 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 39(3); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Biomarkers are playing an increasingly important role in antimicrobial stewardship. Their applications have included use in algorithms that evaluate suspected bacterial infections or provide guidance on when to start or stop antibiotic therapy, or when therapy should be repeated over a short period (6–12 h). Diseases in which biomarkers are used as complementary tools to determine the initiation of antibiotics include sepsis, lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), COVID-19, acute heart failure, infectious endocarditis, acute coronary syndrome, and acute pancreatitis. In addition, cut-off values of biomarkers have been used to inform the decision to discontinue antibiotics for diseases such as sepsis, LRTI, and febrile neutropenia. The biomarkers used in antimicrobial stewardship include procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), presepsin, and interleukin (IL)-1β/IL-8. The cut-off values vary depending on the disease and study, with a range of 0.25–1.0 ng/mL for PCT and 8–50 mg/L for CRP. Biomarkers can complement clinical diagnosis, but further studies of microbiological biomarkers are needed to ensure appropriate antibiotic selection.
Antimicrobial stewardship is a coordinated intervention designed to guide optimal antibiotic use in terms of the antibiotics regimen, dosing, administration route, and treatment duration [1]. Among its goals are improvement of clinical outcomes, minimization of harms such as microbial resistance and Clostridioides difficile infection, and reductions in antimicrobial consumption, cost, and adverse events. The core elements of an antimicrobial stewardship program (ASP) consist of leadership commitment, an operating system, actionable measures, tracking and reporting systems, and educational programs [2]. Interventional activities are concerned with auditing and feedback, antimicrobial restriction, authorization of antibiotic selection, dosing, treatment duration, and administration route, all of which should be based on evidence-supported guidelines. Biomarkers can serve as an objective indicator of the efficacy of these activities. This review examines the biomarkers available for antimicrobial stewardship from a physician’s perspective.
Biomarkers (or biological markers) are objective indicators of normal biological and pathologic processes or treatment responses [3]. They serve as diagnostic tools, support disease staging, indicate disease prognosis, predict clinical responses, and aid the monitoring of various diseases. In infectious diseases, biomarkers are used to facilitate earlier diagnoses, identify pathogens, optimize antibiotics, assess treatment responses, monitor disease progression, and stratify patients according to prognosis and risk [3,4]. Infectious disease biomarkers are divided into host-response biomarkers and pathogen-specific biomarkers. Host-response biomarkers can aid in the decision to initiate or discontinue antibiotics in patients with infectious diseases. Reducing unnecessary antibiotic exposure and overall antibiotic use can in turn reduce the duration of hospital stay, adverse events, and overall hospitalization costs.
Host-response biomarkers include procalcitonin (PCT) and C-reactive protein (CRP). PCT is a precursor of calcitonin, the hormone produced by parafollicular cells in the thyroid and by neuroendocrine cells in the lungs and intestines [5]. PCT production is upregulated hours after an increase in the levels of proinflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1, and IL-6 [6]. PCT is widely used as a biomarker in diagnosing and predicting bacterial infections, including pneumonia and sepsis, and in measuring disease severity [6–8]. CRP, an acute-phase reactant, is synthesized primarily by hepatocytes in response to IL-6 [9]. Increased levels of CRP occur in bacterial and other infections, as well as noninfectious causes of inflammation, and may reflect infection severity [10]. As a biomarker, CRP is used in diagnostic settings, to evaluate disease severity, and to predict outcomes of bacterial infections, including pneumonia and sepsis [11,12].
Pathogen-specific biomarkers specify the causative infectious organisms and thus support the selection of narrow-spectrum antibiotics to target the causative strain. Reducing the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics can help prevent colonization by multidrug-resistant organisms and lower the risk of adverse antibiotic effects, thereby reducing the length of hospital stays and medical costs. The classic pathogen-specific biomarkers consisted of direct antigen tests but they have largely been replaced by microbial nucleic acid methods.
Several guidelines refer to the role of biomarkers in antimicrobial stewardship. According to the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America guideline, biomarkers can be used for antibiotic discontinuation, and PCT can be used in patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) with bacterial infection or sepsis [1,13]. Japan proposed a PCT-guided algorithm as an indicator in antimicrobial stewardship [14] to evaluate whether patients with respiratory infections and sepsis should be admitted to the ICU or undergo PCT testing during the initial clinical assessment. The results showed that antibiotics can be started or stopped based on a PCT cut-off of 0.25 outside the ICU and 0.5 for sepsis.
Korea developed the first guideline for antimicrobial stewardship in 2021 [15]. The guideline states that biomarkers can be used to discontinue antibiotics. Subsequent guideline suggests a consensus algorithm for PCT use in clinical antimicrobial stewardship [16], in which antibiotics can be started or stopped based on PCT levels when an infectious disease is suspected. The cut-off for PCT is 0.5 μg/L in patients with sepsis and 0.25 μg/L in those with respiratory tract infections.
Many patients in the ICU or wards, as well as those in outpatient settings, are suspected of having infectious diseases. Biomarkers can help determine when to start antibiotics in patients with acute respiratory infection, acute heart failure (HF), acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute pancreatitis (AP), pneumonia, or sepsis. Several biomarker studies have provided a reference for antimicrobial stewardship. The findings of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the roles of PCT and CRP in antibiotic stewardship are summarized in Tables 1 and 2, respectively.
The PRORATA trial recommends measuring PCT levels at the start of antibiotics administration and 6–12 hours after withholding antibiotics in ICU patients with sepsis. Antibiotics should be started in patients with PCT levels ≥ 0.5 μg/L, with a strong recommendation for starting antibiotics in those with PCT levels ≥ 1.0 μg/L [17]. For patients in the PRORATA trial, the PCT-guided group had significantly lower rates of antibiotic use than the control group (11.6 vs. 14.3 days; absolute difference = 2.7 days; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.4–4.1; p < 0.0001), but there was no statistically significant difference in mortality, either at 28 days (20.4% vs. 21.2%; absolute difference = 0.8%; 90% CI −4.6 to 6.2) or 60 days (26.1% vs. 30.0%; absolute difference = 3.8%; 90% CI −2.1 to 9.7).
A Belgian RCT evaluated the effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic treatment [18], with PCT levels measured in patients with suspected sepsis who were admitted to the ICU and started on antibiotics at a PCT ≥ 0.5 μg/L. In the PCT-guided group, there was a higher likelihood of withholding antibiotics than in the non-PCT-guided group (46% vs. 32.7%, p = 0.15). The duration of antibiotic administration in the PCT-guided group did not differ from that in the control group (62.6% vs. 57.7%, p = 0.11), and there was no difference in antibiotic consumption between groups. The area under the receiving operating curve (AUROC) of the PCT level to differentiate infection was 0.69. However, biomarker-related studies examining when to start antibiotics in patients with suspected sepsis are limited. Overall, PCT-induced antibiotic use in sepsis was shown to significantly reduce antibiotic use but there were no improvements in clinical outcomes, including mortality.
In the ProHOSP study, PCT was measured in patients with suspected LRTI to determine whether to administer antibiotics [19]. The PCT-guided algorithm recommended starting antibiotics in those with PCT levels > 0.25 μg/L measured within 1 hour of admission. The effectiveness of PCT-guided treatment was evaluated in patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), COPD exacerbation, or acute bronchitis, in addition to the overall population. The duration of antibiotic exposure was lower in all PCT-tested patients than in non-tested patients (5.7 vs. 8.7 days; relative change, −34.8%; 95% CI −40.3% to −28.7%) and all subgroups. Antibiotic-related adverse events were also rarer in the PCT group. Clinical outcomes, including death, ICU admissions, and recurrence, did not differ between the two groups.
The proCAP study measured PCT before antibiotics were started in patients hospitalized with CAP and compared the results with those obtained in the usual-practice group [20]. Antibiotics were considered for patients with a PCT level ≥ 0.25 μg/L at the time of diagnosis. If antibiotics were not administered, PCT levels were measured again after 6–12 hours. The rate of antibiotic prescription was 85% in the PCT-guided group and 99% in the usual-practice group (p < 0.001). The clinical success rates of the two groups were similar (84% vs. 82%, p = 0.65).
A Chinese RCT evaluated PCT-guided treatment in patients with suspected CAP and recommended starting antibiotics for those with PCT levels > 0.25 μg/L [21]. If antibiotics were not started, PCT testing was repeated after 6–12 hours. The rate of antibiotics prescription on admission was 84.4% in the PCT group, which was significantly lower than in the control group (97.5%, p = 0.004). The 4-week treatment success rate did not differ between the two groups (85.2% vs. 88.9%; absolute difference, −3.7; 95% CI −14.1 to 6.7).
Several studies have used CRP point-of-care testing (POCT) to assess the effects of prescribing antibiotics in patients with suspected respiratory tract infections in primary care settings. The IMPAC3T study in the Netherlands evaluated the effectiveness of providing general practitioners with training in communication skills and CRP POCT to aid antibiotic prescriptions [22]. The antibiotic prescription rate for suspected LRTI was significantly lower in the group trained in communication skills than in the group without training (27% vs. 54%, p < 0.01). It was also significantly lower in the group trained in CRP POCT than in the nontrained group (31% vs. 53%, p = 0.02). The GRACE (Genomics to Combat Resistance Against Antibiotics in Community-acquired LRTI in Europe) consortium evaluated the effectiveness of CRP POCT and enhanced communication skills in primary care settings [23]. Training in CRP POCT significantly reduced antibiotic prescriptions compared to the control (33% vs. 48%; adjusted risk ratio [RR], 0.54; 95% CI 0.42–0.69). The combination of CRP POCT and enhanced communication skills resulted in significantly lower prescription rates (RR, 0.53; 95% CI 0.36–0.74; p < 0.0001). A meta-analysis showed that CRP POCT applied to antibiotic prescriptions in primary care patients with suspected acute respiratory infection significantly reduced antibiotic prescriptions compared to controls (397 vs. 516 prescriptions per 1,000; RR, 0.77; 95% CI 0.69–0.86).
CRP was also evaluated when LRTI was suspected in nursing home residents. The UPCARE study of nursing home populations in the Netherlands reported the effectiveness of CRP POCT when LRTI was suspected [24]. The CRP-guided group had a significantly lower antibiotic prescription rate than the control group (53.5% vs. 82.3%; hazard ratio [HR], 4.93; 95% CI 1.91–12.73). Clinical outcomes, including the 3-week complete recovery rate, all-cause mortality, and hospitalization rates, did not differ between the groups.
Overall, PCT-guided antibiotic use reduces antibiotic exposure and antibiotic-related adverse events in patients with CAP, exacerbated COPD, or acute bronchitis. It does not improve clinical outcomes compared with controls. Similarly, CRP testing in ASPs reduces the overall number of antibiotic prescriptions but does not alter clinical outcomes, including mortality.
COVID-19 guidelines do not address the use of biomarkers in antibiotic stewardship, nor does The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommend the routine use of PCT for antibiotic stewardship in COVID-19 patients [25].
In a multicenter observational study performed in the Netherlands, PCT-guided antibiotic treatment significantly reduced antibiotic prescriptions in patients with COVID-19 [26]. Among patients admitted with COVID-19, antibiotics were considered in the PCT-guided group when the PCT level measured within 24 hours after admission was ≥ 0.25 μg/L. The rates of 1-week antibiotic administration (26.8% vs. 44.7%, p < 0.001) and total antibiotic administration (35.2% vs. 54.5%, p < 0.001) were lower in the PCT-guided group than in the usual care group. The rates of 30-day mortality, 90-day mortality, hospital stay, and ICU admission also differed between the two groups.
In the UK, ASPs include the measurement of PCT in patients admitted to the hospital with SARS-CoV-2, with antibiotic discontinuation considered in those with a PCT level < 0.25 ng/L [27]. PCT contributed to antibiotics discontinuation in 32% of patients and reduced the antibiotic prescription rate from 70% to 36.5%. A retrospective cohort study also performed in the UK evaluated the effectiveness of antimicrobial stewardship and recommended antibiotic discontinuation in COVID-19 patients with a PCT level ≤ 0.25 ng/mL measured within 48 hours of hospitalization [28]. In the PCT-negative group, the median duration of antibiotic use was shorter than in the PCT-positive group (2 vs. 5 days, p < 0.001), as was the defined daily dose (DDD) (0.14 vs. 0.37, p < 0.001). Patients in the PCT-negative group were three times less likely to be treated with carbapenem than were those in the PCT-positive group. The PCT-negative group had lower rates of mortality (28% vs. 36%, p = 0.021) and ICU admission (9% vs. 19%, p = 0.007) than the PCT-positive group.
In a single-center retrospective study performed in the UK, PCT was evaluated according to the presence or absence of secondary bacterial infection in patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to the ICU [29]. Median PCT levels did not differ between patients with and without secondary bacterial infection (0.18 vs. 0.235, p > 0.05). Median CRP and white blood cell (WBC) levels also did not differ between these groups.
A retrospective study performed in Belgium, which enrolled patients with COVID-19 who had been admitted to the ICU, examined the association of PCT measured within 48 hours of hospital admission with bacterial co-infection [30]. The AUROC for PCT as a predictor of bacterial co-infection was 0.68 but that for 30-day mortality was 0.77, with significant differences between survivors and non-survivors. PCT was shown to be a biomarker of COVID-19 severity rather than bacterial co-infection. In other studies, PCT was associated with COVID-19 severity, disease progression, and mortality, regardless of bacterial co-infection [31–33]. Measuring PCT levels in patients with COVID-19 may help determine whether antibiotics should be initiated for bacterial co-infection, but the levels may also be elevated in patients with severe COVID-19. Clinical decisions should therefore be based on clinical features or other biomarkers.
No RCT has evaluated the role of CRP alone in antimicrobial stewardship. A retrospective study reported AUROC values for CRP and PCT of 0.86 (p < 0.001) and 0.88 (p < 0.001), respectively, in predicting secondary bacterial infection in patients with COVID-19 [34]. Another study of COVID-19 patients suggested that PCT levels should be measured heterogeneously in those with high CRP values. In the PCT < 0.5 ng/mL group, a low CRP had a negative predictive value and predicted hospital admission in 97.6% of cases. CRP determination in this setting can be used as a supplementary biomarker to PCT [35].
PCT and CRP may not be increased in COVID-19 patients treated with dexamethasone and tocilizumab, even in those with a secondary bacterial infection [36]. PCT is an indicator of infection severity; it cannot be used to discriminate between bacterial and viral infections. Overall, PCT-guided antibiotics in COVID-19 patients can result in a decrease in antibiotic use. While PCT has limited accuracy in diagnosing bacterial co-infection in COVID-19 patients, bacterial co-infection can be diagnosed by measuring CRP in combination with PCT.
Antibiotics are frequently prescribed to treat exacerbated COPD or asthma, as the symptoms are similar to those of pneumonia. A multinational RCT evaluated the role of PCT in the decision to start antibiotics in patients with exacerbated COPD [37]. Antibiotics were recommended for those with PCT levels > 0.25 μg/L, with a repeat PCT measurement performed after 6–24 hours if antibiotics were withheld. The PCT-guided group had a significantly lower rate of antibiotic prescriptions than the group receiving standard therapy (40% vs. 72%, p < 0.0001). Neither clinical outcomes nor an improvement in the forced expiratory volume in one second at 14 days and 6 months differed between the two groups.
A Swiss RCT evaluated the effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic administration in patients with suspected LRTI in a COPD subgroup [38]. In the PCT-guided group, administered antibiotics if their PCT level was ≥ 0.25 μg/L, the antibiotic prescription rate was significantly lower than in the standard-of-care group (38% vs. 87%, p = 0.001). COPD exacerbation and hospital readmission rates did not differ between the two groups. A meta-analysis evaluated the effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic administration (both antibiotic initiation and discontinuation) in patients with exacerbated COPD [39]. The results showed a lower antibiotic prescription rate (RR, 0.56; 95% CI 0.43–0.73) among patients with PCT guidance but no difference in clinical outcomes, including hospital stay, exacerbation of the recurrence rate, and mortality, compared to the control group.
A multicenter RCT performed in the UK evaluated the effectiveness of measuring CRP POCT in patients with exacerbated COPD. Antibiotics were administered to those with CRP levels ≥ 20 mg/L [40]. The CRP-guided group had a lower antibiotic prescription rate than the control group (57.0% vs. 77.4%; adjusted odds ratio [OR], 0.31; 95% CI, 0.20–0.47). The total Clinical COPD Questionnaire score at 2 weeks was also lower in the CRP-guided group (−0.19 points; 90% CI, −0.33 to −0.05). A prospective observational study performed in the UK measured PCT and CRP levels in patients with exacerbated COPD or asthma and suspected pneumonia [41]. The AUROCs of CRP and PCT for distinguishing pneumonia from COPD exacerbation were 0.96 and 0.93, respectively. At a CRP cut-off for starting antibiotics of > 48 mg/L, the sensitivity for pneumonia diagnosis was 91%, and the specificity was 93%. Overall, PCT- and CRP-guided antibiotic use reduced overall antibiotic exposure, without differences in hospital stay, recurrent exacerbation, or mortality, in patients with COPD/asthma exacerbation.
Patients with acute HF may show symptoms and X-ray abnormalities similar to those of patients with pneumonia. Biomarkers can help determine whether antibiotics, which are commonly misused in acute HF, are warranted. The BACH trial evaluated the role of biomarkers in differentiating between pneumonia and noninfectious diseases, such as COPD and acute HF, in patients who visited the hospital with dyspnea [42]. The AUROC for diagnosing pneumonia based on PCT alone was 0.723 (p < 0.0001), which was higher than that of WBCs (0.69). When PCT and clinical signals, including X-ray findings, were evaluated together, the AUROC for the diagnosis of pneumonia increased to 0.863. Among patients with acute HF and a PCT level > 0.21 ng/mL, 5.1% were diagnosed with pneumonia, and 33% required antibiotic treatment during follow-up. Antibiotics were not administered to 32% of the patients with a PCT > 0.5 ng/mL, which indicates limitations of diagnosing bacterial co-infection in patients with acute HF based solely on biomarkers such as PCT.
In the large cohort of HF patients in the PROTECT study, the characteristics of those with a PCT > 0.2 ng/mL (high-PCT) or < 0.2 ng/mL (low-PCT) were compared with those of patients with acute HF and bacterial infection [43]. In the high-PCT group, there was a statistically significant association of a high PCT level with lower serum albumin and hemoglobin levels, and with higher WBC, CRP, and blood urea nitrogen levels, suggesting an association of a high PCT level with bacterial infections in patients with HF. Despite the similar severity of HF between the two groups, the high PCT group had a higher 30-day all-cause mortality risk (HR, 2.3; 95% CI 1.3–4.2; p = 0.005). Overall, PCT was shown to have limited accuracy for diagnosing bacterial infection in patients with acute HF, given that it can also increase with increasing overall mortality.
A prospective cohort study performed in Switzerland evaluated the roles of PCT and CRP as diagnostic biomarkers in patients with suspected IE [44]. The AUROCs for PCT and CRP in the diagnosis of IE were 0.856 and 0.657, respectively. When the PCT cutoff for IE diagnosis was set to 2.3 ng/mL, the sensitivity was 81%, and the specificity was 85%. The study also included infections other than IE. However, PCT was highest in patients with IE (median, 6.56 ng/mL), followed by non-IE bacterial infection (median, 1.06 ng/mL) and viral infection (median, 0.07 ng/mL). The median PCT value in patients with IE caused by Staphylococcus aureus was higher than that in patients with S. aureus sepsis (median, 4.81 vs. 1.06 ng/mL; p = 0.021).
In a meta-analysis of the roles of PCT and CRP in diagnosing patients with suspected IE [45], the AUROCs of PCT and CRP for the diagnosis of IE were 0.71 and 0.80, respectively, indicating a higher accuracy of CRP than PCT. The PCT cut-off values in several studies were 0.19–0.64 ng/mL, and the CRP cut-off value was 10.6 mg/L. The role of biomarkers in the diagnosis of IE is thus limited, and the cut-off values that distinguish bacterial IE from nonbacterial endocarditis remain poorly defined. Overall, PCT and CRP have no clear role as biomarkers in the diagnosis of IE, although the levels of both biomarkers tend to be higher in patients with IE than in those with other bacterial infections.
The role of biomarkers in distinguishing bacterial co-infection in patients with acute myocardial infarction or cardiac arrest is limited. PCT was measured in patients with ACS and cardiogenic shock. Virtually all patients with cardiogenic shock, 33% of those with ST-elevation myocardial infarction, and 8% of those with non-ST elevation myocardial infarction/unstable angina had PCT levels > 0.5 ng/mL [46]. In another study, the PCT levels of patients with ACS without complications were mostly < 0.5 μg/L, but they increased to 5.24 μg/L in patients with cardiac arrest, cardiogenic shock, or concomitant bacterial infection, suggesting an elevated PCT during systemic inflammatory responses [47]. Several studies have examined the role of biomarkers in differentiating bacterial infection from cardiovascular disorders in patients with dyspnea, but the evidence supporting their use remains limited [48]. Further research is warranted to determine the role of biomarkers in patients with ACS/cardiac arrest.
The proCAP study was an RCT conducted in the UK that evaluated the effectiveness of a PCT-guided algorithm recommending antibiotic administration for patients with AP and PCT levels ≥ 1.0 ng/mL [49]. The algorithm also recommended discontinuation of antibiotics for those with PCT levels < 1.0 ng/mL on days 4 and 7 after admission. The PCT-guided algorithm reduced antibiotic prescriptions compared to the usual care group (45% vs. 63%; risk difference [RD], −15.6%; 95% CI −27.0 to −4.2; p = 0.0071). All-cause mortality and hospital-acquired infection rates did not differ between the two groups.
Another study, conducted in Singapore, evaluated the effectiveness of PCT-based guidelines in patients with AP [50]. The guidelines recommended measuring PCT in patients with severe AP and starting antibiotics in those with PCT levels ≥ 0.5 ng/L. If PCT decreased every other day, antibiotics were recommended for 10–14 days. The PCT-guided group had a significantly shorter antibiotic duration than the standard-of-care group (3.3 vs. 6.3 days, p < 0.001), while clinical outcomes, including 30-day mortality, were similar. A meta-analysis indicated that PCT can aid in the diagnosis of severe AP, but not bacterial co-infection, in patients with AP (AUC, 0.89; sensitivity, 0.80; specificity, 0.84) [51]. Overall, PCT-guided antibiotic use in AP patients significantly reduced antibiotic use, with no improvement in clinical outcomes, including mortality.
The PRORATA trial recommended stopping antibiotics if PCT levels decrease from their peak concentration by ≥ 80% or are < 0.5 μg/L [17]. PCT-guided treatment at antibiotic initiation and discontinuation in acutely ill patients in the ICU reduced the duration of antibiotic administration. However, the 28- and 60-day mortality rates did not significantly differ compared to the control group. The SAPS trial recommended measuring PCT daily and stopping antibiotics in patients with a PCT level ≤ 0.5 μg/L or ≤ 20% decrease compared to the baseline [52]. The duration of antibiotic administration was shorter in the PCT-guided group than in the standard-of-care group (6 vs. 7 days, p = 0.0001).
The PROGRESS trial recommended stopping antibiotics in sepsis patients with PCT levels ≤ 0.5 μg/L or with a ≥ 80% reduction after treatment day 5 [53]. In that study, PCT-guided antibiotic cessation shortened the antibiotic treatment duration compared to the control group (5 vs. 7 days, p < 0.001), with better results in the former with respect to infection-associated adverse events (7.2% vs. 15.3%, p = 0.045), 28-day mortality (15.2% vs. 28.2%, p = 0.02), and hospitalization costs.
In a multicenter RCT performed in the Netherlands, PCT was measured daily in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis who were started on antibiotics. Antibiotic treatment was discontinued if PCT levels were ≤ 0.5 μg/L or decreased by 80% from their peak level [54]. In the PCT-guided group, antibiotic use was shortened compared to the standard-of-care group, from 7 to 5 days, and median antibiotic consumption was reduced from 9.3 to 7.5 DDDs. The 28-day mortality rate was lower in the PCT-guided group than in the standard-of-care group (20% vs. 27%, p = 0.0122). CRP and PCT were measured in that study, and no significant differences in CRP levels were found between the two groups.
In the SISPCT trial, a PCT-guided algorithm was applied in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock [55]. PCT was measured at baseline and on days 4, 7, 10, and 14. Antibiotic discontinuation was recommended in patients with PCT levels ≤ 1.0 on day 7 and in those with a > 50% decrease on day 4. The duration of antibiotic administration in the PCT-guided group did not differ from that in the control group at day 7, but antibiotic exposure in the former was reduced by 4.5%. The 28-day mortality rate did not differ significantly between the two groups (25.6% vs. 28.2%, p = 0.34).
An RCT conducted in Germany evaluated the effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic therapy in patients with sepsis admitted to surgical ICUs [56]. Antibiotic discontinuation was recommended when the PCT level, measured upon the improvement of clinical symptoms, was < 1 ng/mL or had decreased by 25–35% from the initial level over 3 days. The duration of antibiotic administration was shorter in the PCT-guided group than in the standard-of-care group (5.9 vs. 7.9 days, p < 0.001). Neither the daily Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score nor the CRP or IL-6 levels differed significantly between the two groups.
A meta-analysis of 15 studies found that PCT-guided antibiotic management in critically ill patients reduced antibiotic use by 1.26 days and short-term mortality by 13% [57]. A prospective cohort study conducted in Canada evaluated an ASP, including a biomarker-guided clinical decision support system [58]. PCT was measured daily in ICU patients with sepsis who were receiving antibiotic treatment. Antibiotics were discontinued in those with a PCT level < 0.25 ng/mL or a 90% decrease from the baseline level. Antibiotics were continued if the PCT level was > 1 ng/mL or increased over time. The PCT-guided antibiotic management system reduced overall antibiotic use by 7.3% (p = 0.010), with no difference in hospital mobility, clinical outcome, or length of ICU stay compared to the control.
A Brazilian RCT of ICU patients receiving antibiotic treatment for sepsis evaluated the effectiveness of an algorithm for stopping antibiotics if the baseline CRP level on day 3 or 5 was < 35 mg/L or there was a > 50% decrease in the CRP level [59]. The duration of antibiotic use was 1 day shorter in the CRP-guided group than in the control group (6 vs. 7 days, p = 0.011) whereas the 28-day mortality rate (28.1% vs. 22.7%, p = 0.480) and ICU mortality rate (18.8% vs. 18.2%, p = 0.933) were not significantly different.
Another multicenter RCT study conducted in Brazil compared PCT- and CRP-guided antibiotic treatment at the time of antibiotic discontinuation in patients with sepsis [60]. Antibiotic discontinuation was recommended on treatment day 4 or 5 in those with PCT levels < 0.1 ng/mL and a 90% decrease from baseline, as well as CRP levels of < 25 mg/L or a 50% decrease from baseline. The median duration of antibiotic therapy was shorter in the CRP group than in the PCT group (6 vs. 7 days, respectively, p = 0.06), with no differences in 28-day mortality (33.3% vs. 32.7%, respectively, p = 1.000) or hospital mortality (46.7% vs. 42.9%, respectively, p = 0.836).
An Egyptian RCT compared the decision to discontinue antibiotics in patients with sepsis who were admitted to the ICU based on PCT versus CRP levels on days 4 and 7 [61]. The cut-off for antibiotic discontinuation was a PCT level < 0.5 ng/mL or a ≥ 80–90% decrease from baseline, and a CRP level < 8.7 mg/L or a ≥ 50% decrease from baseline. The antibiotic discontinuation rate on day 4 was 6% in the CRP-guided group and 23% in the PCT-guided group (p = 0.07), and the antibiotics saving after antibiotic discontinuation on day 4 was 6 days in the CRP group and 30 days in the PCT group (p = 0.005). The 28-day mortality rate was 65.2% in the CRP-guided group and 34.8% in the PCT-guided group (p = 0.063).
Presepsin, a novel biomarker in antimicrobial stewardship, is a soluble form of CD14 with a broad-spectrum affinity for the innate immune system that has been shown to support pathogen recognition [62,63]. Presepsin levels begin to increase 2 hours after infection and peak 3 hours later, suggesting a role for presepsin as an early biomarker for sepsis diagnosis [64]. A multicenter prospective cohort trial conducted in China evaluated the effectiveness of presepsin for antibiotic discontinuation in patients with sepsis [65]. Presepsin levels were measured at baseline and every other day. In the presepsin-guided group, discontinuing antibiotics was recommended in patients with presepsin levels < 350 pg/mL or a ≥ 80% decrease from the peak level measured twice consecutively. The number of days without antibiotics was higher in the presepsin-guided group than in the control group (14.64 vs. 11.00 days, p < 0.001), with no difference in mortality between the two groups either at 28 days (17.7% vs. 18.2%, p = 0.868) or 90 days (19.9% vs. 19.5%, p = 0.891).
Overall, PCT- and CRP-guided antibiotic discontinuation reduces overall antibiotic exposure without improving clinical outcomes such as mortality. Presepsin-induced antibiotic discontinuity was shown to reduce overall antibiotic use but also did not impact clinical outcomes, including mortality.
The above-mentioned ProHOSP study also evaluated the effect of PCT-guided antibiotic management on antibiotic discontinuation in patients with LRTI [19]. PCT was measured on days 3, 5, and 7 of antibiotic treatment. Antibiotics were discontinued in patients with PCT levels ≤ 0.25 μg/L or a ≥ 80% decrease from the peak level. The PCT-guided group had significantly reduced antibiotic use compared to the control group. There were no differences in mortality compared to the CAP, exacerbated COPD, and acute bronchitis subgroups.
The ProCAP study also evaluated the PCT-guided clinical decision to discontinue antibiotics in patients with CAP [20]. PCT was measured on days 4, 6, and 8, with antibiotic discontinuation recommended in patients with PCT levels < 0.25 μg/L or a 10% decrease in the baseline PCT level ≥ 10 μg/L. The median duration of antibiotic use was 7 days shorter in the PCT-guided group than in the control group (5 vs. 12 days, p < 0.001). In subgroup analysis, the duration of antibiotic use in the PCT-guided group was significantly shorter in patients with mild CAP, severe CAP, or nonbacterial CAP (all p < 0.001). The clinical success rates were similar between the PCT-guided and control groups (84% vs. 82%, p = 0.65).
In the Chinese RCT discussed above, PCT-guided clinical decision-making regarding the discontinuation of antibiotics was evaluated in patients with CAP [21]. PCT was measured on days 3, 6, and 8, and antibiotics were discontinued in patients with PCT levels < 0.25μg/L. The total antibiotic exposure risk was 1.8 times higher, and the median duration of antibiotic use was 2 days longer, in the control group than in the PCT-guided group. Four-week clinical outcomes were similar between the two groups.
The ProVAP study evaluated the role of PCT in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) [66]. The recommendations called for a discontinuation of antibiotics in patients with PCT levels < 0.5 μg/L or a decrease from baseline of > 80% at 72 hours after treatment initiation. PCT was measured daily for 10 days in VAP patients maintained on antibiotics. The PCT-guided group had significantly more antibiotic-free days (13 vs. 9.5 days, p = 0.049) and a 27% decrease in the overall duration of antibiotic treatment compared to the control group (10 vs. 15 days, p = 0.038). Mechanical ventilation-free days, ICU-free days, length of hospital stay, and 28-day mortality did not differ significantly between the two groups.
The effectiveness of PCT-guided treatment in terms of the discontinuation of antibiotics was evaluated in a Japanese RCT that included patients with aspiration pneumonia [67]. PCT was measured on days 3, 5, and 7 after antibiotics were started, with discontinuation of antibiotics in patients with PCT levels ≤ 0.5 ng/mL or a > 90% decrease from peak levels. The PCT-guided group had a median reduction of antibiotic duration of 3 days compared to the control group (5 vs. 8 days, p < 0.001). Clinical outcomes, including pneumonia relapse (21% vs. 23%, p = 0.80) and in-hospital death rates (10% vs. 21%, p = 0.26), were not significantly different between the two groups.
The VAPrapid2 study evaluated the effectiveness of IL-1β/IL-8-guided treatment in patients with VAP [68], following a study that identified IL-1β/IL-8 as a VAP marker [69]. Antibiotic discontinuation was recommended for patients whose IL-1β/IL-8 levels, measured in bronchiolar lavage fluid, were below the cutoff. There was no difference in antibiotic-free days or clinical outcomes, including SOFA score and mortality, between the IL-1β/IL-8-guided group and the control group. However, the low compliance rate of the IL-1β/IL-8 induction group may have been a limitation. Further studies are needed to explore this relationship.
Overall, PCT-guided antibiotic discontinuation reduces overall antibiotic use in patients with CAP, exacerbated COPD, acute bronchitis, VAP, or aspiration pneumonia, without affecting clinical outcomes including mortality.
The ProfenC study evaluated the effect of PCT antimicrobial stewardship in children receiving cancer chemotherapy without bone marrow recovery and with a low-risk of febrile neutropenia [70]. Antibiotic cessation was recommended in those with PCT levels < 0.25 ng/mL, measured 48 hours after antibiotic use. PCT-based clinical decision-making significantly reduced antibiotic use (3 vs. 7 days, p < 0.001), with no differences in treatment failure compared to the control group.
Different results may be obtained in real-world clinical practice than in clinical trials. A study in Switzerland thus applied the ProHOSP study algorithm to actual clinical practice [19,71], in which there were more patients with renal disease, cancer, or immunosuppression. Pneumonia severity and CAP rates were higher among real-world patients than in the ProHOSP cohort. The median duration of antibiotic use following the application of PCT-guided antimicrobial stewardship in the real-world group was 6 days, which was 2 days longer than in the PCT group from the ProHOSP study (p = 0.08) and 1 day shorter than in the control group (p < 0.048). Adverse events, including mortality, ICU admission, recurrence, and disease-specific complications, were similar to those of the ProHOSP study (all p > 0.05).
According to a before-and-after analysis of PCT-guided antibacterial management conducted in Germany, PCT-guided ASP reduced antibiotic use density in the surgical ICU by 21.2% (1,005 in 2010 vs. 791.9 DDDs in 2012) [72]. However, while the use of aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, and quinolones decreased, carbapenem use slightly increased, suggesting a limited impact of PCT-guided ASP on antibiotic selection.
A study conducted in the USA evaluated the cost-effectiveness of applying the PRORATA study’s PCT-guided algorithm to patients with suspected bacterial infection or sepsis who were hospitalized in the medical ICU [17,73]. PCT-guided antibiotic treatment significantly reduced antibiotic duration and hospital costs to $45 per patient and increased the quality-adjusted life-years by 0.0001. The economic advantage of biomarkers was exemplified by a total annual hospital cost saving of $8,480.
In another study conducted in the USA, based on the Premier Healthcare Database, 78% of 933,591 adult patients with sepsis underwent biomarker testing [74]. The PCT group had more severe illness and more antibiotic exposure than the other biomarker groups. Patients who had been PCT-tested twice or more had higher hospital costs than those not tested for biomarkers. However, the groups tested for PCT once (OR, 0.88; 95% CI 0.85–0.91) or at least twice (OR, 0.64; 95% CI 0.85–0.91) had a lower risk of death than the group not tested for biomarkers. CRP and lactate testing did not result in a difference in the OR. Consecutive PCT testing was associated with decreased mortality, but it did not reduce hospital costs.
Thus, the use of biomarkers for antimicrobial stewardship in real-world patients with sepsis and LRTI can reduce the duration of antibiotic use without worsening outcomes. However, issues related to antibiotic choice and medical costs remain controversial.
Currently, biomarkers are used in ASP to determine when to start antibiotics in patients with suspected bacterial infections and when to stop antibiotics in treated patients. There is sufficient evidence from ASPs that PCT testing can be used alone. CRP testing has limitations with respect to informing the decision for antibiotic initiation or discontinuation when used alone, but it can be effective when combined with PCT.
PCT testing cannot be applied in the management of all bacterial diseases, but it is relevant regarding the decision to initiate/discontinue antibiotics in sepsis and LRTI. When discriminating between non-infectious organ failure (formerly systemic inflammatory response system) and sepsis, patients who meet the diagnostic criteria for sepsis and have PCT levels ≥ 0.5 ng/mL can be started on antibiotics. If LRTI is suspected, the cut-off for initiating antibiotics is 0.25 ng/mL. However, PCT-guided antibiotic initiation may lead to antibiotic misuse and misdiagnosis (Fig. 1). To reduce the likelihood of misdiagnosis, PCT levels should be measured again within 6–12 hours; to reduce the risk of antibiotic misuse, a clinician may decide to not administer antibiotics even if the PCT criteria are met. If antibiotics are maintained, short-term PCT measurements are needed before treatment discontinuation.
PCT-guided antibiotic discontinuation is recommended in patients with PCT levels < 0.5 ng/mL (< 0.25 ng/mL in LRTI) or a decrease of ≥ 80% in their peak PCT level. PCT should be measured 5–7 days after antibiotic administration begins. If the levels do not meet the antibiotic discontinuation criteria, they can be measured again after 2 days. In Korea, unjustified PCT measurements may not be covered by insurance, which can increase costs. Furthermore, while biomarkers can provide objective evidence in universal ASPs, their use should never take precedence over a clinician’s judgment.
Several research gaps regarding biomarkers and antimicrobial stewardship remain. Most studies have focused on reducing the total amount or duration of antibiotics. However, the purpose of antimicrobial stewardship is not only to reduce antibiotic use but also to identify patients who need antibiotics and administer the appropriate drug in a timely manner. Further studies on biomarkers are needed to support clinical decision-making as it pertains to empirical antibiotic selection and to shed light on the role of microbiological biomarkers. Microbiological biomarkers based on classical antibody measurements are of low sensitivity, and recent PCR techniques do not distinguish colonizers from pathogens. Further research on microbiological biomarkers should focus on the rapid discrimination of pathogens. The combination of novel microbiological biomarkers and existing host-response biomarkers will provide objective evidence for ASP and reduce the likelihood of clinical misjudgment.
Biomarkers are increasingly being applied in antimicrobial stewardship, especially to inform the decision of when to start or stop antibiotics for various infectious diseases. The most commonly used biomarker is PCT. The cut-off values of PCT for sepsis and pneumonia are 0.5 and 0.25 ng/mL, respectively. A clearly defined role for other host-response and pathogen-specific biomarkers in antimicrobial stewardship is still lacking. Future studies on these biomarkers are warranted to inform antimicrobial stewardship in a broader array of diseases.
Notes
Figure 1
Clinical application of biomarkers for antibiotic use in patients with bacterial infections. PCT, procalcitonin; LRTI, lower respiratory tract infection.
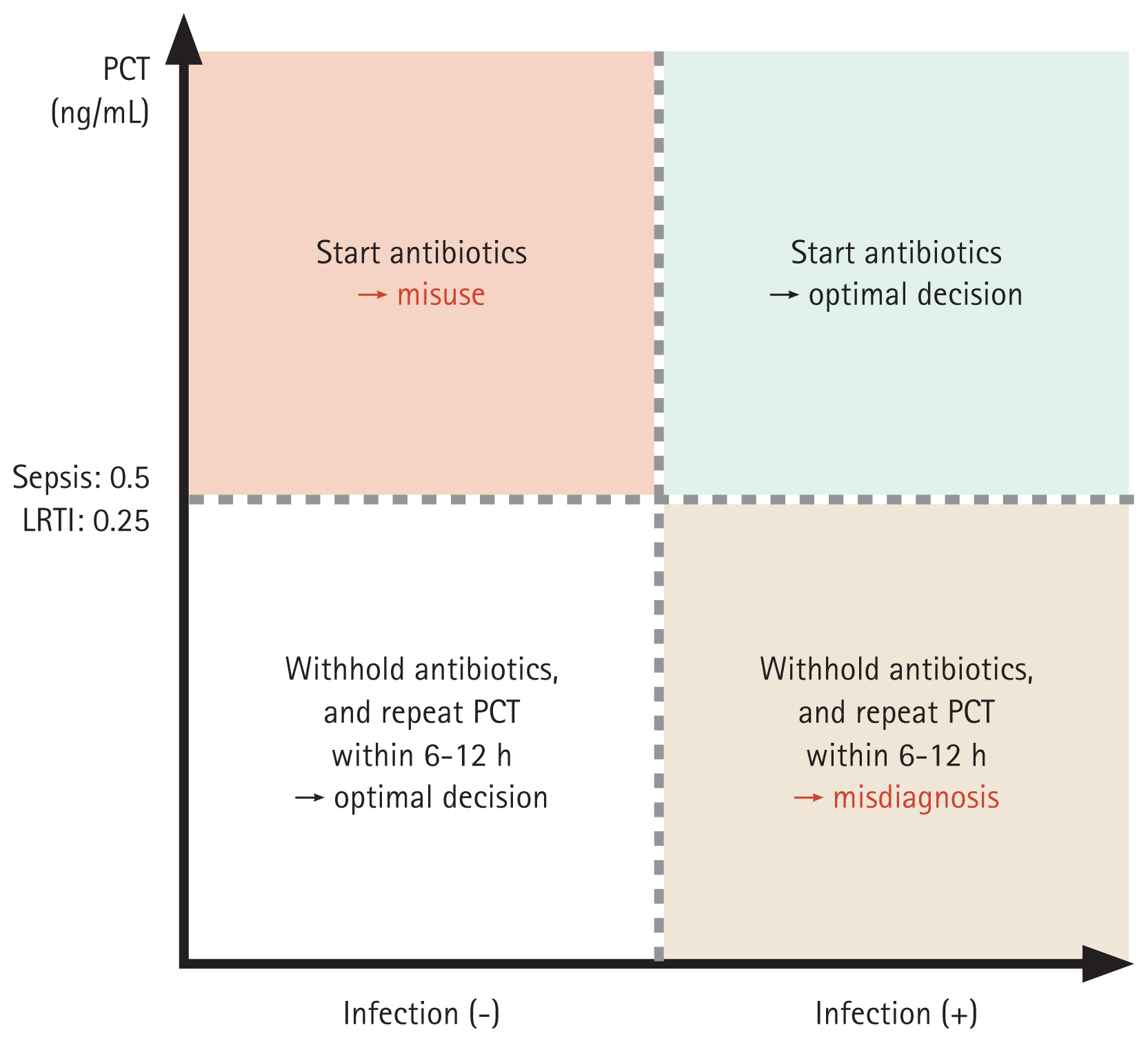
Table 1
Randomized controlled studies evaluating PCT’s role in antimicrobial stewardship
| Trial | Diagnosis | Number of participants (PCT/control) | Timing of PCT measurement (at antibiotic initiation) | PCT cutoff value for antibiotic initiation (ug/L) | Timing of PCT measurement (at antibiotic discontinuation) | PCT cutoff value for antibiotic discontinuation (ug/L) | Antibiotic consumption (PCT/control) | Outcome (PCT/control) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROLATA: Bouadma et al., 2010, France [17] | Sepsis | 307/314 | When infection is suspected, 6–12 h | ≥ 0.5 | Clinical improvement | < 0.5 or ≥ 80% drop from peak level |
Days without antibiotics: 11.6/14.3 (p < 0.001) Days of antibiotic exposure per 1,000 ICU days: 653/812 (p < 0.001) |
28-day mortality: 20.4%/21.2% (p > 0.05) 60-day mortality: 26.1%/30.0% (p > 0.05) |
| SAPS: Shajiei et al., 2023, Netherlands [52] | Sepsis | 439/482 | N/A | N/A | Daily | ≤ 0.5 or decrease to ≤ 20% of the baseline level |
Duration of antibiotic administration: 6/7 days, p = 0.0001 DDD in first 28 days: 7.9/9.0, p = 0.002 |
28-day mortality: 19%/24%, p = 0.11 ICU stay: 9/9 days, p = 0.80 Hospital stay: 24/24 days, p = 0.76 |
| PROGRESS: Kyriazopoulou et al., 2021 [53] | Sepsis | 125/131 | N/A | N/A | Day 5 | ≤ 0.5 μg/L or ≥ 80% reduction | Duration of antibiotic administration: 5/7, p < 0.001 |
Infection-related adverse events: 7.2%/15.3%, p = 0.045 28-day mortality: 15.2%/28.2%, p = 0.02 Hospitalization cost (€): 956.99/1183.49, p = 0.05 |
| de Jong et al., 2016, Netherlands [54] | Sepsis | 761/785 | N/A | N/A | Daily | ≤ 0.5 or 80% drop from peak level |
Median length of antibiotic consumption: 7.5 DDD/9.3 DDD (p < 0.0001) Median number of treatment days: 5/7 (p < 0.0001) |
28-day mortality: 20%/27% (p = 0.0122) |
| SISPCT: Bloos et al., 2016, Germany [55] | Sepsis | 279/267 | N/A | N/A | Day 4, day 7, day 10, and day 14 | ≤ 1.0 or > 50% decrease from the previous level |
Duration of antibiotic use: 7/7 (p = 0.93) Days of antibiotic exposure per 1,000 ICU days: 823/862 (p = 0.02) |
28-day mortality: 25.6%/28.2%, p = 0.34 |
| Hochreiter et al., 2009, Germany [56] | Sepsis | 57/53 | N/A | N/A | Clinical improvement | < 1 or decrease from the initial level over 3 days | Duration of antibiotic use: 5.9/7.9 (p < 0.001) | Daily SOFA score: no difference in either group (p > 0.05) |
| Layios et al., 2012, Belgium [18] | Sepsis | 353/314 | When infection is suspected | ≥ 0.5 | N/A | N/A |
Antibiotic treatment rates in ICU: 62.6%/57.7%, p = 0.11) Antibiotic daily dose per 1,000 ICU days:1 47.3/141.1 (p = 0.96) |
ICU mortality: 56%/53% (p = 0.91) |
| ProHOSP: Schuetz et al., 2009 [19] | LRTI | 671/688 | Within 1 h | > 0.25 | Day 3, day 5, and day 7 | ≤ 0.25 or ≥ 80% decrease from the peak level |
Median duration of antibiotics: 5.7/8.7, RR −34.8%; 95% CI −40.3% to −28.7%) CAP: 7.2/10.7, RR −32.4%; 95% CI −37.6% to −26.9%) COPD: 2.5/5.1, RR −50.4%; 95% CI −64.0% to −34.0%) |
Overall mortality: 15.4%/18.9% RD −3.5% (−7.6% to 0.4%) CAP: 5.2%/5.6%, RD −4.1% (−9.1% to 0.9%) COPD: 13.0%/18.6%, RD −5.3% (−14.8% to 4.4%) |
| Christ-Crain et al., 2004, Switzerland [38] | LRTI | 124/119 | When infection is suspected | ≥ 0.25 | N/A | N/A |
Antibiotic prescription rates: 44%/83%, p < 0.0001 Duration of antibiotic treatment: 10.9/12.8 days, p = 0.03 |
Death: 3%/3%, p = 0.96 Readmission: 0.5%/0.4%, p = 0.96 Exacerbation rate: 1.2%/0.9%, p = 0.65 |
| ProCAP: Christ-Crain et al., 2006, Switzerland [20] | CAP | 151/151 | When infection is suspected | ≥ 0.25 | Day 4, day 6, and day 8 | < 0.25 or ≥ 10% decrease if baseline ≥ 10 μg/L |
Antibiotic prescription rates on admission: 85%/99%, p < 0.001 Median duration of antibiotic treatment: 5/12, p < 0.001 |
Clinical success rates: 84%/82%, p = 0.65 |
| Long et al., 2011, China [21] | CAP | 81/81 | When infection is suspected | > 0.25 | Day 3, day 6, and day 8 | ≤ 0.25 |
Antibiotic prescription rates on admission: 84.4%/97.5%, p < 0.001 Total antibiotic exposure (RR 0.55, 95% CI 0.51–0.60, p = 0.003) Median duration of antibiotics: 5/7, p < 0.001 |
Rates of 4-week treatment success: 85.2%/88.9%, absolute difference −3.7 (−14.1 to 6.7). |
| ProVAP: Stolz et al., 2009 [66] | VAP | 51/50 | N/A | N/A | 72 h, daily until day 10 for antibiotic maintenance | < 0.5 or 80% decrease from day 0 |
Antibiotic free-days: 13/9.5, p = 0.049 Overall duration of antibiotic therapy: 10/15, p = 0.038 |
MV-free days: 21/19, p = 0.455 ICU-free days: 10/8.5, p = 0.526 Length of hospital stay: 26/26, p = 0.153 28-day mortality: 8/12, p = 0.327 |
| Ogasawara et al., 2014, Japan [67] | Aspiration pneumonia | 48/48 | N/A | N/A | Day 3, day 5, and day 7 | ≤ 0.5 ng/mL or 10% decrease from peak level | Median duration of antibiotic treatment: 5/8, p < 0.001 |
Pneumonia relapse: 21%/23%, p = 0.80 In-hospital mortality: 10%/21%, p = 0.26 |
| Stolz et al., 2007 [37] | COPD exacerbation | 102/106 | When infection is suspected | > 0.25 | N/A | N/A |
Antibiotic prescription: 40% vs. 72%, p < 0.0001 Antibiotic exposure: RR 0.56; 95% CI 0.43–0.73, p < 0.0001) Antibiotic exposure up to 6 months: RR 0.76; 95% CI 0.64–0.92; p = 0.004 |
Clinical success: 82.4%/83.9%, p = 0.853 6-month mortality: 4.9%/8.5%, p = 0.409 |
| PROCAP: Siriwardena et al., 2022 [49] | Acute pancreatitis | 132/128 | Day 0 and when infection is suspected | ≥ 1.0 | Day 4, day 7 | < 1.0 |
Antibiotic prescription rates: 45%/63%, 95% CI −27.0 to −4.2, p = 0.0071 Antibiotic duration: 4.5/5.8, 95% CI −2.10 to −0.22, p = 0.015 |
All-cause mortality: 3%/2%, 95% CI −3.24 to 4.62, p = 0.73 |
PCT, procalcitonin; ICU, intensive care unit; DDD, defined daily dose; SOFA, sequential organ failure assessment; LRTI, lower respiratory tract infection; RR, risk ratio; CI, confidence interval; CAP, community-acquired pneumonia; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; RD, risk difference; VAP, ventilator-associated pneumonia; MV, mechanical ventilator.
Table 2
Randomized controlled studies evaluating CRP’s role in antimicrobial stewardship
| Trial | Diagnosis | Number of participants (CRP/control) | Timing of CRP measurement (at antibiotic initiation) | CRP cutoff value for antibiotic initiation (mg/L) | Timing of CRP measurement (at antibiotic discontinuation) | CRP cutoff value for antibiotic discontinuation (mg/L) | Antibiotic consumption (CRP/control) | Outcome (CRP/control) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borges et al., 2020, Brazil [59] | Sepsis | 64/66 | N/A | N/A |
Baseline CRP ≥ 100 → day 5 CRP < 100 → day 3 |
Day 3: CRP < 35 Day 5: 50% drop from baseline |
Median duration of antibiotic treatment: 6/7 days (p = 0.011) |
28-day mortality (28.1%/22.7%, p = 0.480) ICU mortality (18.8%/18.2%, p = 0.933) |
| Oliveria et al., 2013, Brazil [60] | Sepsis | 45/49 (PCT) | N/A | N/A |
CRP < 100 → day 4 CRP ≥ 100 → day 5 PCT < 1.0 ng/mL → day 4 PCT ≥ 1.0 ng/mL → day 5 |
Day: CRP < 25 mg/L, PCT < 0.1 ng/mL Day 5: CRP ≥ 50%, PCT ≥ 90% decrease |
Median duration of antibiotic treatment: 6/7 days (p = 0.06) |
28-day mortality (33.3%/32.7%, p = 1.000) Hospital mortality (46.7%/42.9%, p = 0.836) |
| Ali et al., 2021, Egypt [61] | Sepsis | 30/30 (PCT) | N/A | N/A | Day 1, day 4, and day 7 |
CRP < 8.7 or ≥ 50% decrease PCT < 0.5 ng/mL or ≥ 80–90% decrease |
Antibiotic discontinuation on day 4: 2/10 (p = 0.009) Antibiotic discontinuation on day 7: 2/7 (p = 0.07) Patients on antibacterial agents for more than 7 days: 25/10 (p < 0.001) |
28-day mortality (65.2%/34.8%, p = 0.063) |
| Butler et al., 2019, UK [40] | COPD exacerbation | 325/324 | When infection is suspected | ≥ 20 | N/A | N/A | Antibiotic prescription rate: 57.0%/77.4%; aOR 0.31; 95% CI 0.20–0.47 | Clinical COPD questionnaire at 2 weeks: −0.19 points; 90% CI −0.33 to −0.05 |
REFERENCES
1. Barlam TF, Cosgrove SE, Abbo LM, et al. Implementing an antibiotic stewardship program: guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin Infect Dis 2016;62:e51–e77.




2. Cheong HS, Park KH, Kim B, et al. Developing core elements and checklist items for implementing antimicrobial stewardship programs in Korean general hospitals: a modified Delphi survey. Infect Chemother 2023;55:59–68.




3. Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2001;69:89–95.


4. Póvoa P, Coelho L, Dal-Pizzol F, et al. How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: guide to clinicians. Intensive Care Med 2023;49:142–153.




5. Maves RC, Enwezor CH. Uses of procalcitonin as a biomarker in critical care medicine. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2022;36:897–909.


6. Tang BM, Eslick GD, Craig JC, McLean AS. Accuracy of procalcitonin for sepsis diagnosis in critically ill patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2007;7:210–217.


7. Ramírez P, Ferrer M, Martí V, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers and prediction for intensive care unit admission in severe community-acquired pneumonia. Crit Care Med 2011;39:2211–2217.


8. Self WH, Grijalva CG, Williams DJ, et al. Procalcitonin as an early marker of the need for invasive respiratory or vasopressor support in adults with community-acquired pneumonia. Chest 2016;150:819–828.



9. Gewurz H, Mold C, Siegel J, Fiedel B. C-reactive protein and the acute phase response. Adv Intern Med 1982;27:345–372.

10. Póvoa P, Coelho L, Almeida E, et al. C-reactive protein as a marker of infection in critically ill patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 2005;11:101–108.


11. García Vázquez E, Martínez JA, Mensa J, et al. C-reactive protein levels in community-acquired pneumonia. Eur Respir J 2003;21:702–705.


13. Barlam TF, Al Mohajer M, Al-Tawfiq JA, et al. SHEA statement on antibiotic stewardship in hospitals during public health emergencies. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2022;43:1541–1552.



14. Ito A, Shime N, Fujishima S, Fujitani S, Komiya K, Schuetz P. An algorithm for PCT-guided antimicrobial therapy: a consensus statement by Japanese experts. Clin Chem Lab Med 2022;61:407–411.


15. Yoon YK, Kwon KT, Jeong SJ, et al. Guidelines on implementing antimicrobial stewardship programs in Korea. Infect Chemother 2021;53:617–659.




16. Park DW, Choi JY, Kim CJ, Kim JH, Kim HB, Lee DG. Implementation of procalcitonin in antibiotic stewardship: derivation of a consensus algorithm for procalcitonin use in clinical practice. Infect Chemother 2022;54:621–636.




17. Bouadma L, Luyt CE, Tubach F, et al. Use of procalcitonin to reduce patients’ exposure to antibiotics in intensive care units (PRORATA trial): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010;375:463–474.


18. Layios N, Lambermont B, Canivet JL, et al. Procalcitonin usefulness for the initiation of antibiotic treatment in intensive care unit patients. Crit Care Med 2012;40:2304–2309.


19. Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines vs standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: the ProHOSP randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009;302:1059–1066.

20. Christ-Crain M, Stolz D, Bingisser R, et al. Procalcitonin guidance of antibiotic therapy in community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;174:84–93.


21. Long W, Deng X, Zhang Y, Lu G, Xie J, Tang J. Procalcitonin guidance for reduction of antibiotic use in low-risk outpatients with community-acquired pneumonia. Respirology 2011;16:819–824.


22. Cals JW, Butler CC, Hopstaken RM, Hood K, Dinant GJ. Effect of point of care testing for C reactive protein and training in communication skills on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: cluster randomised trial. BMJ 2009;338:b1374.



23. Little P, Stuart B, Francis N, et al. Effects of internet-based training on antibiotic prescribing rates for acute respiratory-tract infections: a multinational, cluster, randomised, factorial, controlled trial. Lancet 2013;382:1175–1182.



24. Boere TM, van Buul LW, Hopstaken RM, et al. Effect of C reactive protein point-of-care testing on antibiotic prescribing for lower respiratory tract infections in nursing home residents: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2021;374:n2198.



25. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. COVID-19 rapid guideline: antibiotics for pneumonia in adults in hospital. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2020.
26. Hessels LM, Speksnijder E, Paternotte N, et al. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic prescription in patients with COVID-19: a multicenter observational cohort study. Chest 2023;164:596–605.



27. Kiapi G, Gonzalez L, Woodard SL, Urch J. Successful antibiotic stewardship in the electronic era. JAC Antimicrob Resist 2023;5:dlad072.




28. Williams EJ, Mair L, de Silva TI, et al. Evaluation of procalcitonin as a contribution to antimicrobial stewardship in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective cohort study. J Hosp Infect 2021;110:103–107.



29. Harte E, Kumarasamysarma S, Phillips B, et al. Procalcitonin values fail to track the presence of secondary bacterial infections in COVID-19 ICU patients. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023;12:709.



30. Vanhomwegen C, Veliziotis I, Malinverni S, et al. Procalcitonin accurately predicts mortality but not bacterial infection in COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care unit. Ir J Med Sci 2021;190:1649–1652.




31. Dolci A, Robbiano C, Aloisio E, et al. Searching for a role of procalcitonin determination in COVID-19: a study on a selected cohort of hospitalized patients. Clin Chem Lab Med 2020;59:433–440.


32. Heer RS, Mandal AK, Kho J, et al. Elevated procalcitonin concentrations in severe Covid-19 may not reflect bacterial co-infection. Ann Clin Biochem 2021;58:520–527.



33. Langford BJ, So M, Raybardhan S, et al. Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19: a living rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect 2020;26:1622–1629.



34. Pink I, Raupach D, Fuge J, et al. C-reactive protein and procalcitonin for antimicrobial stewardship in COVID-19. Infection 2021;49:935–943.




35. Houghton R, Moore N, Williams R, et al. C-reactive protein-guided use of procalcitonin in COVID-19. JAC Antimicrob Resist 2021;3:dlab180.




36. Kooistra EJ, van Berkel M, van Kempen NF, et al. Dexamethasone and tocilizumab treatment considerably reduces the value of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin to detect secondary bacterial infections in COVID-19 patients. Crit Care 2021;25:281.




37. Stolz D, Christ-Crain M, Bingisser R, et al. Antibiotic treatment of exacerbations of COPD: a randomized, controlled trial comparing procalcitonin-guidance with standard therapy. Chest 2007;131:9–19.


38. Christ-Crain M, Jaccard-Stolz D, Bingisser R, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided treatment on antibiotic use and outcome in lower respiratory tract infections: cluster-randomised, single-blinded intervention trial. Lancet 2004;363:600–607.


39. Mathioudakis AG, Chatzimavridou-Grigoriadou V, Corlateanu A, Vestbo J. Procalcitonin to guide antibiotic administration in COPD exacerbations: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev 2017;26:160073.



40. Butler CC, Gillespie D, White P, et al. C-reactive protein testing to guide antibiotic prescribing for COPD exacerbations. N Engl J Med 2019;381:111–120.


41. Bafadhel M, Clark TW, Reid C, et al. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in hospitalized adult patients with community-acquired pneumonia or exacerbation of asthma or COPD. Chest 2011;139:1410–1418.



42. Maisel A, Neath SX, Landsberg J, et al. Use of procalcitonin for the diagnosis of pneumonia in patients presenting with a chief complaint of dyspnoea: results from the BACH (Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure) trial. Eur J Heart Fail 2012;14:278–286.




43. Demissei BG, Cleland JG, O’Connor CM, et al. Procalcitonin-based indication of bacterial infection identifies high risk acute heart failure patients. Int J Cardiol 2016;204:164–171.


44. Mueller C, Huber P, Laifer G, Mueller B, Perruchoud AP. Procalcitonin and the early diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Circulation 2004;109:1707–1710.


45. Yu CW, Juan LI, Hsu SC, et al. Role of procalcitonin in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: a meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med 2013;31:935–941.


46. Picariello C, Lazzeri C, Chiostri M, Gensini G, Valente S. Procalcitonin in patients with acute coronary syndromes and cardiogenic shock submitted to percutaneous coronary intervention. Intern Emerg Med 2009;4:403–408.



47. Remskar M, Horvat M, Hojker S, Noc M. Procalcitonin in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2002;114:205–210.

48. Schuetz P, Daniels LB, Kulkarni P, Anker SD, Mueller B. Procalcitonin: a new biomarker for the cardiologist. Int J Cardiol 2016;223:390–397.


49. Siriwardena AK, Jegatheeswaran S, Mason JM. A procalcitonin-based algorithm to guide antibiotic use in patients with acute pancreatitis (PROCAP): a single-centre, patient-blinded, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;7:913–921.


50. Cai Y, Ee J, Liew YX, et al. A procalcitonin-based guideline promotes shorter duration of antibiotic use safely in acute pancreatitis. J Infect 2014;69:412–415.


51. Chen L, Jiang J. The diagnostic value of procalcitonin in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis. Turk J Gastroenterol 2022;33:722–730.



52. Shajiei A, Berends MS, Luz CF, et al. Impact of reduced antibiotic treatment duration on antimicrobial resistance in critically ill patients in the randomized controlled SAPS-trial. Front Med (Lausanne) 2023;10:1080007.



53. Kyriazopoulou E, Liaskou-Antoniou L, Adamis G, et al. Procalcitonin to reduce long-term infection-associated adverse events in sepsis. a randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2021;203:202–210.



54. de Jong E, van Oers JA, Beishuizen A, et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing the duration of antibiotic treatment in critically ill patients: a randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2016;16:819–827.


55. Bloos F, Trips E, Nierhaus A, et al. Effect of sodium selenite administration and procalcitonin-guided therapy on mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2016;176:1266–1276.


56. Hochreiter M, Köhler T, Schweiger AM, et al. Procalcitonin to guide duration of antibiotic therapy in intensive care patients: a randomized prospective controlled trial. Crit Care 2009;13:R83.



57. Lam SW, Bauer SR, Fowler R, Duggal A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of procalcitonin-guidance versus usual care for antimicrobial management in critically ill patients: focus on subgroups based on antibiotic initiation, cessation, or mixed strategies. Crit Care Med 2018;46:684–690.


58. Sligl WI, Chen JZ, Wang X, et al. Antimicrobial stewardship, procalcitonin testing, and rapid blood-culture identification to optimize sepsis care in critically ill adult patients: a quality improvement initiative. Antimicrob Steward Healthc Epidemiol 2023;3:e107.



59. Borges I, Carneiro R, Bergo R, et al. Duration of antibiotic therapy in critically ill patients: a randomized controlled trial of a clinical and C-reactive protein-based protocol versus an evidence-based best practice strategy without biomarkers. Crit Care 2020;24:281.



60. Oliveira CF, Botoni FA, Oliveira CR, et al. Procalcitonin versus C-reactive protein for guiding antibiotic therapy in sepsis: a randomized trial. Crit Care Med 2013;41:2336–2343.

61. Ali WA, Bazan NS, Elberry AA, Hussein RRS. A randomized trial to compare procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in assessing severity of sepsis and in guiding antibacterial therapy in Egyptian critically ill patients. Ir J Med Sci 2021;190:1487–1495.



62. Yaegashi Y, Shirakawa K, Sato N, et al. Evaluation of a newly identified soluble CD14 subtype as a marker for sepsis. J Infect Chemother 2005;11:234–238.


63. Turgman O, Schinkel M, Wiersinga WJ. Host response biomarkers for sepsis in the emergency room. Crit Care 2023;27:97.




64. Lee S, Song J, Park DW, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of presepsin and procalcitonin in non-infectious organ failure, sepsis, and septic shock: a prospective observational study according to the Sepsis-3 definitions. BMC Infect Dis 2022;22:8.




65. Xiao H, Wang G, Wang Y, et al. Potential value of presepsin guidance in shortening antibiotic therapy in septic patients: a multicenter, prospective cohort trial. Shock 2022;57:63–71.


66. Stolz D, Smyrnios N, Eggimann P, et al. Procalcitonin for reduced antibiotic exposure in ventilator-associated pneumonia: a randomised study. Eur Respir J 2009;34:1364–1375.


67. Ogasawara T, Umezawa H, Naito Y, et al. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy in aspiration pneumonia and an assessment of the continuation of oral intake. Respir Investig 2014;52:107–113.


68. Hellyer TP, McAuley DF, Walsh TS, et al. Biomarker-guided antibiotic stewardship in suspected ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAPrapid2): a randomised controlled trial and process evaluation. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:182–191.



69. Conway Morris A, Kefala K, Wilkinson TS, et al. Diagnostic importance of pulmonary interleukin-1beta and interleukin-8 in ventilator-associated pneumonia. Thorax 2010;65:201–207.



70. Srinivasan P, Meena JP, Gupta AK, et al. Safety of procalcitonin guided early discontinuation of antibiotic therapy among children receiving cancer chemotherapy and having low-risk febrile neutropenia: a randomized feasibility trial (ProFenC Study). Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2024;41:89–102.


71. Schuetz P, Batschwaroff M, Dusemund F, et al. Effectiveness of a procalcitonin algorithm to guide antibiotic therapy in respiratory tract infections outside of study conditions: a post-study survey. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2010;29:269–277.



72. Hohn A, Heising B, Hertel S, Baumgarten G, Hochreiter M, Schroeder S. Antibiotic consumption after implementation of a procalcitonin-guided antimicrobial stewardship programme in surgical patients admitted to an intensive care unit: a retrospective before-and-after analysis. Infection 2015;43:405–412.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



