 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 39(3); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
The identification of antimicrobial use patterns is essential for determining key targets for antimicrobial stewardship interventions and evaluating the effectiveness thereof. Accurately identifying antimicrobial use patterns requires quantitative evaluation, which focuses on measuring the quantity and frequency of antimicrobial use, and qualitative evaluation, which assesses the appropriateness, effectiveness, and potential side effects of antimicrobial prescriptions. This paper summarizes the quantitative and qualitative methods used to evaluate antimicrobials, drawing insights from overseas and domestic cases.
The use of antimicrobials saves many lives by effectively combating bacterial infections. However, the rampant overuse and misuse of antimicrobials poses a significant threat to global health, contributing to the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant strains [1]. This has led to severe consequences, including prolonged hospital stays, high treatment costs, and mortality due to infections caused by antimicrobial-resistant pathogens [2,3]. Recognizing the severity of the situation, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared antimicrobial resistance a critical health crisis and, in 2015, released the Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance [4]. This plan calls for a concerted global response to curb indiscriminate antimicrobial use and combat resistance.
The increasing inappropriate use of antimicrobials has created a vicious cycle, leading to increased antimicrobial resistance, continued widespread and inappropriate antimicrobial use, and a further increase in resistance. Globally, there is a concerted focus on implementing antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) to interrupt this cycle, improve clinical outcomes, mitigate collateral damage, including from Clostridioides difficile infection [5,6], and reduce costs. These programs involve comprehensive interventions aimed at assessing and enhancing the appropriateness of antimicrobial use, including in terms of type, dose, duration, and administration route [6,7]. Similar to the situation in other countries, several Korean hospitals are actively engaged in the implementation of ASPs [8ŌĆō10].
A fundamental aspect of ASP is the identification of antimicrobial use patterns [6,7], which sheds light on key targets for interventions and facilitates the evaluation of intervention effectiveness [11]. Furthermore, it provides data essential for establishing correlations between antimicrobial use and the development of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, thereby raising awareness among health professionals, consumers, and policymakers regarding antimicrobial resistance and inappropriate use [12]. Acknowledging the significance of this process, evaluating antimicrobial use and providing feedback are key strategies for implementing ASPs, as outlined by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) [6,13ŌĆō15]. This approach is further designated as a core strategy within the Second National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance in Korea, 2021ŌĆō2025 [16].
Accurate identification of antimicrobial use patterns necessitates both quantitative and qualitative assessments [12]. Quantitative assessment evaluates the quantity and frequency of antimicrobial use to determine distributions and trends [8]. Conversely, qualitative assessment focuses on adherence to guidelines, as well as the adequacy, effectiveness, and side effects of antimicrobial prescriptions [17]. These two evaluation methods provide complementary information. Quantitative assessments alone cannot determine the appropriateness of antimicrobial use, whereas qualitative assessments alone do not account for overall trends. Hence, both methods are essential for the effective implementation of ASPs.
This article summarizes the quantitative and qualitative methods for evaluating antimicrobial use within the framework of ASP activities, examining the current situation in Korea and abroad.
The diverse array of antimicrobials are categorized into classes. Traditionally, antimicrobials with similar chemical structures or mechanisms for killing microbes are categorized together. Example representative classes include aminoglycosides, carbapenems, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and penicillin [18]. However, antimicrobials within the same class often exhibit significant differences in indications and antimicrobial spectrums, particularly against resistant bacteria. Consequently, efforts are underway to categorize antimicrobials based on the antimicrobial spectrum rather than adhering to traditional classifications. The WHO has introduced the WHO Access, Watch, and Reserve (AWaRe) system, categorizing antimicrobials according to the associated risk of developing resistant bacteria (Table 1). ŌĆ£AccessŌĆØ (A) antimicrobials are frequently prescribed and always available, ŌĆ£watchŌĆØ (Wa) antimicrobials are recommended only in limited circumstances, and ŌĆ£ReserveŌĆØ (Re) antimicrobials are considered the final resort when other options are unavailable [19].
The US CDC has collaborated with expert groups to develop a classification system for measuring antimicrobial use. The standardized antimicrobial administration ratio (SAAR), an indicator of antimicrobial use, is applied within the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN)-Antimicrobial Use (AU) module, a national antimicrobial use monitoring system [20]. In Korea, a classification system for measuring antimicrobial use was developed by a group of ASP experts in 2019 based on benchmarking from the CDC classification system and a Delphi survey [21]. This system incorporates both spectrum- and class-based classifications and is utilized in the Korea National Antimicrobial Use Analysis System (KONAS), an antimicrobial use monitoring system in Korea. The spectrum-based classification is presented in Table 2.
Antimicrobial use is commonly quantified using the defined daily dose (DDD) or days of therapy (DOT) (Table 3). The WHO defines DDD as the average daily dose administered to adults for treating infectious diseases when a specific antimicrobial is the primary indication [22]. When assessing antimicrobial use, the actual antimicrobial dose is divided by the standard DDD of the respective antimicrobial (actual use/standard DDD). For instance, if Hospital A utilizes 40,000 g of ceftriaxone in 1 year and the standard DDD for ceftriaxone is 2 g, the result is 20,000 DDD. This indicates that ceftriaxone was prescribed to 20,000 adult patients at Hospital A throughout the year.
However, DDD may be overestimated in situations requiring combination therapy or high-dose antimicrobials, such as central nervous system infections. Conversely, it may be underestimated when dose reduction is necessary due to renal insufficiency. Moreover, DDD, being a unit designed for adults, is not applicable to children [22]. DOT is the total number of days on which any dose of antimicrobials was administered to individuals. For example, if a patient is administered ceftriaxone for 10 days and metronidazole for 7 days, the DOT for ceftriaxone would be 10, and the DOT for metronidazole would be 7. Unlike DDD, DOT can be applied to pediatric patients. However, similar to DDD, concerns exist regarding potential mismeasurement in patients with renal insufficiency and those requiring combination therapy [8]. Although DDD is advantageous because it does not require individual patient information, DOT is simpler and applicable to pediatric patients. Consequently, the antimicrobial stewardship guidelines published by Infectious Diseases Society of America/The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America recommend measuring antimicrobial use with DOT to assess antimicrobial stewardship performance [7]. Antimicrobial use measured by DDD or DOT is reported as 1,000 patient-days or 1,000 inhabitant-days to provide an objective indicator of antimicrobial use within a group. Moreover, comparisons with other groups are facilitated by adjusting for the number of patients within a specific group/population.
As noted previously, both DDD and DOT indicate the number of antimicrobials used. However, if more than one antimicrobial is administered to a patient, there is a possibility of overestimating the number of antimicrobials used, even when used appropriately. To address this concern, the length of therapy is occasionally employed to measure antimicrobial use based on the number of antimicrobial administration days per patient, irrespective of the antimicrobial type [8].
Benchmarking refers to comparisons of antibiotic usage among times and locations, which is necessary to evaluate the extent of antimicrobial use at individual institutions and set appropriate improvement targets. Internal benchmarking measures changes in antimicrobial use over time within a hospital, whereas external benchmarking involves comparisons with other institutions. Internal benchmarking can be affected by external factors (outbreaks and policy changes). In the case of external benchmarking, there are many antimicrobials with similar efficacy and effects, but patterns may differ among hospitals; this makes interpretation challenging [23,24]. Therefore, it is preferable to interpret benchmarking using both methods. Antimicrobial use indicators are sometimes employed to facilitate benchmarking because of the difficulty of collecting data from multiple institutions for external benchmarking [25]. A representative example is the SAAR in the NHSN-AU module of US CDC, which compares expected and actual antimicrobial use according to hospital characteristics [20]. The SAAR is calculated as the ratio of actual and predicted antimicrobial use, with values > 1 indicating higher-than-predicted antimicrobial use and values < 1 indicating a level of antimicrobial use below that predicted. In Korea, K-SAAR was developed by modeling expected antimicrobial usage according to institutional characteristics using data from general hospitals, including tertiary ones. The K-SAAR for each participating institution of KONAS is presented in the KONAS Web-based reporting and analysis system (WRAP) [26].
Multiple countries have national systems that determine antimicrobial use and provide feedback on the results (Table 4). For instance, in Australia, the National Antimicrobial Utilization Surveillance Program monitors antimicrobial usage in adult acute care hospitals using drug dispensing data, assigning unique anonymization codes to participating hospitals for data comparison. This program publishes antimicrobial use reports for participating hospitals across Australia every 1ŌĆō2 years, which are accessible to the public [27]. Furthermore, the National Prescribing Service MedicineWise, a nonprofit service funded by the National Health Department, operates Medicine Insight, a drug prescription pattern analysis and feedback system for general practitioners. It uses the Medicare pharmacy claims database to analyze antimicrobial prescribing patterns of general practitioners and compares data with regional and national averages [28].
In the United States, the CDC-led NHSN includes an AU module that analyzes antimicrobial use by participating institutions. Organizations that voluntarily participate can easily convert their antimicrobial prescription data into a file that can be uploaded to the NHSN through the antimicrobial usage analysis software of the Electronic Health Record program, provided by the CDC or program vendors. The staff from each organization can upload the converted file to NHSN, which calculates the monthly antimicrobial use by class. Additionally, SAARs are provided to help individual institutions understand the level of antimicrobial use by class, which can be used to formulate antimicrobial stewardship strategies in each hospital [29].
In the United Kingdom, Public Health England, the responsible governing body of the Department of Health and Social Care, collects and analyses antimicrobial use data from all National Health Service (NHS) hospitals. For primary and dental care, prescription data are collected and analyzed through the NHS. For secondary care, drug prescription data collected by IQVIA, a multinational company, along with NHS data are analyzed to assess antimicrobial usage. The collected data are provided online (https://fingertips.phe.org.uk/) on a public website where various types of health and medical information are easily available, including the results of antimicrobial use analyses for each medical institution from various perspectives. Graphical representations make it easy for the general public to understand the data. Notably, antimicrobials managed according to national policy are periodically selected, and usage trends are presented [30]. It also publishes the annual report of the English surveillance program for antimicrobial utilization and resistance [31].
The Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System, operated by the Public Health Agency of Canada, implemented a quantitative assessment and surveillance program for antimicrobial use in healthcare settings and pharmacies across Canada. For the healthcare sector, they analyze data from representative medical institutions using drug sales and purchase records from Canadian pharmacies and hospitals collected by IQVIA, estimate total usage based on these data, and analyze data collected from institutions participating in the Public Health Agency of CanadaŌĆÖs Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program. For the community sector, drug sales and purchase records collected by IQVIA from representative pharmacies and outpatient clinics are used to estimate total usage. The results are published in a publicly available annual report [32].
In Japan, an antimicrobial usage analysis and surveillance program for participating medical institutions is included in the Japan Surveillance for Infection Prevention and Healthcare Epidemiology System (J-SIPHE), which monitors healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). When medical billing data are entered into the program, the antimicrobial usage for each institution is calculated, and the data files are uploaded to J-SIPHE. The data can then be visualized as graphs or charts and are provided to individual institutions. The data are then used to generate annually published national antimicrobial use statistics [33,34].
As part of the First National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance in Korea, 2016ŌĆō2020, a national antimicrobial usage analysis and monitoring system was developed in Korea [35]. In 2019, the Development of National Antimicrobial Monitoring System project was launched, led by the Korean Society of Infectious Diseases but with participation from the Korean Society of Antimicrobial Therapy and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) [23]. This project led to the establishment of KONAS, a Korean antimicrobial usage monitoring system, which commenced operations for tertiary and secondary care hospitals in 2022 following a successful pilot run in 2021. In 2023, 110 institutions, comprising 42 tertiary care hospitals and 68 secondary care hospitals, voluntarily joined the KONAS initiative [23,36]. While currently limited to tertiary and general hospitals, there are plans to progressively expand the program to include standard hospitals, long-term care hospitals, and clinics [37].
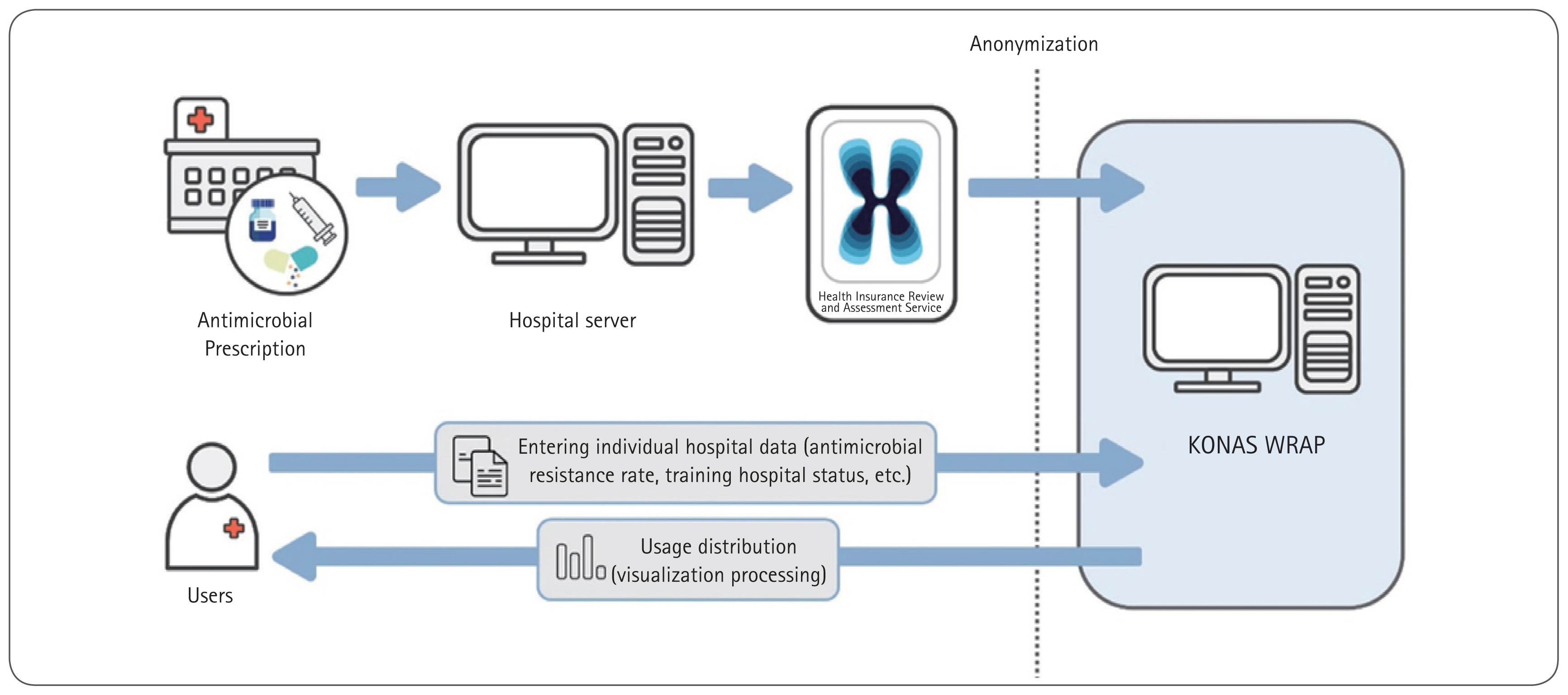
The antimicrobial usage analysis conducted within KONAS primarily relies on claims data provided by HIRA. Claims data related to antimicrobial use from the participating hospitals are categorized and analyzed according to the KONAS Antimicrobial Classification System. After analysis, anonymized data are entered into the KONAS WRAP (https://www.konas.or.kr) and are distributed to each institution (Fig. 1) [23]. In addition to the quantity of antimicrobials used, information related to the participating institutions is collected, such as the number of hospital beds, whether or not the hospitals are used for training, and the presence of special centers. Furthermore, data on the frequency of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are periodically collected from designated personnel at each participating institution. All information related to the participating institutions is confidential, and data from individual institutions are accessible solely by the designated personnel within the organization and the KONAS Secretariat through the KONAS WRAP. Using the assigned ID, the responsible individuals at each institution can access KONAS WRAP to perform various analyses using external and internal benchmarking. During this process, the designated persons at individual institutions can customize the analysis based on treatment duration, age group (adult or pediatric), unit of analysis (DOT/1,000 patient-days or DDD/1,000 patient-days), intensive care unit visits, route of administration (injectable or oral), and specific antimicrobials (Fig. 2). Additionally, the K-SAAR index is provided to provide a clearer understanding of antimicrobial usage at individual institutions.
The data collected through KONAS not only provide individual participating institutions with insights into antimicrobial usage patterns, but also facilitate the development of national antimicrobial use reports. The inaugural nationwide antimicrobial use report for Korea, published in 2023 [23], analyzed antimicrobial usage across 26 participating institutions in 2021 for 2018ŌĆō2019 and across 58 participating institutions in 2022 for 2020ŌĆō2021. This report offered a comprehensive national overview of antimicrobial usage trends in medical institutions for 2018ŌĆō2021 [23]. In the future, KONAS will release the results of regular national-level analyses of antimicrobial usage, providing valuable insights into antimicrobial usage trends [36].
While the HIRA claims data, which are the primary data source for KONAS, have the significant advantage of including prescription data from nearly all medical institutions in Korea, they also have certain drawbacks. Discrepancies with actual antimicrobial usage by medical institutions are a concern. Non-insured prescriptions are not included in claims data, and the drugs prescribed at the time of discharge are classified as drugs prescribed to inpatients, leading to overestimation of the use of some drug classes. Additionally, the timing of an insurance claim can impact the pattern of monthly antimicrobial prescriptions [37]. Notably, there is a temporal gap between data collection and distribution, as data are typically compiled for review with a latency of about 1.5ŌĆō2 years, leading to delays in data availability [23]. To address these limitations, a program that allows easy submission of long-term prescription data from individual institutions to KONAS WRAP is needed, similar to practices in the United States and Japan [38].
Since the 2000s, several countries, including Korea, have undertaken qualitative evaluations of antimicrobial prescriptions, mainly involving assessment of the antimicrobial prescription process based on specific indicators. However, no international standardized criteria exist due to variations in the incidence of major infectious diseases, antimicrobial resistance rates, antimicrobial prescription patterns, and healthcare utilization among countries. Differences also exist among countries conducting qualitative assessments in terms of the infectious diseases evaluated, antibiotic types, evaluation methods, and evaluation cycles.
Qualitative evaluations of antimicrobials are broadly categorized into two methods: the first combines antimicrobial prescription variables into a single qualitative indicator, or evaluates individual indicators, while the second and more, comprehensive method assesses the appropriateness of several antimicrobial prescription processes. The comprehensive method considers microbiological culture results, antibiotic susceptibility results, and the physical condition of patients, including underlying diseases and renal function, allowing for the diagnosis of infectious diseases [39ŌĆō41].
In 2015, van den Bosch et al. [40] introduced nine patient-level and two medical institution-level indicators of the quality of antimicrobial prescriptions in the Netherlands. Additionally, the DRIVE-AB project in Europe presented 51 indicators for inpatients, 34 for outpatients, and 22 for emergency department patients [42ŌĆō44]. In Korea, in 2019, a systematic review and consensus among 25 ASP experts led to the publication of 13 indicators for inpatients, 7 for outpatients, and 5 for surgical prophylactic antibiotics. These standardized metrics derived from a systematic evaluation and expert consensus are useful for the assessment of antimicrobial prescription quality [45] (Table 5).
Quality indicators for the qualitative assessment of antimicrobial prescriptions assess individual components of the antimicrobial prescription process and thus differ from integrated assessments of antimicrobial prescribing expertise. The integrated assessment encompasses the diagnosis of infectious diseases and the entire course of antibiotic treatment, including the application of treatment guidelines according to the specific infection, readjustment of antibiotics according to the microbiological diagnosis, changes in antibiotics due to adverse drug reactions, and changes in dosage and usage according to renal or liver function. Based on the evaluation, antimicrobial prescriptions are categorized as appropriate or inappropriate and supported or unsupported [46,47] (Table 6).
The integrated assessment of antimicrobial prescriptions, categorized as appropriate or inappropriate, is a crucial evaluation method. This approach allows for detailed analysis of antimicrobial prescription patterns, enabling the identification of issues with prescriptions and the application of targeted interventions.
However, conducting an expert-centered integrated evaluation requires specialized medical knowledge and expertise in infectious diseases and antimicrobials, which demands significant time and effort.
To effectively assess antimicrobial quality and manage ASPs, it is essential to develop evaluation guidelines and algorithms. This ensures the participation of physicians, pharmacists, and nurses trained in ASPs alongside infectious disease specialists. Additionally, implementing professional development programs is essential [17]. For sustainable operation of national-level antibiotic qualitative evaluations, it is crucial to consider the strengths and limitations of using standard indicators and expert-centered integrated evaluations. Developing a standardized evaluation method that achieves a balance between these aspects is essential.
The qualitative evaluation of antimicrobials commenced in the 2000s, primarily in the United States, Australia, and Europe. Evaluations have been carried out using methods and systems tailored to individual countries.
In the United States, starting with a survey of the prevalence of HAIs across nine hospitals in Jacksonville, Florida in 2009 [48], followed by use of the Marker Scan Hospital Drug Database and CDCŌĆÖs Emerging Infections Program data in 2010, 111 urinary tract infections (UTIs) and 185 injectable vancomycin prescriptions were evaluated in terms of antimicrobial quality to improve antimicrobial prescriptions for hospitalized patients. In total, 110 of 296 cases (37.2%) needed improvement [49]. Then, in 2011, the CDC and Emerging Infections Program conducted a survey of antimicrobial prescriptions in acute hospitals in 10 US states (California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Maryland, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, and Tennessee), categorizing the prescriptions according to purpose (e.g., to treat infectious diseases, community-acquired infections, or HAIs) [50]. In 2015, 199 hospitals across 10 US states analyzed antibiotic prescriptions for therapeutic antimicrobials and evaluated the quality of antimicrobials, including injectable vancomycin and fluoroquinolone, for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and UTIs. This evaluation used standard indicators or relied on expert judgment, and the data were collected and analyzed using an antimicrobial quality assessment form covering UTIs, CAP, resistant gram-negative organisms, and general antimicrobial use. Each of these four categories includes diagnosis, empirical antibiotics, adjunctive non-antimicrobial therapy, de-escalation, and appropriate treatment duration. The data were collected in a standardized manner, and the analysis did not rely on the judgments of infectious disease experts. The evaluation results for antimicrobials were categorized as ŌĆ£supportedŌĆØ or ŌĆ£unsupportedŌĆØ rather than as ŌĆ£appropriateŌĆØ or ŌĆ£inappropriate/unnecessaryŌĆØ use [46]. To qualify as a supported prescription, the following conditions must be satisfied: antimicrobial treatment has been administered according to the patientŌĆÖs diagnosis, the antibiotic was selected according to guidelines or antibiotic susceptibility data, and treatment duration was consistent with guidelines (for severe or complicated infections, treatment duration is not considered). Prescriptions were considered unsupported if antibiotics were prescribed when bacterial infection was not suspected due to an absence of symptoms or signs of infection or missing microbiological results; if they differed from guidelines; or if the recommended treatment period was exceeded. Of the 12,299 patients in 192 hospitals, 1,566 (12.7%) were included in the study, including 219 with CAP, 452 with UTIs, 550 with fluoroquinolone prescriptions, and 403 with vancomycin prescriptions. Prescriptions were considered unsupported in 55.9% of all cases, 79.5% of CAP cases, 76.8% of UTIs, 46.5% of fluoroquinolone prescriptions, and 27.3% of vancomycin prescriptions. Common reasons for prescriptions to be considered unsupported were excessively long treatment duration (59.2% of CAP cases) and no symptoms or signs of infection (50.1% of UTIs) [46].
A national-scale evaluation of antimicrobial quality was conducted in the United States to determine the status of antimicrobial prescriptions and propose goals for improvement, while emphasizing the roles of the government, individual medical institutions, and medical professionals. Since 2010, ASPs have been in operation at individual US medical institutions, with the use of antibiotics reported to the NHSN led by the CDC. Furthermore, the ASP team, comprising physicians and pharmacists, conducts qualitative evaluations of antimicrobial use based on the characteristics of medical institutions and implements interventions based on the results.
European Union/European Economic Area countries and European Union candidate countries participated in a point prevalence survey on HAIs and antimicrobial use led by the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. The survey evaluated the status of antimicrobial use based on various indicators. Acute care hospitals were evaluated in 2011ŌĆō2012 and 2016ŌĆō2017 [51,52], whereas long-term care facilities were evaluated in 2010, 2013, and 2016ŌĆō2017 [53ŌĆō55]. In 2011ŌĆō2012, the survey evaluated antimicrobial prescriptions for 273,753 patients across 1,149 acute hospitals in 30 countries. The evaluation indicators were the proportion of patients prescribed antimicrobials, average number of antimicrobials administered per patient, type of antimicrobials prescribed, prescription rate of injectable antimicrobials, proportion of complete medical records with respect to antimicrobial use, proportion of infectious diseases targeted for antimicrobial prescription, and rate of prophylactic antibiotic use for > 24 hours [51]. The 2016ŌĆō2017 survey involved 1,735 acute hospitals in 27 countries and investigated antimicrobial prescription de-escalation (change from intravenous to oral) during the treatment period. Data from long-term care facilities were investigated to determine the proportion of patients prescribed antimicrobials, number of antimicrobials administered per patient, administration route, purpose of antimicrobial prescription and infected organ, type of antimicrobials prescribed, performance rate of microbial culture tests, and types of microorganisms identified.
In Australia, the National Antimicrobial Prescribing Survey (NAPS), administered by the National Centre for Antimicrobial Stewardship at the Melbourne Doherty Institute, collects data for antimicrobial qualitative assessments. In 2010, it started operating the Hospital NAPS as an offline tool to prompt individual medical institutions to improve their antimicrobial use patterns by benchmarking similar institutions. Since 2013, it has additionally developed and implemented the Aged Care NAPS, Quality Improvement NAPS, Surgical NAPS, and Antifungal NAPS, which collect online data from institutions for various drugs. The number of hospitals participating in the Hospital NAPS increased from 76 in 2011 to 151 in 2013; as of 2020, 406 hospitals are participating. The number of long-term care facilities participating in the Aged Care NAPS increased from 186 in 2015 to 823 in 2019.
The Hospital NAPS is applicable to hospitalized patients receiving antimicrobials not targeting specific diseases. The Aged Care NAPS is applicable to patients with infectious diseases suspected on the day of the survey and patients receiving antimicrobials. The Surgical NAPS evaluates perioperative antimicrobial use in patients undergoing incisional or non-incisional surgical procedures, and the Antifungal NAPS evaluates hospitalized patients receiving antifungal medications that do not target a specific disease [56ŌĆō58]. The Hospital NAPS identified areas that must be prioritized to address problems. The results showed that, according to their particular characteristics, the participating medical institutions implement strategies to increase the adequacy of antimicrobial use in accordance with the Antibiotic Stewardship Group. The surveys promote access to treatment guidelines and decision-making tools for specific infectious diseases. They are conducted in collaboration with professional groups and societies to improve the adequacy of antimicrobial use for conditions characterized by low adequacy (e.g., CAP and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Dedicated management guidelines have been developed for antimicrobials with a high rate of inappropriate prescriptions (e.g., amoxicillin-clavulanic acid), and efforts are being made to develop strategies that can improve inappropriate antimicrobial prescriptions through collaboration with regional clinical experts.
In 2017, the WHO introduced the AWaRe classification as part of the Model List of Essential Medicines (Table 1). The WHO aims to keep Ōēż 60% of global antimicrobial use within access groups. The purpose of this system is to provide simple clinical guidelines for common infectious diseases, empirical antimicrobial recommendations, and strategies for avoiding antimicrobial use. The Ōēż 60% target includes high-, middle-, and low-income countries and covers all medical institutions, including primary healthcare institutions. The AWaRe book does not replace existing country- or region-level guidelines for antimicrobial prescriptions. However, it provides basic guidelines to medical institutions covering topics not addressed by previous guidelines. It describes 19 and 18 infectious diseases relevant for primary care and acute hospitals, respectively. For each major infectious disease, the following information is provided (in order): the main message, WHO references, disease definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology, most common causative bacteria, clinical manifestations, related tests, imaging tests, and antimicrobial recommendations. The WHO AWaRe book is an essential toolkit for antimicrobial quality assessment in low- and middle-income countries with limited workforces and resources [19].
Since the early 2000s, various ŌĆ£administrative antimicrobial stewardshipŌĆØ policies have been introduced in Korea to encourage appropriate antimicrobial use and reduce antimicrobial prescription costs. Management policies include ŌĆ£Separation of Dispensing and Prescribing in Medicine,ŌĆØ evaluation of drug use, assessing the quality of health services, and public reporting [59]. The Korean policy on Separation of Dispensing and Prescribing in Medicine aims to distinguish the medication-prescribing responsibilities of physicians and pharmacists. The primary objectives of this policy are to optimize rational medication use, prevent medication misuse or overuse, and reduce healthcare costs, including those associated with antibiotics. In this system, physicians focus on diagnosing patients and prescribing suitable medications, whereas pharmacists dispense the prescribed medications. This separation of roles adds an extra layer of scrutiny, ensuring patient safety and effective medication management. Furthermore, HIRA has introduced a policy- and administration-led antimicrobial management evaluation system to review reimbursement claims for medicine prescriptions, including antimicrobials [59]. Since 2001, the rate of antimicrobial prescriptions for upper respiratory tract infections in outpatients has been analyzed using the HIRA system, and the results have been provided to each participating medical institution [59]. In 2007, the adequacy of antimicrobial use for perioperative prophylaxis was evaluated. Since 2014, administrative-led qualitative evaluation and monitoring of antimicrobials has been conducted, including evaluating the prescription rate of third-generation or higher cephalosporins and quinolones and assessing the antimicrobial prescription rate for acute lower respiratory tract infections in 2020 [59]. This administrative antimicrobial management significantly reduced antimicrobial prescriptions for upper respiratory tract infections between 2002 and 2013, as well as the duration of perioperative prophylactic antimicrobials [60]. However, government-led claims review-based antimicrobial management and individual medical institution-based antimicrobial quality evaluations were only effective during the evaluation period. Moreover, errors such as exclusion from the analysis occurred due to changes in disease names.
After establishing the ŌĆ£National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance in Korea,ŌĆØ qualitative assessment of antimicrobials was needed. Therefore, the KDCA completed a policy project, ŌĆ£Prevalence of Antimicrobial Use in Hospital and Assessment of the Appropriateness of Antibiotic Prescribing in Korea,ŌĆØ in 2018. Between 2019 and 2022, a study evaluating the appropriateness of antibiotic prescriptions in domestic medical institutions was conducted, and a roadmap for assessing the appropriateness of antibiotics at the national level was developed (Strategies to Assess Antibiotic Use to Drive Improvements in Hospitals)ŌĆØ.
In 2018, 20 medical institutions (10 tertiary general hospitals, 9 general hospitals, and 1 long-term care hospital) evaluated the quality of all antimicrobials prescribed on a given day as appropriate or inappropriate based on expert judgment [61]. In 2019, the participating hospitals were expanded to include 75 medical institutions nationwide (37 tertiary general hospitals, 36 general hospitals, 1 hospital, and 1 long-term care hospital). Instead of a comprehensive survey, certain antimicrobials prescribed on a specific day were selected through random sampling. Antimicrobial use was categorized as optimal, adequate, suboptimal, or inadequate based on expert judgment. In 2020, a qualitative evaluation of antimicrobials prescribed for UTIs was conducted in 26 medical institutions nationwide [62]. In 2022, a qualitative evaluation of antimicrobials prescribed for bacteremia was conducted in 27 medical institutions nationwide. According to a national-scale evaluation of antimicrobials, about 25% of antimicrobials were prescribed inappropriately in hospitals in Korea [48]. In addition, in 2021, a qualitative evaluation of antimicrobials was conducted in 10 small- and medium-sized hospitals with < 400 beds nationwide. It was found that 34.2% of antimicrobials prescribed for inpatients and 36.7% prescribed for inpatients in long-term care hospitals were inappropriate [63].
In Korea, qualitative evaluations of antimicrobial use were conducted at individual centers before the national-scale evaluation. For example, in 2003, eight university hospitals performed qualitative evaluations of injectable ciprofloxacin use [64]. In 2007 and 2014, prophylactic antimicrobial use during surgery was evaluated [60,65]. Additionally, in 2015, studies evaluated inappropriate antimicrobial prescriptions for asymptomatic bacteriuria [66]. In addition to the integrated evaluation of antimicrobial quality based on expert judgment, a qualitative evaluation of key aspects of antimicrobial prescriptions was also conducted, including a survey on the applicability of therapeutic antimicrobial prescription guidelines [67], an evaluation of the change from intravenous to oral antimicrobials [68,69], an evaluation of the adequacy of empirical selection of antimicrobials according to the antimicrobial prescription guidelines in medical institutions [70], and an evaluation of duplicate prescriptions of anti-anaerobic antimicrobials [71], led by pharmacists or through collaboration between pharmacists and physicians
Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of antimicrobials is crucial for effectively implementing antimicrobial stewardship activities. In Korea, efforts are being made at both the governmental and academic levels to establish such evaluation programs. However, due to limitations in the workforce and resources, individual institutions face significant challenges in operating ASPs effectively. To successfully establish an ASP, specific strategies and long-term goals need to be formulated, including training experts in ASP delivery and infectious diseases, educating a diverse range of professionals (such as pharmacists and nurses) in the performance of quantitative and qualitative assessments of antimicrobials, and developing a national-level plan for the long-term evaluation of antibiotics. Amid the global crisis of antimicrobial resistance, efforts aimed at appropriate antimicrobial use are urgently needed. The achievement of antimicrobial stewardship goals requires a combination of efficient policies, financial support from the government, and commitment from the healthcare sector. Nationwide efforts are needed at this crucial time.
Notes
Figure┬Ā1
Flowchart of the Korea National Antimicrobial Use Analysis System (KONAS). Adapted from 2023 Annual report on antimicrobial use in Korean hospitals [23].
Figure┬Ā2
Representative external benchmarking using the web-based Korea National Antimicrobial Use Analysis System analysis program.

Table┬Ā1
WHO AWaRE classification
Table┬Ā2
Spectrum-based classification of antimicrobials according to KONAS
Table┬Ā3
Comparison between DDD and DOT
Adapted from 2023 Annual report on antimicrobial use in Korean hospitals [23].
Table┬Ā4
Comparison of nationwide surveillance systems among various countries
Table┬Ā5
Quality indicators for the qualitative assessment of antimicrobial prescriptions in inpatient, outpatient, and emergency rooms based on a consensus of Korean experts
Table┬Ā6
Definitions of appropriate therapeutic use and surgical antimicrobial prophylaxis according to experts
REFERENCES
1. Spellberg B, Guidos R, Gilbert D, et al. The epidemic of antibiotic-resistant infections: a call to action for the medical community from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2008;46:155ŌĆō164.


2. Cassini A, H├Čgberg LD, Plachouras D, et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2019;19:56ŌĆō66.


3. Touat M, Brun-Buisson C, Opatowski M, et al. Costs and outcomes of 1-year post-discharge care trajectories of patients admitted with infection due to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J Infect 2021;82:339ŌĆō345.


4. World Health Organization. Comprehensive review of the WHO Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance: Evaluation brief ŌĆō September 2021 [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization, c2021. [cited 2023 Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/comprehensive-review-of-the-who-global-action-plan-on-antimicrobial-resistance-evaluation-brief-september-2021.
5. Hwang S, Kwon KT. Core elements for successful implementation of antimicrobial stewardship programs. Infect Chemother 2021;53:421ŌĆō435.




6. Yoon YK, Kwon KT, Jeong SJ, et al. Guidelines on implementing antimicrobial stewardship programs in Korea. Infect Chemother 2021;53:617ŌĆō659.




7. Barlam TF, Cosgrove SE, Abbo LM, et al. Implementing an antibiotic stewardship program: guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin Infect Dis 2016;62:e51ŌĆōe77.




8. Hwang H, Kim B. Impact of an infectious diseases specialist-led antimicrobial stewardship programmes on antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance in a large Korean hospital. Sci Rep 2018;8:14757.




9. Shin DH, Kim HS, Heo E, et al. Stepwise expansion of antimicrobial stewardship programs and its impact on antibiotic use and resistance rates at a tertiary care hospital in Korea. Microbiol Spectr 2022;10:e0033522.




10. Heo E, Choi Y, Kim HS, et al. Current status of outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy in Korea: experience of a single university-affiliated acute-care hospital. Infect Chemother 2023;55:185ŌĆō193.




11. Yarrington ME, Moehring RW. Basic, advance, and novel metrics to guide antibiotic use assessments. Curr Treat Opt Infect Dis 2019;11:145ŌĆō160.
12. World Health Organization. WHO report on surveillance of antibiotic consumption: 2016ŌĆō2018 early implementation [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization, c2019. [cited 2023 Oct 2]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-report-on-surveillance-of-antibiotic-consumption.
13. Pollack LA, Srinivasan A. Core elements of hospital antibiotic stewardship programs from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clin Infect Dis 2014;59:Suppl 3 (Suppl 3): . S97ŌĆōS100.



14. Cheong HS, Park KH, Kim HB, et al. Core elements for implementing antimicrobial stewardship programs in Korean general hospitals. Infect Chemother 2022;54:637ŌĆō673.




15. Cheong HS, Park KH, Kim B, et al. Developing core elements and checklist items for implementing antimicrobial stewardship programs in Korean general hospitals: a modified Delphi survey. Infect Chemother 2023;55:59ŌĆō68.




16. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National action plan on antimicrobial resistance 2021ŌĆō2025 [Internet] Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare, cYear. [cited 2023 Oct 2]. Available from: https://www.mohw.go.kr/react/al/sal0301vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=04&MENU_ID=0403&page=133&CONT_SEQ=368388.
17. Park SY, Kim YC, Lee R, et al. Current status and prospect of qualitative assessment of antibiotics prescriptions. Infect Chemother 2022;54:599ŌĆō609.




18. Kim B, Hwang H, Kim J, Lee MJ, Pai H. Ten-year trends in antibiotic usage at a tertiary care hospital in Korea, 2004 to 2013. Korean J Intern Med 2020;35:703ŌĆō713.




19. World Health Organization. 2021 AWaRe classification [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization, c2021. [cited 2023 Oct 3]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/2021-aware-classification.
20. OŌĆÖLeary EN, Edwards JR, Srinivasan A, et al. National Healthcare Safety Network Standardized Antimicrobial Administration Ratios (SAARs): a progress report and risk modeling update using 2017 data. Clin Infect Dis 2020;71:e702ŌĆōe709.




21. Kim B, Yoon YK, Kim DS, et al. Development of antibiotic classification for measuring antibiotic usage in Korean Hospitals using a modified Delphi method. J Korean Med Sci 2020;35:e241.




22. Morris AM. Antimicrobial stewardship programs: appropriate measures and metrics to study their impact. Curr Treat Options Infect Dis 2014;6:101ŌĆō112.




23. Korea National Antimicrobial Use Analysis System (KONAS). Annual report on antimicrobial use in Korean hospitals: Results of 58 participating hospitals in 2022 [Internet] Seoul: KONAS, c2023. [cited 2024 Apr 18]. Available from: https://www.konas.or.kr:44538/xe/pds/1005.
24. Reddy SC, Jacob JT, Varkey JB, Gaynes RP. Antibiotic use in US hospitals: quantification, quality measures and stewardship. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2015;13:843ŌĆō854.


25. Kim B, Hwang H, Kim J, Lee MJ, Pai H. A few antibiotics can represent the total hospital antibiotic consumption. BMC Infect Dis 2018;18:247.




26. Kim B, Ahn SV, Kim DS, et al. Development of the Korean standardized antimicrobial administration ratio as a tool for benchmarking antimicrobial use in each hospital. J Korean Med Sci 2022;37:e191.




27. Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. National Antimicrobial Utilisation Surveillance Program: 2019 Key Findings [Internet] Sydney: Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, c2021. [cited 2023 Oct 3]. Available from: https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/publications-and-resources/resource-library/2019-annual-report-national-antimicrobial-utilisation-surveillance-program-nausp.
28. NPS MedicineWise. MedicineInsight [Internet]. Sydney: NPS MedicineWise, 2023. [cited 2023 Oct 3]. Available from: https://www.nps.org.au/medicine-insight.
29. National Healthcare Safety Network Antimicrobial use and resistance (AUR) module [Internet] Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, c2024. [cited 2024 Apr 16]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/11pscaurcurrent.pdf.
30. Office for Health Improvement & Disparities. AMR local indicators - produced by the UKHSA [Internet] London: Office for Health Improvement & Disparities, c2023. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://fingertips.phe.org.uk/profile/amr-local-indicators.
31. UK Health Security Agency. English surveillance programme for antimicrobial utilisation and resistance (ESPAUR) report [Internet] London: UK Health Security Agency, c2014. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/english-surveillance-programme-antimicrobial-utilisation-and-resistance-espaur-report.
32. Public Health Agency of Canada. Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (CARSS) report 2022 [Internet] Ottawa (ON): Public Health Agency of Canada, c2022. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/drugs-health-products/canadian-antimicrobial-resistance-surveillance-system-report-2022.html.
33. Kagami K, Ishiguro N, Iwasaki S, et al. Correlation between antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance: a multicenter study using the Japan Surveillance for Infection Prevention and Healthcare Epidemiology (J-SIPHE) system in Hokkaido, Japan. Am J Infect Control 2023;51:163ŌĆō171.


34. National Center for Global Health and Medicine, AMR Clinical Reference Center. Surveillance for Infection Prevention and Healthcare Epidemiology (J-SIPHE) Annual Report 2021 [Internet]. Tokyo: National Center for Global Health and Medicine, c2022. [cited 2024 Apr 16]. Available from: https://j-siphe.ncgm.go.jp/files/JSIPHE_AnnualReport_2021en.pdf.
35. Ryu S. The new Korean action plan for containment of antimicrobial resistance. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 2017;8:70ŌĆō73.


36. Kim B, Kim YC, Kim HS, Park SY, Choi JY. Significance of the regular publication of statistics on national health indicators in academic journals and the prospects of Korea National Antimicrobial Use Analysis System (KONAS). Infect Chemother 2023;55:306ŌĆō307.




37. Kim Y, Chae J, Shin S, et al. Trends in national pharmaceutical expenditure in Korea during 2011 ŌĆō 2020. Infect Chemother 2023;55:237ŌĆō246.




38. Kim HS, Park SY, Choi H, et al. Development of a roadmap for the antimicrobial usage monitoring system for medical institutions in Korea: a Delphi study. Infect Chemother 2022;54:483ŌĆō492.




40. van den Bosch CM, Geerlings SE, Natsch S, Prins JM, Hulscher ME. Quality indicators to measure appropriate antibiotic use in hospitalized adults. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:281ŌĆō291.


41. Aviatin M, Sauriasari R, Yunir E, Risni HW. Evaluation of the use of antimicrobial therapy for treating diabetic foot infections in an Indonesia referral hospital: a retrospective cohort study. Infect Chemother 2023;55:80ŌĆō89.




42. Le Mar├®chal M, Tebano G, Monnier AA, et al. Quality indicators assessing antibiotic use in the outpatient setting: a systematic review followed by an international multidisciplinary consensus procedure. J Antimicrob Chemother 2018;73(suppl_6):vi40ŌĆōvi49.



43. Monnier AA, Schouten J, Le Mar├®chal M, et al. Quality indicators for responsible antibiotic use in the inpatient setting: a systematic review followed by an international multidisciplinary consensus procedure. J Antimicrob Chemother 2018;73(suppl_6):vi30ŌĆōvi39.



44. Schoffelen T, Schouten J, Hoogerwerf J, et al. Quality indicators for appropriate antimicrobial therapy in the emergency department: a pragmatic Delphi procedure. Clin Microbiol Infect 2021;27:210ŌĆō214.


45. Kim B, Lee MJ, Park SY, et al. Development of key quality indicators for appropriate antibiotic use in the Republic of Korea: results of a modified Delphi survey. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2021;10:48.




46. Magill SS, OŌĆÖLeary E, Ray SM, et al. Assessment of the appropriateness of antimicrobial use in US hospitals. JAMA Netw Open 2021;4:e212007.



47. National Centre for Antimicrobial Stewardship. National Antimicrobial Prescribing Survey [Internet] Melbourne: National Centre for Antimicrobial Stewardship, c2018. [cited 2023 Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.ncas-australia.org/ncas-publications.
48. Magill SS, Hellinger W, Cohen J, et al. Prevalence of healthcare-associated infections in acute care hospitals in Jacksonville, Florida. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2012;33:283ŌĆō291.



49. Fridkin S, Baggs J, Fagan R, et al. Vital signs: improving antibiotic use among hospitalized patients. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2014;63:194ŌĆō200.


50. Magill SS, Edwards JR, Beldavs ZG, et al. Prevalence of antimicrobial use in US acute care hospitals, May-September 2011. JAMA 2014;312:1438ŌĆō1446.



51. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals 2011ŌĆō2012 [Internet]. Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, c2013. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/point-prevalence-survey-healthcare-associated-infections-and-antimicrobial-use-0.
52. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals 2016ŌĆō2017 [Internet] Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, c2023. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/point-prevalence-survey-healthcare-associated-infections-and-antimicrobial-use-5.
53. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European long-term care facilities MayŌĆōSeptember 2010 [Internet]. Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, c2014. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/point-prevalence-survey-healthcare-associated-infections-and-antimicrobial-use-1.
54. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European long-term care facilities. AprilŌĆōMay 2013[Internet] Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, c2014. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/point-prevalence-survey-healthcare-associated-infections-and-antimicrobial-use-2.
55. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in European long-term care facilities 2016ŌĆō2017 [Internet] Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, c2023. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/point-prevalence-survey-healthcare-associated-infections-and-antimicrobial-use-2016-2017.
56. Royal Melbourne Hospital and the National Centre for Antimicrobial Stewardship. Antimicrobial prescribing practice in Australian hospitals. Results of the 2020 Hospital National Antimicrobial Prescribing Survey [Internet] Canberra: Department of Health and Aged Care, Australian Government, c2023. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.amr.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-09/antimicrobial-prescribing-practice-in-australian-hospitals-results-of-the-2020-hospital-national-antimicrobial-prescribing-survey.pdf.
57. Royal Melbourne Hospital and the National Centre for Antimicrobial Stewardship. Surgical prophylaxis prescribing in Australian hospitals. Results of the 2020 Hospital National Antimicrobial Prescribing Survey [Internet] Canberra: Department of Health and Aged Care, Australian Government, c2023. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.amr.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-09/surgical-prophylaxis-prescribing-in-australian-hospitals-results-of-the-2020-surgical-national-antimicrobial-prescribing-survey_0.pdf.
58. Royal Melbourne Hospital and the National Centre for Antimicrobial Stewardship. Antimicrobial prescribing practice in Australian residential aged care facilities. Results of the 2020 Hospital National Antimicrobial Prescribing Survey [Internet] Canberra: Department of Health and Aged Care, Australian Government, c2023. [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.amr.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-09/antimicrobial-prescribing-in-australian-residential-aged-care-facilities-results-of-the-2020-aged-care-national-antimicrobial-prescribing-survey.pdf.
59. Kim BN, Kim HB, Oh MD. Antibiotic control policies in South Korea, 2000ŌĆō2013. Infect Chemother 2016;48:151ŌĆō159.




60. Kim ES, Park SW, Lee CS, et al. Impact of a national hospital evaluation program using clinical performance indicators on the use of surgical antibiotic prophylaxis in Korea. Int J Infect Dis 2012;16:e187ŌĆōe192.


61. Park SY, Moon SM, Kim B, et al. Appropriateness of antibiotic prescriptions during hospitalization and ambulatory care: a multicentre prevalence survey in Korea. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 2022;29:253ŌĆō258.


62. Jung J, Moon SM, Kim DY, et al. Appropriateness of antibiotic use for patients with asymptomatic bacteriuria or urinary tract infection with positive urine culture: a retrospective observational multi-centre study in Korea. J Hosp Infect 2023;140:79ŌĆō86.


63. Kim YC, Park JY, Kim B, et al. Prescriptions patterns and appropriateness of usage of antibiotics in non-teaching community hospitals in South Korea: a multicentre retrospective study. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2022;11:40.




64. Kim SW, Park HJ, Oh WS, et al. Drug use evaluation of intravenous ciprofloxacin in university hospitals in Korea. Infect Chemother 2004;36:350ŌĆō356.
65. Nam EY, Kim HB, Bae H, et al. Appropriateness of surgical antibiotic prophylaxis in a tertiary hospital. Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control 2014;19:64ŌĆō70.

66. Lee MJ, Kim M, Kim NH, et al. Why is asymptomatic bacteriuria overtreated?: a tertiary care institutional survey of resident physicians. BMC Infect Dis 2015;15:289.




67. Kim HI, Kim SW, Chang HH, Lee JM, Peck KR. A 2011ŌĆō2012 survey of doctorsŌĆÖ perceptions of Korean guidelines and empirical treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. Infect Chemother 2013;45:394ŌĆō405.



68. Kim SW. Antimicrobial stewardship with intravenous to oral conversion and future directions of antimicrobial stewardship. Infect Chemother 2017;49:87ŌĆō89.




69. Park SM, Kim HS, Jeong YM, et al. Impact of intervention by an antimicrobial stewardship team on conversion from intravenous to oral fluoroquinolones. Infect Chemother 2017;49:31ŌĆō37.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



