 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 39(3); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
A poor prognostic factor for CrohnŌĆÖs disease (CD) includes perianal fistulizing disease, including perianal fistula and/or perianal abscess. Currently, a tool to assess perianal symptoms in patients with CD remains nonexistent. This study aimed to develop a perianal fistulizing disease self-screening questionnaire for patients with CD.
Methods
This prospective pilot study was conducted at three tertiary referral centers between January 2019 and May 2020. We formulated questions on perianal symptoms, including tenesmus, anal discharge, bleeding, pain, and heat. A 4-point Likert scale was used to rate each question. Patients with CD completed a questionnaire and underwent pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Results
Overall, 93 patients were enrolled, with 51 (54.8%) diagnosed with perianal fistulizing disease, as determined by pelvic MRI. The Spearman correlation findings demonstrated that anal pain (p = 0.450, p < 0.001) and anal discharge (p = 0.556, p < 0.001) were the symptoms that most significantly correlated with perianal disease. For anal pain and discharge, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of the scores was significantly higher than that of the combined score for all five symptoms (0.855 vs. 0.794, DeLongŌĆÖs test p = 0.04). For the two symptoms combined, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive and negative predictive values were 88.2, 73.8, 80.4, and 83.8%, respectively, with 81.7% accuracy for detecting perianal fistulizing disease.
CrohnŌĆÖs disease (CD) is described as a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract with a relapsing and remitting clinical course. A peculiar CD phenotype is perianal fistulizing Chron's disease (pCD), such as perianal fistula and abscess. A recent nationwide cohort study reported that approximately 15ŌĆō30% of CD patients develop pCD [1]. At least two-thirds of patients with CD undergo fistulotomy or percutaneous drainage procedures at some point in their lives [2]. In the incidence of perianal involvement, racial differences exist, in which it is higher among Asian (23%) and Black (31%) patients with CD than in Caucasians (14%) [3].
Furthermore, pCD is well known as a poor prognostic factor for CD. It is associated with increased symptom severity and the need for immunosuppressive treatment, hospitalization, and bowel resection, ultimately leading to an impaired quality of life [4,5]. Thus, early detection of pCD and robust disease activity monitoring are important in managing pCD in patients with CD.
Early detection of pCD enables the early use of appropriate antibiotics, thiopurines, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-╬▒ inhibitors, which possess strong evidence supporting their use in pCD treatment [6,7], and/or surgical drainage with seton insertion depending on whether the perianal fistula type is simple or complex [8,9]. Serious complications can be prevented through a timely and multidisciplinary approach such as anal stricture or total proctectomy with ileostomy [10,11].
Hence, it is vital for patients with CD to identify their pCD symptoms. However, no self-screening tool is available for pCD management. We aimed to develop a self-screening questionnaire that can promptly detect perianal fistula or abscess in patients with CD.
This pilot study, with a prospective cross-sectional design, was conducted at three tertiary referral centers between January 2019 and May 2020. Consecutive adult and pediatric patients diagnosed with CD were enrolled. The diagnosis of CD was based on symptoms, laboratory tests, endoscopic and radiological findings, and pathologic features [12,13]. The Montreal Classification of CD, based on disease location (L1 ileal, L2 colonic, and L3 ileocolonic) and behavior (B1 nonstricturing non-penetrating, B2 stricturing, B3 penetrating), was employed [14]. At enrollment, disease activity was assessed using the HarveyŌĆōBradshaw index (HBI) [15], and laboratory tests including C-reactive protein (CRP) and white blood cell (WBC) count were performed. Patients completed a questionnaire for their perianal symptoms and underwent pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) within 2 weeks of the survey as the gold standard for determining the presence of a perianal fistula and/or abscess [16]. Informed consent was obtained from the patients and guardians. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of each participating hospital (Kyungpook National University Hospital, protocol code KNUH 2016-11-008) and conducted in compliance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Five gastroenterologists (E.S.K., B.K., K.O.K., H.S.L., and B.I.J.) with greater than 10 years of experience in managing patients with CD devised questions regarding perianal symptoms after a literature review. Anal pain and discharge, rectal bleeding, swelling, and incontinence were confirmed as the major pCD symptoms [17,18]. They discussed and rated each symptom several times via E-mail to modify and select the final symptoms. Swelling was excluded as a variable as anal swelling or induration is more accurately evaluated by surgeons and not the patient. Incontinence was excluded because it tends to occur late or is related to surgically induced damage to the anal sphincter. Instead, tenesmus and ŌĆ£anal heatŌĆØ sensation, which are more easily assessed by patients, were included. The five selected questions were on anal discharge, anal bleeding, anal pain, tenesmus, and anal heat (Fig. 1). For the questionnaire, each question was rated on a 4-point (0 to 3) Likert scale.
Categorical variables are expressed as numbers and proportions, and to compare clinical characteristics between the groups, FisherŌĆÖs exact test was used. Continuous variables are presented as mean ┬▒ standard deviation (SD) or median with interquartile range and were compared using studentŌĆÖs t-test or MannŌĆōWhitney U test. The Spearman correlation coefficient was used to evaluate the correlation between perianal lesions and questionnaire items, CRP level, WBC count, and HBI. The optimal cutoff values of independent variables for differentiation between the total score and the presence of perianal disease were selected using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Diagnostic accuracy was evaluated using the area under the curve (AUC), and AUCs between groups were compared using DeLongŌĆÖs test. We analyzed the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy for predicting pCD. Statistical significance was set at a p value < 0.05. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS software (version 19.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Overall, 93 patients aged 9 to 64 years (mean age ┬▒ SD: 21.8 ┬▒ 8.5 years) were enrolled in this study. Table 1 demonstrates the baseline characteristics of the patients, in which the patients were divided by the presence of pCD according to findings on pelvic MRI. Most baseline variables were not significantly different between the two groups. The perianal lesion group had a relatively higher proportion of ileocolic locations than the group without perianal lesions (80.4% vs. 59.5%, p = 0.084), although with no statistical significance.
In the groups with and without pCD, the median HBI was 6 vs. 3 (p = 0.014), respectively, and the CRP level was 1.41 vs. 0.32 (p = 0.008). No significant difference was found between the groups in the WBC count. Regarding perianal symptoms, the pCD group revealed a significantly higher median score of anal discharge (1 vs. 0, p < 0.001) and pain (1 vs. 0, p < 0.001) than patients without pCD. No significant difference was found between the groups in the scores for bleeding, tenesmus, and anal heat (Table 2). The Spearman correlation coefficient (p) of anal discharge and anal pain were the highest at 0.556 (p < 0.001) and 0.45 (p < 0.001), respectively, suggesting a moderate level of correlation of anal discharge and pain symptoms with pCD. HBI (0.255, p = 0.014) and CRP (0.276, p = 0.007) were weakly correlated (Table 3) [19]. WBC count, bleeding, tenesmus, and anal heat exhibited no correlation with pCD.
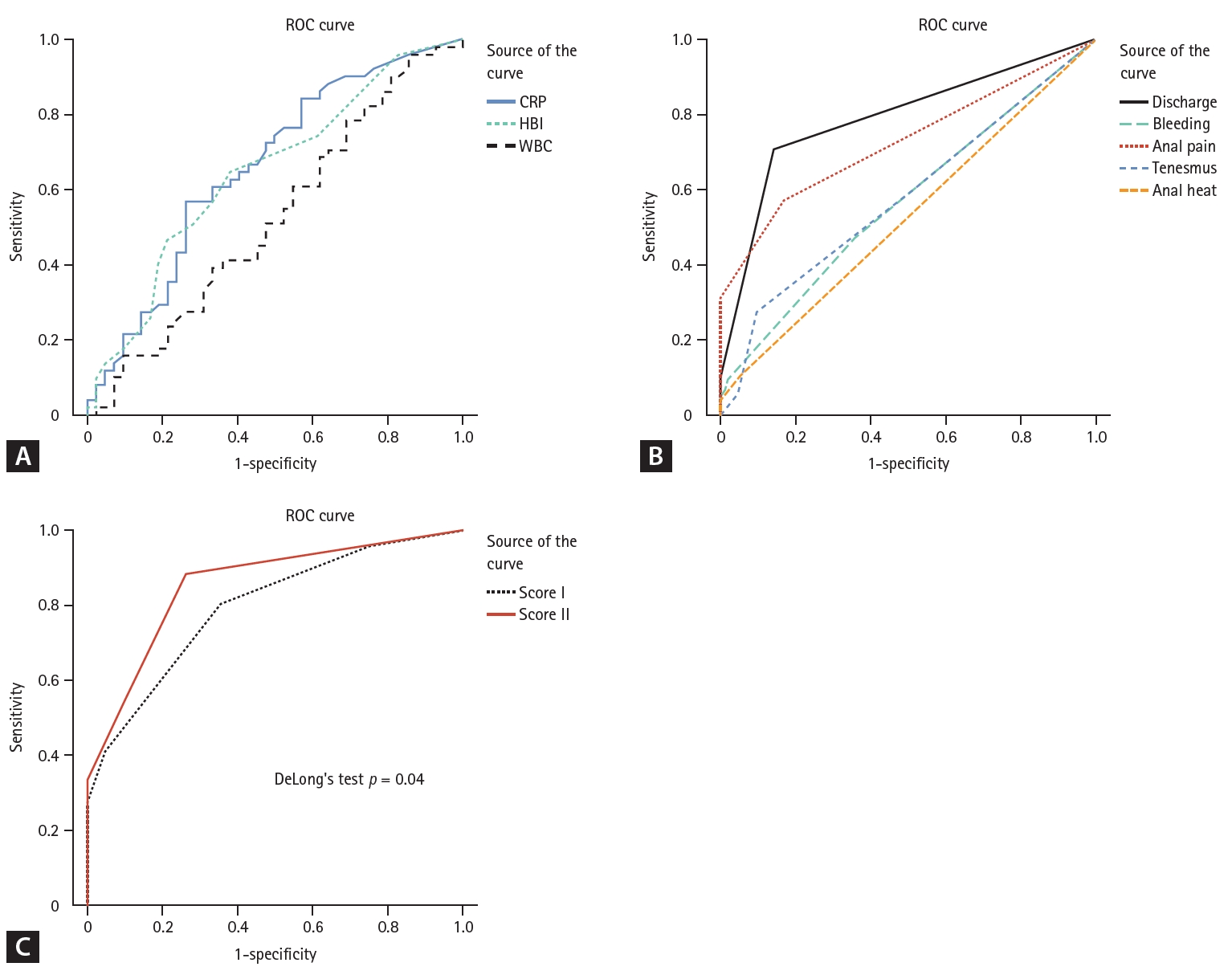
The AUCs of HBI, CRP, and WBC count were 0.647 (p = 0.015), 0.660 (p = 0.008), and 0.525 (p = 0.685), respectively (Table 4, Fig. 2A). The AUCs of anal discharge and anal pain were 0.788 (p < 0.001) and 0.727 (p < 0.001), respectively. This was higher than those of anal bleeding (0.569, p = 0.253), heat (0.526, p = 0.666), and tenesmus (0.581, p = 0.180) (Fig. 2B). Next, we calculated the composite scores for predicting pCD in patients with CD. Score I was the sum of all five questionnaire item scores, and Score II was the sum of anal discharge and pain scores. The AUC of Score II was significantly higher than that of Score I (0.855, p < 0.001 vs. 0.794, p < 0.001, DeLongŌĆÖs test p = 0.04, Table 4, Fig. 2C).
The performance of the composite questionnaire scores, Score I and Score II, for predicting pCD is illustrated in Table 5. According to the ROC curve, score 1 (among 0ŌĆō3) was found to be the optimal cutoff value for the highest accuracy. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV were 96.1, 23.8, 60.5, and 83.3%, respectively, for Score I and 88.2, 73.8, 80.4, and 83.8%, respectively, for Score II. Score II was more accurate than Score I (accuracy 81.7% vs. 63.4%, respectively, Table 5).
We developed a self-screening tool for pCD in patients with CD. The questionnaire constituted five simple questions regarding anal discharge, anal pain, bleeding, tenesmus, and anal heat. In a cross-sectional study, we found that anal discharge and pain had a moderate correlation with pCD, whereas other symptoms were not significantly correlated. The composite score of anal discharge and pain detected perianal disease with 81.7% accuracy.
One of the unmet needs in pCD management is the lack of a clinical index that can be easily utilized by patients. Given that pCD is more common in pediatric patients [20], a simple, child-friendly tool is warranted. In 1992, an anal disease activity index was developed for use in the outpatient clinic or at the patientŌĆÖs bedside [21]. It evaluated seven symptoms or activities, including perianal pain, itching, pain during defecation, anal leakage, inhibition of locomotion, and social and sexual activity. Only pain-related symptoms such as perianal pain, pain after defecation, and inhibition of locomotion by pain demonstrated a high discriminative value as an index of response to therapy. However, this index was not developed to detect perianal fistulas. Furthermore, the sexual activity variable was not suitable for children. Other activity indices, such as the perianal disease activity index [22], fistula drainage assessment [6], and PikarskyŌĆÖs perianal activity index [23], assess disease severity and response to therapy and help predict outcomes. However, they are complex and have variables that need to be measured by the doctor and are not useful as a self-screening tool for pCD.
The first manifestation of CD in approximately 10% of patients is perianal fistula and/or abscess. It can occur several years prior to luminal CD onset [24]. Perianal disease activity does not always parallel luminal activity and may be present when the luminal disease is inactive in a subset of patients [25]. Hence, traditional clinical indices for evaluating luminal CD activity may not be appropriate for pCD activity. In this study, Spearman correlation and ROC analysis revealed that pCD was mostly associated with anal pain and discharge rather than with HBI, CRP, and WBC (Table 3, 4). Therefore, anal pain and discharge are more accurate variables for predicting the presence of perianal complications than indicators of luminal CD activity and biomarkers of systemic inflammation. We included CRP (cutoff 1.33 mg/dL) and HBI (cutoff score 4) in the Score model (anal pain, anal discharge, HBI, and CRP). The AUC of this model was 0.849 (0.774ŌĆō0.924, p < 0.001, sensitivity 82.4%, specificity 73.8%, positive predictive value 79.2%, negative predictive value 77.5%), which was not greater than the AUC of Score II (anal pain and anal discharge).
Early detection of anorectal disease is pivotal for the decision making in CD management. pCD assessment using an easily administered screening tool in routine clinical practice may help detect patients who require pelvic MRI or anal ultrasonography and promote timely management of pCD. In patients with complex pCD, this approach with a screening tool may allow the prompt use of advanced therapies, such as mesenchymal stem cell local therapy [26,27] or TNF-╬▒ inhibitors, which can be effective in reducing the need for surgical treatment or in minimizing postoperative complications [6,28]. In the present study, the questionnaire can help detect pCD early and easily in outpatients, rendering it as an effective anorectal disease screening tool in CD. Moreover, 25 of the 93 study patients were under 18 years of age, an age at which early disease detection is important. We conducted a subgroup analysis in the adult vs. childrenŌĆÖs group according to age. The AUC (95% confidence interval) of Score II in the children group (0.792, 0.599ŌĆō0.984, p = 0.132) appeared to be lower than the AUC in the adult group (0.851, 0.768ŌĆō0.934, p = 0.009). However, caution must be exercised in interpreting data as the small sample size in the children group might have affected the performance of the Score II model.
One might argue that the perianal fistula in CD should be evaluated by colorectal surgeons. However, gastroenterologists can initially assess the status of patients and refer them to surgeons with suspicion of perianal symptoms. Thus, gastroenterologists and even patients themselves need to understand the typical symptoms of perianal disease in CD patients to be timely sent to and further evaluated by surgeons. There has been no study to estimate perianal symptoms from the patientsŌĆÖ or gastroenterologistsŌĆÖ perspectives. We believe that the study results might aid gastroenterologists screen the appropriate patients for further evaluation of pCD by surgeons or MRI.
This study has limitations. This study was designed as a pilot study, and the sample size was small. However, statistically significant differences were observed among variables in detecting pCD. Furthermore, because this was a cross-sectional study, the study results were not validated in an independent cohort, and the effectiveness of this tool for measuring response to therapy remains unclear. We acknowledge that anal pain and discharge are among the already known symptoms of pCD. However, there is paucity of research on the extent to which these symptoms are associated with concurrent perianal disorders. In a future longitudinal study, assessment of the prognosis of screened patients with perianal complications who are promptly referred to colorectal surgeons is warranted to validate the efficacy of the screening tool.
In conclusion, this study identified anal discharge and pain as the most effective predictive factors for pCD among various anal symptoms. The self-screening questionnaire on anal discharge and pain is an effective and a valuable tool for detecting pCD in children and adults with CD. This screening toolŌĆÖs performance should be confirmed in an independent cohort, and its efficacy for monitoring patients with pCD should be evaluated in further longitudinal studies.
1. Simple questions regarding anal pain and discharge can help accurately identify the presence of perianal fistulizing disease in patients with CD.
2. A simple questionnaire regarding anal pain and discharge, which can be easily filled in by patients at outpatient clinics, can be used as an effective screening tool for detecting perianal fistula or abscess in children and adult patients with CD.
Notes
CRedit authorship contributions
O Seong Kweon: methodology, resources, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, software, writing - original draft, writing - review & editing; Ben Kang: resources, data curation; Yoo Jin Lee: resources, data curation; Eun Soo Kim: conceptualization, methodology, resources, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, validation, writing - review & editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition; Sung Kook Kim: resources, data curation; Hyun Seok Lee: resources, data curation; Yun Jin Chung: resources, data curation; Kyeong Ok Kim: resources, data curation; Byung Ik Jang: resources, data curation
Figure┬Ā1.
Self-screening questionnaire for perianal disease. A 4-point Likert scale was used to rate each symptom, with 0 indicating no symptoms and 3 reflecting severe symptoms.
Figure┬Ā2.
ROC curve analysis of the clinical and laboratory results. (A) CRP level, HBI value, and WBC count, (B) the five questionnaire symptoms, and (C) the composite scores. Score I is the sum of the five questionnaire item scores. Score II is the sum of the anal discharge and anal pain scores. ROC, receiver operating characteristic; CRP, C-reactive protein; HBI, HarveyŌĆōBradshaw index; WBC, white blood cell.
Table┬Ā1.
Baseline characteristics of patients
Table┬Ā2.
Comparison of clinical factors and scores of each symptom between patients with or without perianal fistula
Table┬Ā3.
Correlation of clinical factors and each symptom with pCD
| HBI | CRP | WBC | Discharge | Bleeding | Anal pain | Tenesmus | Anal heat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient | 0.255 | 0.276 | 0.042 | 0.556 | 0.137 | 0.450 | 0.151 | 0.099 |
| p value | 0.014 | 0.007 | 0.688 | < 0.001 | 0.191 | < 0.001 | 0.15 | 0.347 |
Table┬Ā4.
The area under the curve of clinical factors and symptoms
REFERENCES
1. Wewer MD, Zhao M, Nordholm-Carstensen A, Weimers P, Seidelin JB, Burisch J. The incidence and disease course of perianal CrohnŌĆÖs disease: a Danish nationwide cohort study, 1997-2015. J Crohns Colitis 2021;15:5ŌĆō13.



2. Gajendran M, Loganathan P, Catinella AP, Hashash JG. A comprehensive review and update on CrohnŌĆÖs disease. Dis Mon 2018;64:20ŌĆō57.


3. Shi HY, Levy AN, Trivedi HD, Chan FKL, Ng SC, Ananthakrishnan AN. Ethnicity influences phenotype and outcomes in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;16:190ŌĆō197.e11.



4. Kaur M, Dalal RL, Shaffer S, Schwartz DA, Rubin DT. Inpatient management of inflammatory bowel disease-related complications. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;18:1346ŌĆō1355.


5. Adegbola SO, Dibley L, Sahnan K, et al. Burden of disease and adaptation to life in patients with CrohnŌĆÖs perianal fistula: a qualitative exploration. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2020;18:370.




6. Present DH, Rutgeerts P, Targan S, et al. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with CrohnŌĆÖs disease. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1398ŌĆō1405.


7. Lichtiger S, Binion DG, Wolf DC, et al. The CHOICE trial: adalimumab demonstrates safety, fistula healing, improved quality of life and increased work productivity in patients with CrohnŌĆÖs disease who failed prior infliximab therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010;32:1228ŌĆō1239.


8. Pan├®s J, Rimola J. Perianal fistulizing CrohnŌĆÖs disease: pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;14:652ŌĆō664.



9. Meima-van Praag EM, van Rijn KL, et al. Short-term anti-TNF therapy with surgical closure versus anti-TNF therapy in the treatment of perianal fistulas in CrohnŌĆÖs disease (PISA-II): a patient preference randomised trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;7:617ŌĆō626.


10. Badla O, Goit R, Saddik SE, et al. The multidisciplinary management of perianal fistulas in CrohnŌĆÖs disease: a systematic review. Cureus 2022;14:e29347.



11. Laland M, Fran├¦ois M, DŌĆÖAmico F, et al. Identification of the optimal medical and surgical management for patients with perianal fistulising CrohnŌĆÖs disease. Colorectal Dis 2023;25:75ŌĆō82.



12. Ye BD, Jang BI, Jeen YT, Lee KM, Kim JS, Yang SK, IBD Study Group of the Korean Association of the Study of Intestinal Diseases. [Diagnostic guideline of CrohnŌĆÖs disease]. Korean J Gastroenterol 2009;53:161ŌĆō176Korean.

13. Koh SJ, Hong SN, Park SK, et al.; IBD Research Group of the Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases. Korean clinical practice guidelines on biologics for moderate to severe CrohnŌĆÖs disease. Intest Res 2023;21:43ŌĆō60.




14. Satsangi J, Silverberg MS, Vermeire S, Colombel JF. The Montreal classification of inflammatory bowel disease: controversies, consensus, and implications. Gut 2006;55:749ŌĆō753.



16. Panes J, Bouhnik Y, Reinisch W, et al. Imaging techniques for assessment of inflammatory bowel disease: joint ECCO and ESGAR evidence-based consensus guidelines. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:556ŌĆō585.


17. Steinhart AH, Panaccione R, Targownik L, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the medical management of perianal fistulizing CrohnŌĆÖs disease: the Toronto consensus. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2019;25:1ŌĆō13.


18. Juncadella AC, Alame AM, Sands LR, Deshpande AR. Perianal CrohnŌĆÖs disease: a review. Postgrad Med 2015;127:266ŌĆō272.


19. Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA. Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth Analg 2018;126:1763ŌĆō1768.


20. Atia O, Focht G, Lujan R, et al. Perianal Crohn disease is more common in children and is associated with complicated disease course despite higher utilization of biologics: a population-based study from the epidemiology group of the Israeli IBD Research Nucleus (epiIIRN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2022;74:788ŌĆō793.


21. Allan A, Linares L, Spooner HA, Alexander-Williams J. Clinical index to quantitate symptoms of perianal CrohnŌĆÖs disease. Dis Colon Rectum 1992;35:656ŌĆō661.


22. Irvine EJ. Usual therapy improves perianal CrohnŌĆÖs disease as measured by a new disease activity index. McMaster IBD Study Group. J Clin Gastroenterol 1995;20:27ŌĆō32.

23. Pikarsky AJ, Gervaz P, Wexner SD. Perianal Crohn disease: a new scoring system to evaluate and predict outcome of surgical intervention. Arch Surg 2002;137:774ŌĆō777discussion 778.

24. Schwartz DA, Loftus EV Jr, Tremaine WJ, et al. The natural history of fistulizing CrohnŌĆÖs disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology 2002;122:875ŌĆō880.


25. Gecse KB, Sebastian S, Hertogh Gd, et al. Results of the fifth scientific workshop of the ECCO [II]: clinical aspects of perianal fistulising CrohnŌĆÖs disease-the unmet needs. J Crohns Colitis 2016;10:758ŌĆō765.


26. Garc├Ła-Olmo D, Garc├Ła-Arranz M, Herreros D, Pascual I, Peiro C, Rodr├Łguez-Montes JA. A phase I clinical trial of the treatment of CrohnŌĆÖs fistula by adipose mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Dis Colon Rectum 2005;48:1416ŌĆō1423.


-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 681 View
- 263 Download
- Related articles
-
Endoscopic unusual appearance of stomach in a patient with CrohnŌĆÖs disease2023 March;38(2)
Vaccination strategies for Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease2022 September;37(5)
Nutritional management in patients with chronic kidney disease2020 November;35(6)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print


