 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 39(3); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
The SAMe-TT2R2 score is used for assessing anticoagulation control (AC) quality with warfarin. However, it is hard to apply SAMe-TT2R2 score in Asian patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), because it has not been proven in those populations. This study aimed to validate the SAMe-TT2R2 score in Asian patients with AF and suggest a modified SAMe-TT2R2 score for this population.
Methods
We analyzed 710 Korean patients with AF who were using warfarin. The AC quality was assessed as the mean time in therapeutic range (TTR). Each component of SAMe-TT2R2 score was evaluated for the relationship with AC. Further clinical factors that predict AC were analyzed. Identified factors were re-assorted and constructed as SA2Me-TTR scoring system.
Results
Of the components of the SAMe-TT2R2 score, female, age, and rhythm control were associated with AC. Heart failure and renal insufficiency were newly identified factors associated with AC. The modified SA2Me-TTR score was reconstructed with the relevant risk factors (S, female gender, 1 point; A, age < 60 yr, 2 points; Me, medical history of heart failure, 1 point; T, treatment for rhythm control, 1 point; T, history of stroke or transient ischemic attack, 1 point; R, renal insufficiency, 1 point). The modified SA2Me-TTR score demonstrated an excellent relationship with the grading of AC. The modified SA2Me-TTR score Ōēż 1 identified patients with good AC (hazard ratio 2.46, 95% CI 1.75ŌĆō3.47).
Despite of emergence of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs), warfarin is still used for many patients [1]. Warfarin is inexpensive and is a very potent anticoagulant. However, it has critical limitations including the need to monitor individualized titration, such as the target prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) of 2.0ŌĆō3.0 [2ŌĆō5]. Warfarin interacts with numerous other drugs and food, making it difficult to maintain the therapeutic range of PT INR in certain patients. The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) recommends the ŌĆ£time in therapeutic range (TTR)ŌĆØ should be kept as high as possible in the patients who are treated with warfarin, and the crude value of the target TTR is at least 70%. Current guidelines suggest that switching warfarin to a NOAC and maintaining an adequate TTR cannot be sustained [2ŌĆō5]. Therefore, the quality of anticoagulation control (AC) prediction model with TTR is needed, and the SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system (Sex, female; Age, < 60 yr; Medical history, more than two comorbidities; Treatment, interacting drug, e.g., Amiodarone; Tobacco use (doubled); and Race (doubled) is available for this purpose [6ŌĆō17]. The patients with SAMe-TT2R2 score more than 1 point are less likely to achieve a good TTR and alternative strategies may be required [8].
The SAMe-TT2R2 score is hard to apply to Asian patients because it has not been proven in the Asian population, and the Asian race is already a risk factor (ŌĆ£RŌĆØ, race). If the SAMe-TT2R2 scoring is applied to Asian patients, they would already have at least 2 points by default, leading to NOAC being recommended rather than warfarin. The pharmacodynamics of warfarin in the Asian population differ substantially from CaucasiansŌĆÖ [18,19]. The necessity of a tailored guideline for Asians with atrial fibrillation (AF) has come to the fore. Therefore, a modified scoring system is required which is adaptable to Asian patients who are on warfarin.
We aimed to validate the SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system in Asian patients with non-valvular AF (NVAF) and to evaluate the relationship of each component of the SAMe-TT2R2 score with good INR control. We also aimed to suggest and validate a modified scoring system for the Asian population for anticoagulation therapy decision-making (warfarin or NOAC). Our objective is to contribute a guideline for anticoagulant selection for Asian patients with AF.
This cross-sectional analysis included 2,971 Asian patients with AF who are using oral anticoagulants from the Department of Cardiology and Neurology, a Chonnam National University Hospital (Gwangju, Korea), between January 2016 and December 2018. The inclusion criteria were patients with NVAF, Ōēź 18 years, CHA2DS2-VASc score Ōēź 1, and on warfarin. The exclusion criteria were patients with valvular heart disease (> moderate severity mitral stenosis), the presence of an artificial valve, and previous changes to the class of oral anticoagulants prescribed (e.g., from warfarin to NOAC, and vice versa). In total, 732 patients (66% male; mean age, 69 yr) who had taken warfarin for up to 2 years (median time 596 d) and whose INR were measured serially were included in the study. The patients with insufficient medical records were also excluded. Finally, the analysis included 710 Korean patients with NVAF and on warfarin. The study was approved by the ethics committee at Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, South Korea (CNUH-2018-109). As the study was retrospective in nature, informed consent was waived.
The quality of AC was assessed by TTR using the Rosendaal method, which uses linear interpolation to assign an INR value to each day between two successive observed INR values [20]. The target range of INR was 2.0ŌĆō3.0. A TTR of 60% or more was defined as good AC during a 2-year follow-up. Each component of the SAMe-TT2R2 score, except race, was used to re-evaluate AC, because all of the patients were Koreans.
We used the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) as an indicator of renal function. The CKD-EPI creatinine formula (141 ├Ś min(SCr/╬║, 1)╬▒ ├Ś max(SCr/╬║, 1)ŌłÆ1.209 ├Ś 0.993Age ├Ś 1.018 [if female] ├Ś 1.159 [if Black]) was used for calculating eGFR. An eGFR of < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 was defined as renal insufficiency.
Cardiac systolic function was reflected by left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) which was calculated from the apical 2- and 4-chamber images using the bi-plane SimpsonŌĆÖs rule in two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiogram. In this study, heart failure was defined as an LVEF reduction of < 40%.
ŌĆ£More than 2 morbiditiesŌĆØ was defined as more than two of the following in the original SAMe-TT2R2 score: hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease/myocardial infarction, peripheral arterial disease, congestive heart failure, previous stroke, pulmonary disease, and hepatic or renal disease. To re-evaluate other clinical factors relevant to Asians, all of the factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, heart failure, renal insufficiency, and specific medications including antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), were analyzed for the prediction of good AC during warfarin therapy. AAD including class I (e.g., propafenone, flecainide), and class III (e.g., amiodarone, dronedarone, sotalol) AAD were included.
Continuous variables were presented as means, standard deviations, and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of the means, while discrete variables were expressed as frequencies and percentages and the differences between groups were analyzed using a chi-square test or FisherŌĆÖs exact test between groups as appropriate. All potentially relevant variables including age, sex, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, previous history of angina, myocardial infarction or documented coronary artery disease, smoking, renal dysfunction, heart failure, and concomitant drugs, were analyzed using univariate analysis. Univariate analyses were used to correlate between mean TTR and the presence of clinical factors. The ratio of factor-present patients with good or poor AC group was considered. Statistical significance was defined as values of p < 0.05, but the clinical relevance between a single factor and good AC was defined as p < 0.20.
Covariates associated with TTR at a p value of < 0.20 in the univariate analyses were incorporated into a multivariate stepwise linear regression model. Based on the regression coefficients, we gave weight to each extracted factor and collated them into a modified predictive scoring system. The risk score was calculated as the sum of the points of the following: S (Sex, female gender, 1 point), A (Age, < 60 yr, 2 points), Me (Medical history of heart failure, 1 point), T (Treatment for rhythm control, any AAD, 1 point), T (sTroke, history of stroke or TIA, 1 point), and R (Renal insufficiency, eGFR < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2, 1 point). The predictive accuracy of the scoring system was then assessed using the area under the receiver operator characteristics (c statistics). Analysis was performed with SPSS, version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
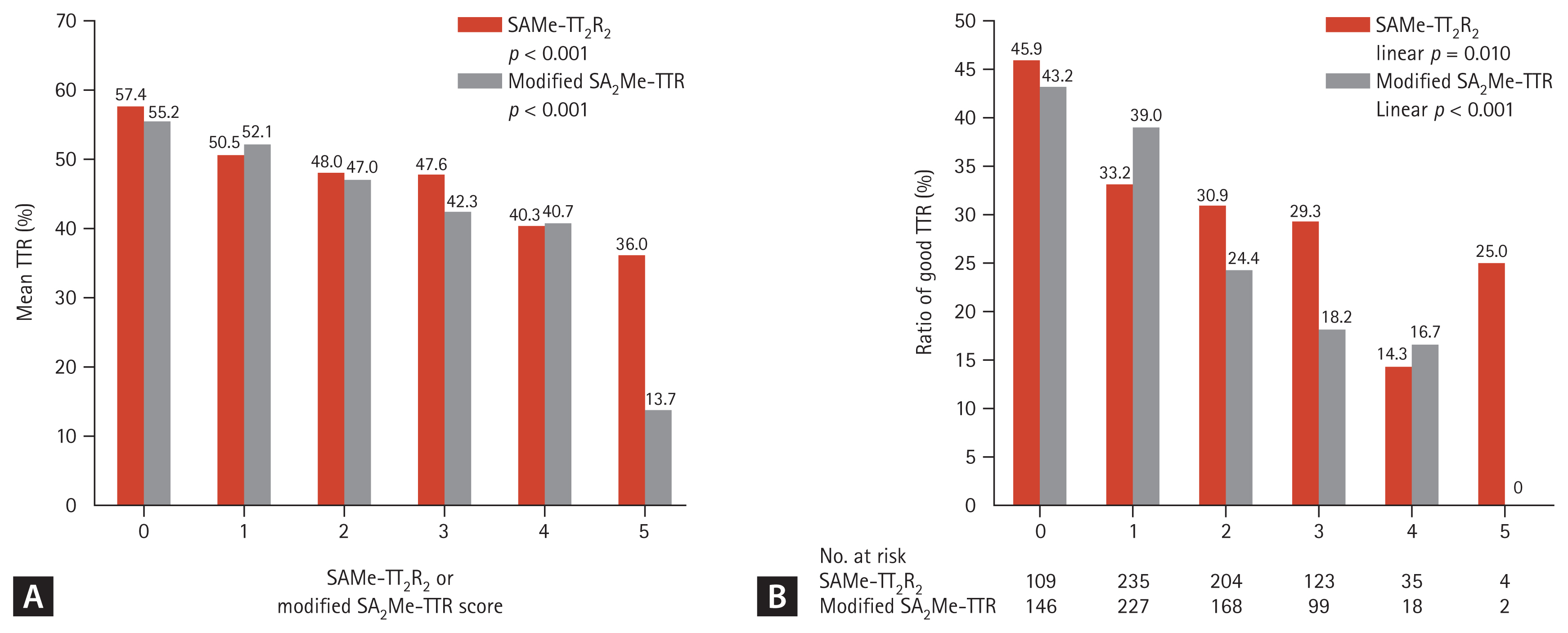
Univariate analysis was performed for each component of the SAMe-TT2R2 score, except R2. The mean TTR (according to the factors present) was significantly different for female gender (48.2% vs. 50.6%, p = 0.182), age < 60 years (39.7% vs. 51.9%, p < 0.001), and the use of AAD (45.8% vs. 51.2%, p = 0.004). In contrast, ŌĆ£two or more comorbiditiesŌĆØ and ŌĆ£tobacco useŌĆØ were not significantly different (Table 1). The SAMe-TT2R2 score demonstrated a linear association with mean TTR (Fig. 1A, p < 0.001)
We divided the patients into two groups (TTR Ōēź 60% [Good AC] and < 60% [Poor AC]) and analyzed the ratio of factor-present patients for each component of SAMe-TT2R2 score, except R2. The results for mean TTR according to the presence of the factor were statistically significant. Female gender (28.8% vs. 36.9%, p = 0.032), age < 60 years (9.4% vs. 21.4%, p < 0.001), and the use of AAD (20.2% vs. 30.0%, p = 0.006) and the ratio of factor-present patients were statistically significant. In contrast, ŌĆ£two or more comorbiditiesŌĆØ and ŌĆ£tobacco useŌĆØ were not significant (Table 1). The SAMe-TT2R2 score was significantly associated with the ratio of patients with good AC but it failed to show a linear association because the ratio of good AC in patients with 4 points was lower than that of patients with 5 points (Fig. 1B, p = 0.010).
First, the mean TTR was analyzed according to the presence of each factor (Table 2). The mean TTR did not significantly differ for factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, smoking, angina history, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, and comorbidities (Ōēź 1, Ōēź 2). A lower mean TTR was significantly associated with female gender (48.2% vs. 50.6%, p = 0.182), < 60 years (39.7% vs. 51.9%, p < 0.001), renal insufficiency (51.7% vs. 56.0%, p = 0.153), heart failure (50.8% vs. 56.2%, p = 0.062), and stroke or TIA history (48.8% vs. 51.7%, p = 0.130). Comparing the mean TTR according to the use of cardiovascular drugs demonstrated that aspirin, clopidogrel, statin, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI), angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), calcium channel blocker (CCB), digoxin, and beta-blocker (BB) did not associated significantly with the mean TTR. In analyzing the AAD, amiodarone (44.6% vs. 50.3%, p = 0.048), flecainide (43.8% vs. 50.2%, p = 0.043), class III AAD (46.0% vs. 50.4%, p = 0.062), and any other AAD (45.8% vs. 51.2%, p = 0.004) showed a significant difference in the mean TTR.
The factors were analyzed according to the ratio of patients in the good AC and poor AC groups (Table 2). Factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, smoking, history of angina, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, and comorbidities (Ōēź 1, Ōēź 2) had no association with good AC. Female gender (28.8% vs. 36.9%, p = 0.032), < 60 years (9.4% vs. 21.4%, p < 0.001), renal insufficiency (5.6% vs. 9.9%, p = 0.045), EF < 40% (6.5% vs. 11.0%, p = 0.045), stroke or TIA history (27.0% vs. 32.1%, p = 0.169) were lower in the good AC group than in the poor AC group. We also compared the ratio of cardiovascular drugs used between the good AC and poor AC groups. Aspirin, clopidogrel, statin, ACEI, ARB, CCB, digoxin, and BB were not statistically significant. Patients with good AC used fewer AAD including amiodarone (7.3% vs. 10.5%, p = 0.173), sotalol (2.6% vs. 5.2%, p = 0.103), flecainide (4.7% vs. 8.4%, p = 0.076), class III AAD (10.7% vs. 16.4%, p = 0.046), and any AAD (20.2% vs. 30.0%, p = 0.006) than the poor AC group.
In linear regression analysis, sex, age, medical history (heart failure), treatment, stroke, renal insufficiency (GFR < 50 mL/min.1.73 m2) were significantly associated with a lower ratio of good AC (Table 3). Considering factors for satisfying both mean TTR and the ratio of good TTR control, sex, age, medical history (heart failure), treatment, stroke, and renal insufficiency were risk factors for poor AC. Furthermore, among the original factors included in the SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system, medical history as ŌĆ£more than 2 comorbiditiesŌĆØ; this and tobacco use were not associated with good AC. In contrast, heart failure, stroke, and renal insufficiency were associated with good AC. Therefore, the risk factors included in the SAMe-TT2R2 score were modified. The original components: medical history (Me), tobacco (T), and race (R), were substituted with medical history of heart failure (Me), stroke (T), and renal insufficiency (R). The modified SA2Me-TTR included the relevant risk factors for the Asian population including S, female gender (1 point); A, age < 60 years (2 points); Me, medical history of heart failure (1 point); T, treatment for rhythm control (1 point); T, stroke or TIA history (1 point); R, renal insufficiency (1 point) (Table 4).
For the original SAMe-TT2R2 score, race (R) was designated as 0. According to the original SAMe-TT2R2 system score, the mean TTR decreased in a stepwise manner (57.4% vs. 50.5% vs. 48.0% vs. 47.6% vs. 40.3% vs. 36.0%, linear p < 0.001). However, the original SAMe-TT2R2 score did not demonstrate a linear relationship for the ratio of good AC, with a sudden incremental increase at score 5. According to the modified SA2Me-TTR system score, the mean TTR decreased in a stepwise manner (55.2% vs. 52.1% vs. 47.0% vs. 42.3% vs. 40.7% vs. 13.7%, linear p < 0.001). Additionally, the modified SA2Me-TTR scoring system demonstrated an excellent linear relationship with the ratio of patients with good AC (43.2% vs. 39.0% vs. 24.4% vs. 18.2% vs. 16.7% vs. 0.0%, linear p < 0.001) (Fig. 1B).
The prediction of good AC (score Ōēż 1) was validated for the original SAMe-TT2R2 and the modified SA2Me-TTR scoring systems (Table 5). For the mean TTR, both the original SAMe-TT2R2 (52.7 ┬▒ 21.7% vs. 47.0 ┬▒ 22.1%, p = 0.001) and the modified SA2Me-TTR (53.1 ┬▒ 22.1% vs. 44.8 ┬▒ 21.0%, p < 0.001) scores showed significant discrimination power. For the ratio of good AC, both the original SAMe-TT2R2 (54.9% vs. 45.1%, odds ratio [OR] 1.47, 95% CI 1.08ŌĆō2.02, p = 0.016) and the modified SA2Me-TTR (73.4% vs. 26.6%, OR 2.46, 95% CI 1.75ŌĆō3.47, p < 0.001) systems showed significant discrimination power.
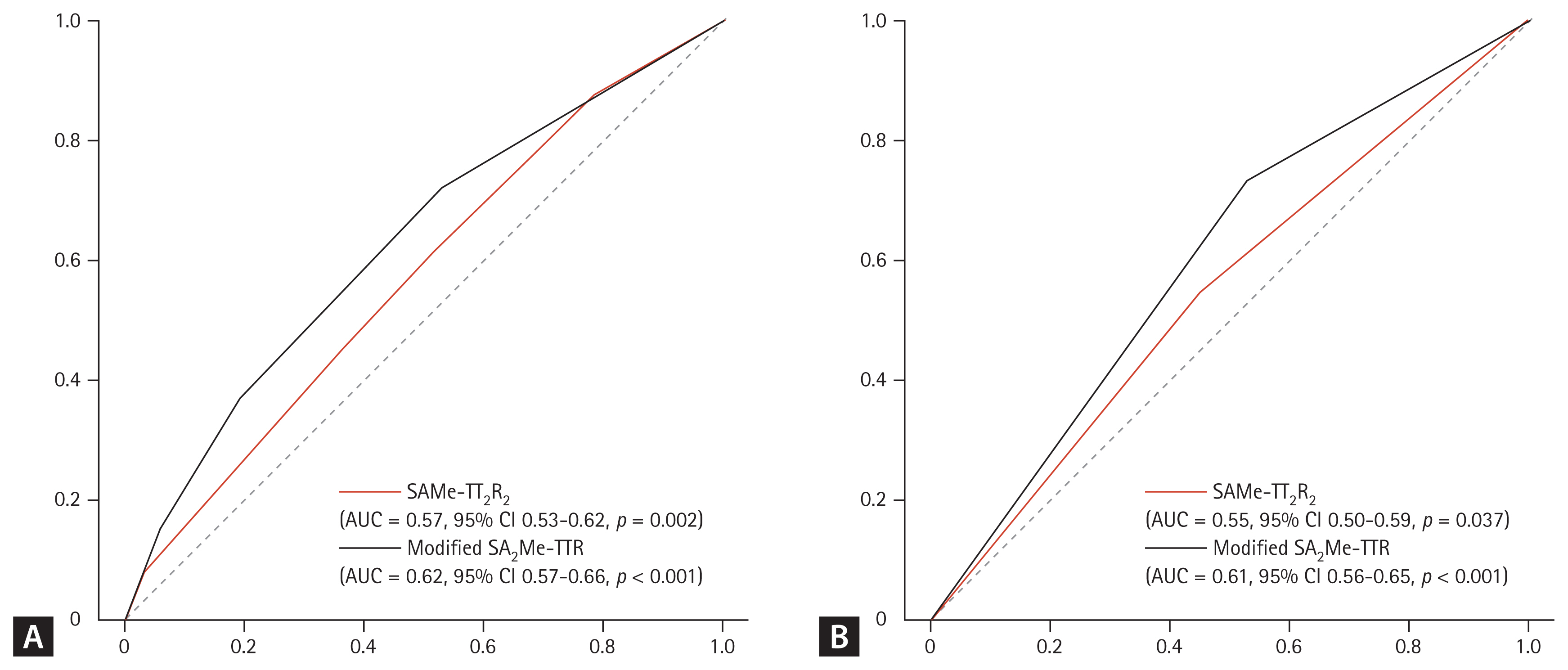
For the model performance evaluation, a ROC curve was created (Fig. 2). Considering the scores as continuous variables, both the original SAMe-TT2R2 (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.57, 95% CI 0.53ŌĆō0.62, p = 0.002) and the modified SA2Me-TTR (AUC = 0.62, 95% CI 0.57ŌĆō0.66, p < 0.001) scoring systems demonstrated good predictive power. Considering the scores as dichotomous variables (1), both the original SAMe-TT2R2 (AUC = 0.55, 95% CI 0.50ŌĆō0.59, p = 0.037) and the modified SA2Me-TTR (AUC = 0.61, 95% CI 0.56ŌĆō0.65, p < 0.001) systems demonstrated good predictive power. Comparing the two systems (as dichotomous variables) for the prediction of good AC, the modified SA2Me-TTR scoring system showed better predictive power than the original SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system (p < 0.001).
Good AC as determined by both the scoring systems were evaluated against hard clinical outcomes. In terms of the original SAMe-TT2R2 system, there was no difference in the rate of stroke, major bleeding, mortality, or composite clinical outcomes (the sum of stroke or major bleeding, and the sum of stroke, major bleeding, or death) between the good and poor AC groups. similarly, when considering the modified SA2Me-TTR system, there was no difference in the rate of stroke, major bleeding, mortality, or composite clinical outcomes (the sum of stroke or major bleeding, and the sum of stroke, major bleeding, or death) between the good and poor AC groups (Table 6).
The SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system is used to identify patients who cannot maintain appropriate therapeutic INR (cut-off value = 2). For patients who score > 2, good AC is unlikely and the clinician may prescribe NOAC instead of warfarin [7]. Meta-analyses have proven that the score is a potent predictor of TTR [21]. However, to date, the meta-analyses have excluded Asian studies because they all have 2 or more points due to the factor R (race) in the scoring system, which makes analysis and direct comparison difficult. Furthermore, Asian studies of the SAMe-TT2R2 score are limited.
This study is the first report to suggest a modified version of the SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system for Asian patients with AF. In a study by Park et al., the SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system was applied to Korean patients with AF in the Department of Neurology [22]. They collected clinical and genetic data from Korean patients with AF and concluded that the time in specific INR ranges depended on the VKORC1 genotype but not on the SAMe-TT2R2 score. This led to the suggestion that the scoring system may not be predictive of good AC in Asian populations including Koreans. Although studies of various sample sizes of Asian patients with AF have been conducted, the results relating to the SAMe-TT2R2 score have been inconsistent [9,10,22,23]. When compared to Western populations, Asian populations generally have a lower body mass index and different pharmacodynamics to various drugs [24,25]. Even among Asians, some characteristics may differ depending on the specific race. Hence, heterogeneous results in studies that validated the SAMe-TT2R2 score in Asians may be caused by racial differences. A multi-center multi-ethnic cohort study that included Malay, Chinese, and non-Malay patients showed that the SAMe-TT2R2 score failed to predict a TTR Ōēź 65% [23]. Subgroup analyses revealed that the median TTR significantly differed for each ethnic group and hospital setting.
The objectives of the present study were to validate the SAMe-TT2R2 score for an Asian population. Considering the factor R as 0 points, we investigated the predictability of TTR using the SAMe-TT2R2 score. Our results showed that the categorical application of the SAMe-TT2R2 score (0ŌĆō1 vs. Ōēź 2) was predictive of poor AC. In contrast, the original SAMe-TT2R2 score failed to show a linear association with the mean TTR in Asian patients. Moreover, some original components of the SAMe-TT2R2 score, such as smoking or comorbidities, were not significantly associated with good AC. Consequently, we suggested a modified version that considered renal insufficiency and stroke history instead of smoking and comorbidities. We verified the modified SA2Me-TTR score among Asian patients, and demonstrated superior predictability for AC relative to the original SAMe-TT2R2.
A good AC quality determined by the SAMe-TT2R2 or the modified SA2Me-TTR scores of Ōēż 1 was not associated with a reduced risk of hard clinical outcomes. Composed risk factors both in risk factors might explain the reason. Old age is the strongest risk factor for stroke, major bleeding, and mortality in patients with AF [2,4,5]. However, in both scoring systems, younger ages (< 60 yr) were considered for poor AC. Recent studies confirmed that good rhythm control is associated with a reduced risk of stroke or death [26,27]. AADs are fundamental to improving rhythm control. Yet, both scoring systems considered AAD use as a risk factor for poor AC. Race, specifically non-Caucasians, in the SAMe-TT2R2 score, is not a known risk factor for stroke or major bleeding. Hence, the inclusion of non-relevant and opposing risk factors to recognize stroke risks in the SAMe-TT2R2 or the modified SA2Me-TTR scores in the prediction of AC interrupted the relation between improved clinical outcomes and good AC. These findings suggest that the utilization of the SAMe-TT2R2 or the modified SA2Me-TTR scores is not useful for predicting stroke, major bleeding, or death in patients with AF and on warfarin.
This study has some limitations. First, this is a retrospective single-center study. It is difficult to fully represent Asian patients with AF from the present data. Second, the recommended TTR in warfarin-treated patients is Ōēź 70% but we utilized 60% as the cut-off value of good AC. This was because at a TTR of 70%, the number of patients in the good AC group was too small, which limits adequate comparisons. Conversely, this could also be a testament to the difficulty of maintaining adequate AC in Asian patients who are placed on warfarin therapy. Therefore, a more accurate tool for the prediction of TTR in Asians is warranted.
The study also has some strengths. In this study, not only each component of the SAMe-TT2R2 score but also other clinical factors, such as underlying diseases, and concomitant medications, were also considered when analyzing the association between TTR and good AC. Based on these analyses, we modified the scoring system for Asians and validated the modified model. We concluded that the modified model predicted TTR better than the original SAMe-TT2R2 score in Asians. Our findings are especially useful for clinicians who treat patients with NVAF.
1. The SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system is not suitable for Asians who are using warfarin.
2. Some factors in the SAMe-TT2R2 scoring system did not correlate with TTR prediction in the Asian population.
3. The modified version of the SA2Me-TTR score was re-evaluated against the identified factors. Then, the SA2Me-TTR scoring system was constructed for Asian patients with NVAF.
4. It consists of 6 factors with a maximum of 7 points (S, female gender, 1 point; A, age < 60 yr, 2 points; Me, medical history of heart failure, 1 point; T, treatment for rhythm control, 1 point; T, history of stroke or TIA, 1 point; and R, renal insufficiency, 1 point).
5. The modified SA2Me-TTR score shows better TTR predictability for Asian patients with NVAF.
6. The modified SA2Me-TTR score can assist clinicians in identifying Asian patients who do not tolerate warfarin.
Notes
CRedit authorship contributions
Seong Won Jeon: methodology, resources, investigation, software, writing - original draft; Nuri Lee: conceptualization, methodology, resources, software, writing - original draft; Ki Hong Lee: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, validation, writing - review & editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition; Minjeong Ha: investigation, validation, visualization, supervision, funding acquisition; Changhyun Kim: resources, formal analysis, software; Yoo Ri Kim: resources, software, visualization, supervision, project administration; Nam Sik Yoon: validation, visualization, supervision; Hyung Wook Park: conceptualization, validation, visualization, supervision, project administration
Figure┬Ā1
Mean TTR and the ratio of patients with good TTR according to the SAMe-TT2R2 and modified SA2Me-TTR scores. (A) The mean TTR according to the SAMe-TT2R2 and the modified SA2Me-TTR score. (B) The ratio of patients with good TTR according to the SAMe-TT2R2 and the modified SA2Me-TTR. TTR scores. Patients with good TTR had a TTR of Ōēź 60%. TTR, time in the therapeutic range.
Figure┬Ā2
The predictive accuracy of the SAMe-TT2R2 and modified SA2Me-TTR scoring systems. (A) The scores as continuous variables. (B) The scores as dichotomous variables. AUC, area under the curve; CI, confidence interval; TTR, time in the therapeutic range.
Table┬Ā1
Mean TTR according to the factors included in SAMe-TT2R2 score and the distribution of each factors according to the status of anticoagulation quality
Table┬Ā2
Mean TTR according to the various clinical factors and the distribution of each factors according to the status of anticoagulation quality
Table┬Ā3
Factors associated for anticoagulation quality
Table┬Ā4
The original SAMe-TT2R2 score and modified SA2Me-TTR score
Table┬Ā5
Comparison of the mean TTR and the ratio of the patients with good AC according to the SAMe-TT2R2 score and modified SA2Me-TTR score
Table┬Ā6
Clinical according to the SAMe-TT2R2 score and modified SA2Me-TTR score
REFERENCES
1. De Caterina R, Husted S, Wallentin L, et al. Vitamin K antagonists in heart disease: current status and perspectives (Section III). Position paper of the ESC Working Group on Thrombosis--Task Force on Anticoagulants in Heart Disease. Thromb Haemost 2013;110:1087ŌĆō1107.


2. Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2021;42:373ŌĆō498.

3. Ono K, Iwasaki YK, Akao M, et al. JCS/JHRS 2020 guideline on pharmacotherapy of cardiac arrhythmias. Circ J 2022;86:1790ŌĆō1924.

4. Chao TF, Joung B, Takahashi Y, et al. 2021 Focused update of the 2017 consensus guidelines of the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS) on stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythm 2021;37:1389ŌĆō1426.




5. January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;74:104ŌĆō132.

6. Fauchier L, Angoulvant D, Lip GY. The SAMe-TT2R2 score and quality of anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation: a simple aid to decision-making on who is suitable (or not) for vitamin K antagonists. Europace 2015;17:671ŌĆō673.


7. Abumuaileq RR, Abu-Assi E, Raposeiras-Roubin S, et al. Evaluation of SAMe-TT2R2 risk score for predicting the quality of anticoagulation control in a real-world cohort of patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation on vitamin-K antagonists. Europace 2015;17:711ŌĆō717.


8. Apostolakis S, Sullivan RM, Olshansky B, Lip GYH. Factors affecting quality of anticoagulation control among patients with atrial fibrillation on warfarin: the SAMe-TT2R2 score. Chest 2013;144:1555ŌĆō1563.


9. Bernaitis N, Ching CK, Chen L, et al. The Sex, Age, Medical History, Treatment, Tobacco Use, Race Risk (SAMe TT2R2) score predicts warfarin control in a singaporean population. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2017;26:64ŌĆō69.


10. Chan PH, Hai JJ, Chan EW, et al. Use of the SAMe-TT2R2 score to predict good anticoagulation control with warfarin in Chinese patients with atrial fibrillation: relationship to ischemic stroke incidence. PLoS One 2016;11:e0150674.



11. Gallego P, Rold├Īn V, Marin F, et al. SAMe-TT2R2 score, time in therapeutic range, and outcomes in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Med 2014;127:1083ŌĆō1088.


12. Szymanski FM, Lip GY, Filipiak KJ, Platek AE, Karpinski G. Usefulness of the SAME-TT2R2 score to predict anticoagulation control on VKA in patients with atrial fibrillation and obstructive sleep apnea. Int J Cardiol 2016;204:200ŌĆō205.


13. Ruiz-Ortiz M, Bertomeu V, Cequier ├ü, Mar├Łn F, Anguita M. Validation of the SAMe-TT2R2 score in a nationwide population of nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients on vitamin K antagonists. Thromb Haemost 2015;114:695ŌĆō701.


14. Rold├Īn V, Cancio S, G├Īlvez J, et al. The SAMe-TT2R2 score predicts poor anticoagulation control in AF patients: a prospective ŌĆśReal-worldŌĆÖ inception cohort study. Am J Med 2015;128:1237ŌĆō1243.


15. Proietti M, Lane DA, Lip GY. Relation of the SAMe-TT2R2 score to quality of anticoagulation control and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillation patients: observations from the SPORTIF trials. Int J Cardiol 2016;216:168ŌĆō172.


16. Poli D, Antonucci E, Testa S, Lip GY. A prospective validation of the SAME-TT2R2 score: how to identify atrial fibrillation patients who will have good anticoagulation control on warfarin. Intern Emerg Med 2014;9:443ŌĆō447.



17. Lobos-Bejarano JM, Barrios V, Polo-Garc├Ła J, et al. Evaluation of SAMe-TT2R2 score and other clinical factors influencing the quality of anticoagulation therapy in non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a nationwide study in Spain. Curr Med Res Opin 2016;32:1201ŌĆō1207.


18. Cho JG, Lee KH, Kim YR, et al. Standard-intensity versus low-intensity anticoagulation with warfarin in Asian patients with atrial fibrillation: a multi-center, randomized controlled trial. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2023;29:10760296231171081.




19. Lee KH, Cho JG, Lee N, et al. Impact of anticoagulation intensity in Korean patients with atrial fibrillation: is it different from Western population? Korean Circ J 2020;50:163ŌĆō175.




20. Rosendaal FR, Cannegieter SC, van der Meer FJ, Bri├½t E. A method to determine the optimal intensity of oral anticoagulant therapy. Thromb Haemost 1993;69:236ŌĆō239.


21. van Miert JHA, Bos S, Veeger NJGM, Meijer K. Clinical usefulness of the SAMe-TT2R2 score: a systematic review and simulation meta-analysis. PLoS One 2018;13:e0194208.



22. Park YK, Lee MJ, Kim JH, et al. Lack of association of clinical factors (SAMe-TT2R2) with CYP2C9/VKORC1 genotype and anticoagulation control quality. J Stroke 2015;17:192ŌĆō198.




23. Khaw CS, Lim MSH, Tiong LL, et al. Validation of the SAMe-TT2R2 score in a multiethnic cohort of asian patients with atrial fibrillation on warfarin therapy - a multicenter study. Int J Cardiol 2017;249(Supplement):S2.

24. Shen AY, Yao JF, Brar SS, Jorgensen MB, Chen W. Racial/ethnic differences in the risk of intracranial hemorrhage among patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;50:309ŌĆō315.


25. Kitamura A, Nakagawa Y, Sato M, et al. Proportions of stroke subtypes among men and women > or =40 years of age in an urban Japanese city in 1992, 1997, and 2002. Stroke 2006;37:1374ŌĆō1378.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



