCorp).
Figure 1 presents the trends in fresh fruit and fresh vegetable consumptions in 2013–2022 among Korean male and female. The age-standardized mean intake of fresh fruits (excluding fruit juice) substantially decreased from 209.4 g/d in 2013 to 132.6 g/d in 2022 (Fig. 1A). The overall decreasing trend was similar between male and female. While the age-standardized mean intake of fresh fruits was consistently higher in female compared with male, the gap between the two groups narrowed over time (difference in mean: 72.6 g/d in 2013; 17.9 g/d in 2022). When stratified by age group, mean fresh fruit consumption was generally higher in older adults (Fig. 1B). The mean fresh fruit consumption decreased in all age groups, except in adults aged ≥ 70 years. The overall decreasing trend in fresh fruit consumption was observed in all income groups, except that in low income group the age-standardized mean fresh fruit consumption started to increase since 2020 (Fig. 1C).
The age-standardized mean intake of vegetables (excluding kimchi and pickles) substantially decreased from 232.4 g/d in 2013 to 171.0 g/d in 2022 (Fig. 1D). The age-standardized mean vegetable consumption was consistently higher in male compared with female but both groups showed the similar decreasing trend in 2013–2022. The mean vegetable consumption was generally higher in older age groups compared with younger age groups (Fig. 1E). The decreasing trend in vegetable intake was observed in all age groups, except in adults aged 70 years or older. The mean vegetable intake was highest in the high-income group and lowest in the low-income group (Fig. 1F). The difference in vegetable intake between the high- and low-income groups narrowed over time (62.3 g/d in 2013 to 21.2 g/d in 2022).
Figure 2 presents the trends in whole grain (2013–2022) and fiber (2016–2022) consumption. The age-standardized mean whole grain intake substantially decreased from 53.0 g/d in 2013 to 22.5 g/d in 2022 (Fig. 2A). During the study period, the age-standardized mean whole grain intake was similar between male and female. The mean whole grain intake was higher in older age groups but the gap between the age groups narrowed over time (difference in mean: 60.4 g/d in 2013 to 18.4 g/d in 2022; Fig. 2B). When stratified by income group, the age-standardized mean whole grain intake was similar in all income groups and, in all income groups, mean intake decreased over time (Fig. 2C).
Among both men and women, there was a slight decrease in the age-standardized mean intake of dietary fiber in 2016–2022 (25.3 g/d to 23.0 g/d; Fig. 2D). The age-standardized mean intake of dietary fiber was consistently higher in men than in women (Fig. 2D), older adults than in younger adults (Fig. 2E), and higher income than in lower income groups (Fig. 2F). The trends varied by age. In 2016–2022, the mean dietary fiber intake decreased among adults aged 19–59 years, whereas in adults aged ≥ 70 years the mean fiber intake increased (Fig. 2E). The mean fiber intake did not change over time in adults aged 60–69 years. The overall decreasing trend was observed in all income groups (Fig. 2F).
Figure 3 presents the trend in dietary protein consumption in 2013–2022. The age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from dietary protein slightly increased from 14.6% in 2013 to 16.2% in 2022 (Fig. 3A). Although the increasing trends were consistently observed in all stratified groups, higher mean percentage of energy intake from dietary protein was observed among men (vs. women; Fig. 3A) and younger (vs. older) age groups (Fig. 3B). The age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from dietary protein was similar among all income groups (Fig. 3C).
Figure 4 presents the age-standardized trend in dietary fat consumption (total fat, saturated fat, polyunsaturated fat) in 2013–2022. The age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from dietary fat increased from 20.4% in 2013 to 25.5% in 2022 (Fig. 4A). The mean dietary fat intake was similar between male and female. Although the increasing trends in dietary fat intake were consistently observed in all age and income groups, the mean dietary fat intake was higher among younger (vs. older) adults (Fig. 4B) and higher (vs. lower) income groups (Fig. 4C). Similar results were observed with both saturated (Fig. 4D–F) and polyunsaturated fat intake (Fig. 4G–I). Total energy intake declined in both male and female (Supplementary Table 2).
Figure 5 presents the age-standardized trend in SSB consumption in 2013–2022. The age-standardized mean intake of SSBs substantially increased from 38.8 g/d in 2011 to 58.2 g/d in 2022 (Fig. 5A). While the mean SSB intake was higher among male (vs. female) and younger (vs. older) age groups, the increasing trends were consistently observed in all sex and age groups (Fig. 5A, B). There was no apparent difference in mean SSB intake by income group (Fig. 5C).
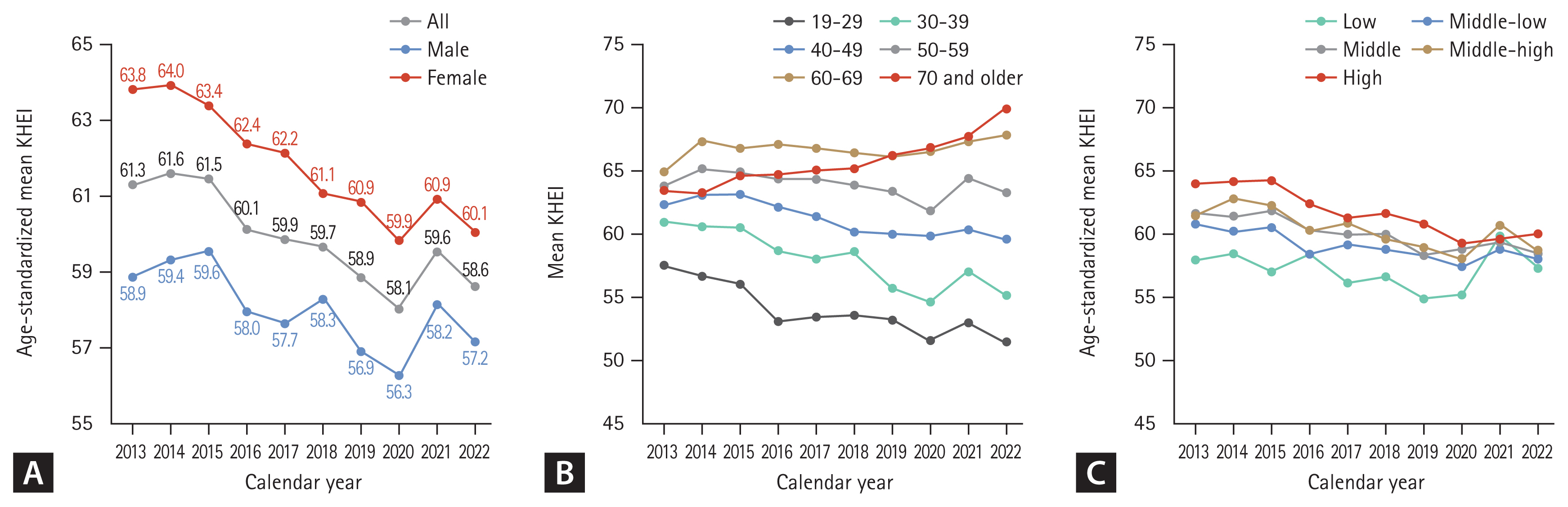
Figure 6 presents the trends in mean KHEI diet quality score in 2013–2022 among Korean male and female. The age-standardized mean KHEI decreased from 61.3 in 2013 to 58.6 in 2022 (Fig. 6A). Throughout the study period, the age-standardized mean KHEI was consistently higher among female compared with male. The mean KHEI was also generally higher among older (vs. younger) age groups (Fig. 6B) and higher (vs. lower) income groups (Fig. 6C). During the study period, mean KHEI increased among older adults aged ≥ 60 years, whereas it decreased among younger adults aged 19–49 years, widening the age difference in mean KHEI (mean difference between the highest vs. lowest KHEI: 5.93 to 18.31; Fig. 6B). During the study period, the difference in mean KHEI among income groups narrowed over time (6.0 to 2.7; Fig. 6C).
Using nationally representative data, this study investigated the nationwide trends in dietary intakes among Korean adults from 2013 to 2022. During the study period, there were overall decreasing trends in age-standardized mean intakes of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and dietary fiber; and overall increasing trends in mean intakes of SSBs, protein, and dietary fat among both male and female. The overall diet quality, assessed by the KHEI score, decreased during this period, indicating a shift toward an unhealthy diet at the population level. However, when stratified by age groups, the trends varied by age. The KHEI score increased in older adults aged ≥ 60 years, whereas it decreased among younger adults. Consistently, the decreasing trends in fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, and dietary fiber were not observed in older adults. We also observed variations in intake levels by age, sex, and income throughout the study period. Younger adults tended to have lower intakes of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, and whole grains; higher intakes of SSBs, protein, and dietary fat (both saturated and polyunsaturated fats); and lower KHEI score. Compared with female, male generally had higher intakes of fresh vegetables and dietary fiber but lower intakes of fresh fruits. Male also had higher intakes of SSBs, higher energy intake from protein, and lower mean KHEI score. There was minimal sex difference in intakes of whole grains and dietary fat. Compared with lower income groups, higher income groups generally had higher mean KHEI score, which is consistent with their higher intakes of fresh fruits, vegetables, and dietary fiber. There was minimal difference in intake levels of whole grains, SSBs, and protein among different income groups.
In this study, we observed an overall decreasing trend in mean KHEI diet quality score among Korean adults in 2013–2022. The decreasing trend is not consistent with a previous finding that showed an increasing trend in mean KHEI score from 2008 to 2013 [21]. These findings collectively suggest that an unfavorable change in diet quality has recently occurred among Korean adults since 2013, following a modest improvement in diet quality in 2008–2013. In our study, the decline in diet quality from 2013 to 2022 was associated with a substantial decrease in the intake of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, and whole grains and an increase in the intake of SSBs. Additionally, we observed an increase in energy intake from dietary fat (both saturated and polyunsaturated fats) and protein, suggesting a shift in macronutrient composition of Korean diet over time. The traditional Korean diet is rich in carbohydrates and dietary fiber from whole grains and vegetables and low in red meat and animal fat [23]. With the rapid globalization, it is likely that the diet in Korea has shifted away from the traditional Korean diet toward a high-fat, animal-based Western diet. Although the intake levels of fresh fruits (132.6 g/d in 2022), vegetables (171.0 g/d in 2022), and whole grains (22.5 g/d in 2022) in Korean adults still remain higher than most countries around the world [24], the intakes have declined to levels far below the recommended intakes (250 g/d fruits; 360 g/d vegetables; 125 g/d whole grains) [24,25]. Fruit intake is particularly lower in male, while vegetable intake is particularly lower in female, suggesting the sex difference in dietary intakes. The mean SSB intake in Korean adults is also much lower compared with most countries around the world [24] but the increasing trend, particularly among younger adults, calls for public health effort to raise awareness. Because high dietary intakes of fresh fruits [8,26], vegetables [8,26], and whole grains [27] and low intakes of SSBs [10,17,19,28] and saturated fat [14,15] are associated with reduced risks of cardiometabolic disease and mortality, the unfavorable changes in the intakes of these foods and nutrients may lead to increased disease burdens. Our findings suggest that, to reduce disease burdens, more intense dietary interventions are needed to improve diet quality by increasing fruit, vegetable, and whole grain consumption and reducing SSB and saturated fat consumption.
In this study, we also observed that younger adults tended to have lower mean KHEI scores, suggesting an unhealthier diet, associated with lower intakes of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and higher intakes of SSBs and saturated fat. A decline in mean KHEI score from 2013 to 2022 was also restricted to adults aged < 60 years, and the decline was particularly greater among younger adults aged 19–39 years (−6.04 in age 19–29 yr; −5.79 in age 39–39 yr), highlighting an unfavorable change in diet among younger adults. In contrast to the findings in younger adults, diet quality improved in older adults (aged ≥ 60 yr) during the same study period, suggesting diverging dietary trends by age group. As the nutrition transition occurs over generations [29], younger adults may adopt a dietary pattern that is closer to an animal-based, Western diet, while older adults may be more likely to maintain a plant-based, traditional Korean diet. A previous study suggested that possible birth cohort effect may also create generational gaps in diet quality [21]. In Korea, as the younger adults get older, the burdens of chronic disease, such as cardiovascular disease, are likely to increase in the near future. To reduce the disease burdens, nutrition policies and interventions should focus more heavily on younger adults.
In this study, we also observed some inequalities in diet by income levels. Compared with higher income groups, lower income groups tended to have lower mean KHEI score, contributed by their lower intakes of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, and dietary fiber. In 2013–2022, the difference in mean KHEI score between the highest and lowest income groups narrowed over time largely due to the narrowed gaps in fresh fruit and vegetable intakes between the income groups. The rapid economic growth and expanded food supply have improved the accessibility of affordable foods, which may have contributed to reduced inequalities in diet quality by income. Despite the narrowed gaps, all income groups experienced a decrease in the intakes of fresh fruits and vegetables and an increase in the intakes of SSBs and saturated fat during the study period. Our data suggest that all income groups require improvement in diet quality for disease prevention.
This study has limitations. We used the single-day 24-hour dietary recall data, which do not capture within-person variation in diet. However, the data are likely to provide adequate estimates of group means of a large population. Furthermore, we did not have data on trans fat, another dietary risk factor for cardiovascular disease [30], and thus were not able to investigate the trends in trans fat intake. Despite the limitations, our study has important strengths. Using nationally representative data from 2011–2023, we estimated the most recent trends in dietary intakes among Korean adults. The use of KHEI also enabled the assessment of overall diet quality, which better reflects overall health. In previous studies, the KHEI was shown to play an important role in the etiology of chronic disease and mortality [21,31].
In this study, we observed an unfavorable trend in overall dietary quality and dietary intakes of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, whole grains, dietary fiber, SSBs, and saturated fat in 2013–2022. Our data also suggest that younger (vs. older) adults, male (vs. female), and lower (vs. higher) income groups had an unhealthier diet, indicating inequalities in diet by age, sex, and income. To reduce disease burdens in Korea, more intense interventions and policies are needed to improve diet in these vulnerable populations. Furthermore, as some vulnerable populations presented limited understanding and awareness of healthy diet for prevention and management of dyslipidemia [32], more efforts should also focus on raising awareness among these populations.
1. From 2013 to 2022, Korean adults showed a trend toward unhealthy diets, with decreased intakes of fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, and whole grains, and increased intakes of SSBs and dietary fat.
2. Younger adults, male, and lower-income groups had a poor diet quality, with lower KHEI scores.
3. This finding suggests that targeted interventions are needed to reduce dietary inequalities and promote healthier eating habits among vulnerable populations.
Notes
CRedit authorship contributions
Hannah Oh: conceptualization, investigation, writing - original draft; Garam Jo: data curation, formal analysis, visualization; Oh Yoen Kim: investigation, writing - review & editing; Hyunjung Lim: investigation, writing - review & editing; SuJin Song: investigation, writing - review & editing; Jeong-Hwa Choi: investigation, writing - review & editing; Jae Hyun Bae: investigation, project administration; Eun-Sun Jin: investigation, project administration; Rockli Kim: investigation, writing - review & editing; Yujin Lee: investigation, writing - review & editing; In-Kyung Jeong: conceptualization, writing - review & editing, supervision, project administration; Min-Jeong Shin: conceptualization, writing - review & editing, supervision, project administration
Figure 1
The trends in fresh fruit and fresh vegetable consumptions in 2013–2022. (A) Age-standardized mean intake of fresh fruits. (B) Mean intake of fresh fruits by age groups. (C) Age-standardized mean intake of fresh fruits by household income level. (D) Age-standardized mean intake of fresh vegetables. (E) Mean intake of fresh vegetables by age groups. (F) Age-standardized mean intake of fresh vegetables.
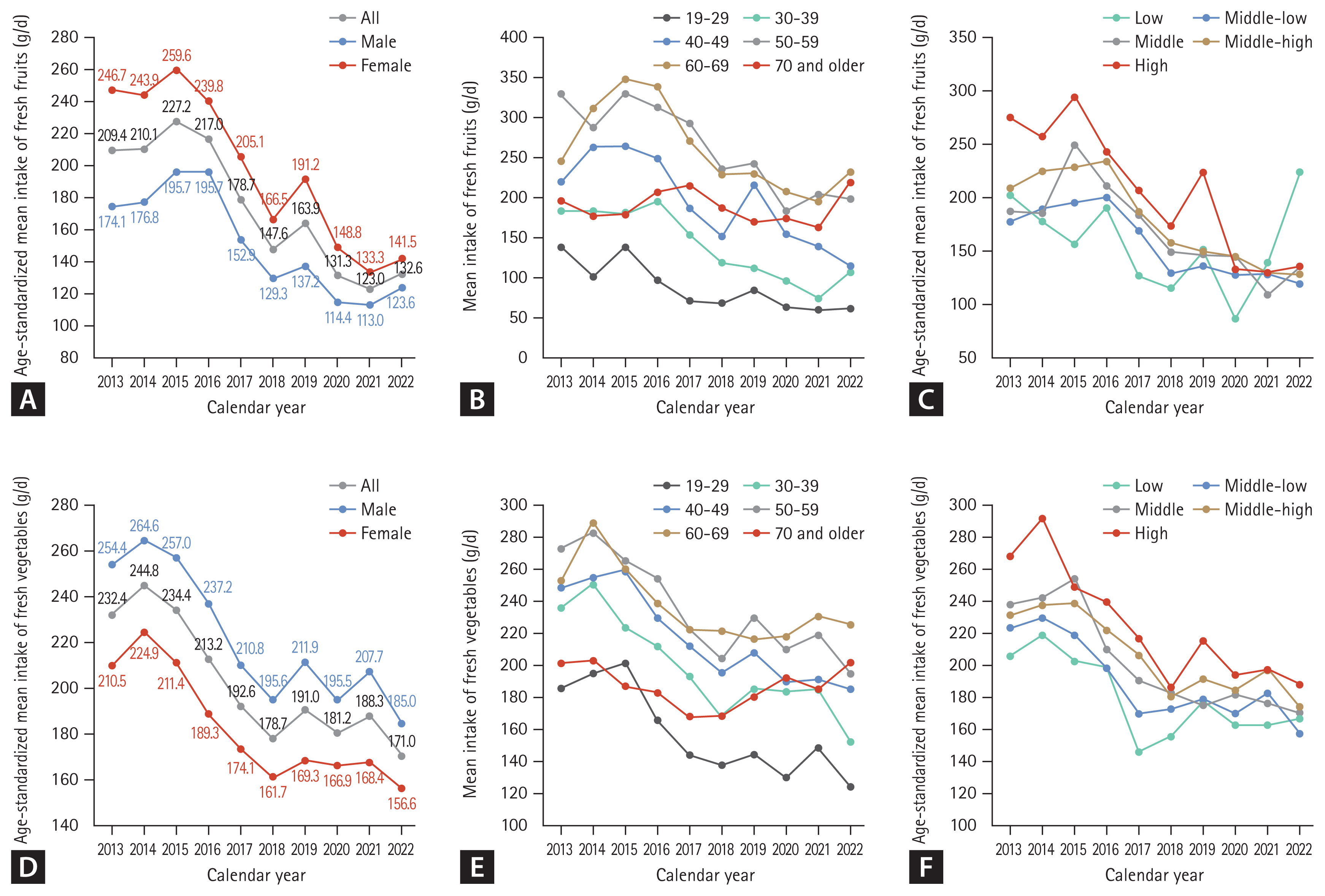
Figure 2
The trends in whole grains and dietary fiber consumptions. (A) Age-standardized mean intake of whole grains in 2013–2022. (B) Mean intake of whole grains by age groups in 2013–2022. (C) Age-standardized mean intake of whole grains by household income level in 2013–2022. (D) Age-standardized mean intake of dietary fiber in 2016–2022. (E) Mean intake of dietary fiber by age groups in 2016–2022. (F) Age-standardized mean intake of dietary fiber by household income level in 2016–2022.
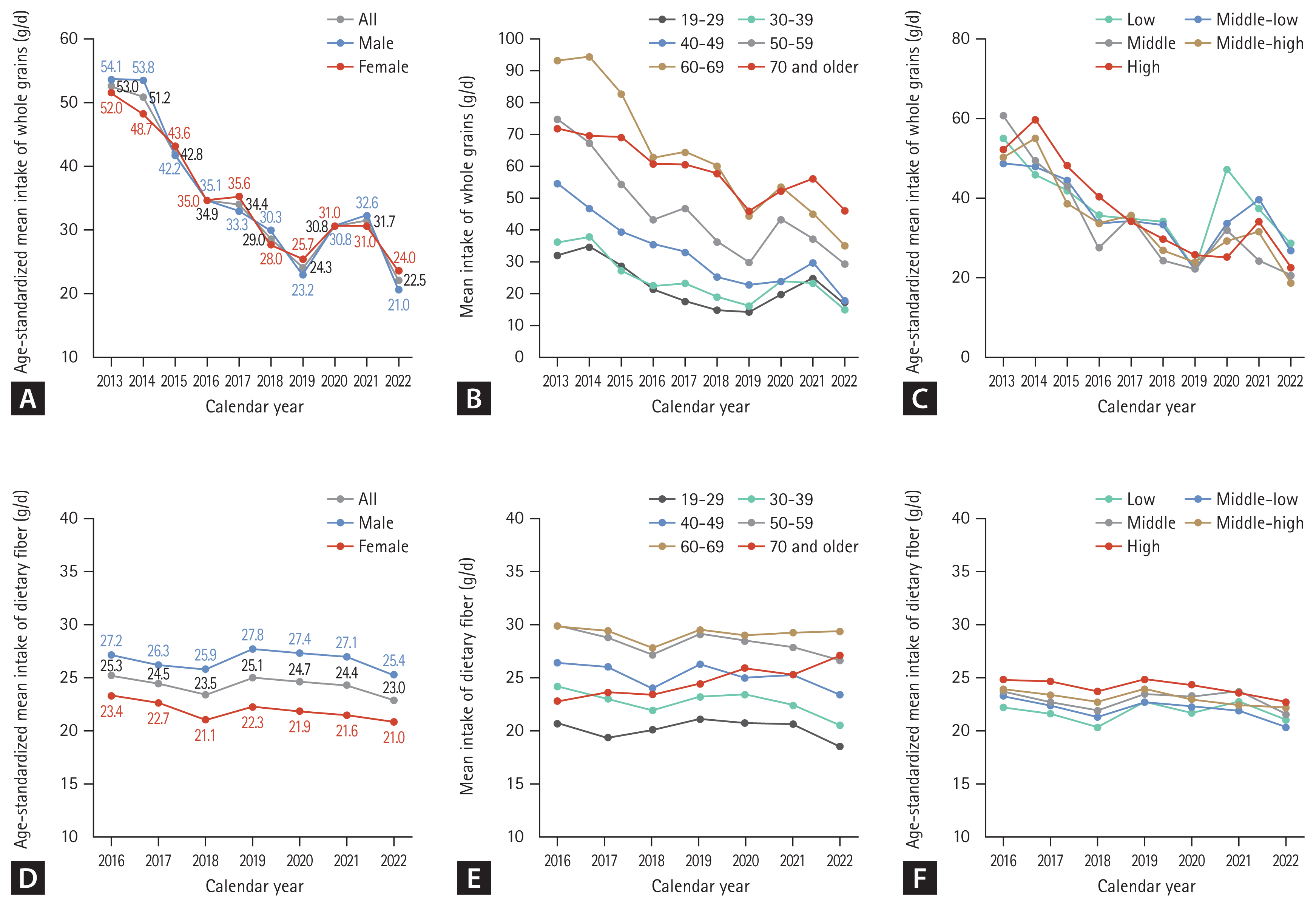
Figure 3
The trends in dietary protein consumption in 2013–2022. (A) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from protein. (B) Mean percentage of energy intake from protein by age groups. (C) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from protein by household income level.

Figure 4
The trends in intake of dietary fat, saturated fat, and polyunsaturated fat in 2013–2022. (A) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from dietary fat. (B) Mean percentage of energy intake from dietary fat by age groups. (C) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from dietary fat by household income level. (D) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from saturated fat. (E) Mean percentage of energy intake from saturated fat by age groups. (F) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from saturated fat by household income level. (G) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from polyunsaturated fat. (H) Mean percentage of energy intake from polyunsaturated fat by age groups. (I) Age-standardized mean percentage of energy intake from polyunsaturated fat by household income level.

Figure 5
The trends in sugar-sweetened beverages consumption in 2013–2022. (A) Age-standardized mean intake of sugar-sweetened beverages. (B) Mean intake of sugar-sweetened beverages by age groups. (C) Age-standardized mean intake of sugar-sweetened beverages by household income level.

REFERENCES
1. World Health Organization. The World Health Organization Fact sheet 2020: the top 10 causes of death Geneva: World Health Organization, c2024. [cited Sep 22, 2024]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/thetop-10-causes-of-death.
2. Mozaffarian D, Wilson PW, Kannel WB. Beyond established and novel risk factors: lifestyle risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2008;117:3031–3038.


3. Jin ES, Shim JS, Kim SE, et al. Dyslipidemia fact sheet in South Korea, 2022. J Lipid Atheroscler 2023;12:237–251.




4. Kuklina EV, Park S. Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and lipid profile: more evidence for interventions. J Am Heart Assoc 2020;9:e015061.



5. Haslam DE, Peloso GM, Herman MA, et al. Beverage consumption and longitudinal changes in lipoprotein concentrations and incident dyslipidemia in US adults: the framingham heart study. J Am Heart Assoc 2020;9:e014083.



6. Mensink RP. Effects of saturated fatty acids on serum lipids and lipoproteins: A systematic review and regression analysis. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016.
7. Jenkins DJ, Popovich DG, Kendall CW, et al. Effect of a diet high in vegetables, fruit, and nuts on serum lipids. Metabolism 1997;46:530–537.


8. Zurbau A, Au-Yeung F, Blanco Mejia S, et al. Relation of different fruit and vegetable sources with incident cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Am Heart Assoc 2020;9:e017728.



9. Lichtenstein AH, Appel LJ, Vadiveloo M, et al. 2021 dietary guidance to improve cardiovascular health: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021;144:e472–e487.


10. Pietrantoni D, Mayrovitz HN. The impacts of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSB) on cardiovascular health. Cureus 2022;14:e26908.



12. Fu L, Zhang G, Qian S, Zhang Q, Tan M. Associations between dietary fiber intake and cardiovascular risk factors: an umbrella review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Front Nutr 2022;9:972399.



13. Hosseini-Esfahani F, Koochakpoor G, Tahmasebinejad Z, Khalili D, Mirmiran P, Azizi F. The association of dietary macronutrients composition with the incidence of cardiovascular disease, using iso-energetic substitution models: Tehran lipid and glucose study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2020;30:2186–2193.


14. Mozaffarian D, Micha R, Wallace S. Effects on coronary heart disease of increasing polyunsaturated fat in place of saturated fat: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med 2010;7:e1000252.



15. Hooper L, Martin N, Abdelhamid A, Davey Smith G. Reduction in saturated fat intake for cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015;(6):CD011737.


16. Endy EJ, Yi SY, Steffen BT, et al. Added sugar intake is associated with weight gain and risk of developing obesity over 30 years: the CARDIA study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2024;34:466–474.



17. Malik VS, Schulze MB, Hu FB. Intake of sugar-sweetened beverages and weight gain: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;84:274–288.


18. Schulze MB, Manson JE, Ludwig DS, et al. Sugar-sweetened beverages, weight gain, and incidence of type 2 diabetes in young and middle-aged women. JAMA 2004;292:927–934.


19. Pacheco LS, Lacey JV Jr, Martinez ME, et al. Sugar-sweetened beverage intake and cardiovascular disease risk in the California Teachers Study. J Am Heart Assoc 2020;9:e014883.



20. Malik VS, Popkin BM, Bray GA, Després JP, Hu FB. Sugar-sweetened beverages, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease risk. Circulation 2010;121:1356–1364.



21. Jo G, Park D, Lee J, et al. Trends in diet quality and cardiometabolic risk factors among Korean adults, 2007–2018. JAMA Netw Open 2022;5:e2218297.



22. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Korea Health Statistics 2022: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) IX-1. Osong: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, 2023.
23. Choi SW. A journey to explore the health properties of traditional Korean diet: a commentary. J Ethn Food 2023;10:9.


24. GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017;390:1345–1422.


25. Micha R, Shulkin ML, Peñalvo JL, et al. Etiologic effects and optimal intakes of foods and nutrients for risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: systematic reviews and meta-analyses from the Nutrition and Chronic Diseases Expert Group (NutriCoDE). PLoS One 2017;12:e0175149.



26. Aune D, Giovannucci E, Boffetta P, et al. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer and all-cause mortality-a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46:1029–1056.



27. Aune D, Keum N, Giovannucci E, et al. Whole grain consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all cause and cause specific mortality: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ 2016;353:i2716.



28. Cho Y, Ryu S, Kim R, Shin MJ, Oh H. Ultra-processed food intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in Korean adults. J Nutr 2024;154:243–251.


29. Kim S, Moon S, Popkin BM. The nutrition transition in South Korea. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;71:44–53.


30. Mozaffarian D, Katan MB, Ascherio A, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. Trans fatty acids and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1601–1613.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
Gender and age differences in obesity among Korean adults2013 January;28(1)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement table 1
Supplement table 1 Print
Print


