 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 38(6); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Although rituximab, an antiCD20 monoclonal antibody, has dramatically improved the clinical outcomes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, rituximab resistance remains a challenge.
Methods
We developed a rituximab-resistant cell line (RRCL) by sequential exposure to gradually increasing concentrations of rituximab in a rituximab-sensitive cell line (RSCL). When the same dose of rituximab was administered, RRCL showed a smaller decrease in cell viability and apoptosis than RSCL. To determine the differences in gene expression between RSCL and RRCL, we performed next-generation sequencing.
Results
In total, 1,879 differentially expressed genes were identified, and in the over-representation analysis of Consensus-PathDB, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway showed statistical significance. MAPK13, which encodes the p38╬┤ protein, was expressed more than four-fold in RRCL. Western blot analysis revealed that phosphop38 expression mainwas increased in RRCL, and when p38 inhibitor was administered, phosphop38 expression was significantly decreased. Therefore, we hypothesized that p38 MAPK activation was associated with rituximab resistance. Previous studies have suggested that p38 is associated with NF-╬║B activation. Deferasirox has been reported to inhibit NF-╬║B activity and suppress phosphorylation of the MAPK pathway. Furthermore, it also has cytotoxic effects on various cancers and synergistic effects in overcoming drug resistance. In this study, we confirmed that deferasirox induced dose-dependent cytotoxicity in both RSCL and RRCL, and the combination of deferasirox and rituximab showed a synergistic effect in RRCL at all combination concentrations.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), accounting for over 40% NHL cases in Korea [1]. DLBCL is an aggressive lymphoma, and appropriate treatment is required at the time of diagnosis. Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD20 B-cell antigen, was developed, and the combination of rituximab with other cytotoxic drugs, such as cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) resulted in a dramatic improvement in therapeutic outcomes [2]. Therefore, the R-CHOP regimen is currently the standard first-line treatment for DLBCL. Although over 60% of DLBCL patients can be cured with R-CHOP chemotherapy, 30ŌĆō40% of patients are still refractory to therapy or relapse after the initial response [3]. Despite various salvage treatment options, including salvage chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, these patients exhibit poor prognosis, and this is a major unmet medical need [4,5].
Rituximab resistance is defined as overt disease progression, insufficient response to a rituximab-containing regimen, or progression within 6 months after treatment with rituximab. Because rituximab is usually used with other cytotoxic drugs, and the contribution of rituximab cannot be clearly assessed, it is difficult to determine the true incidence of rituximab resistance. Nevertheless, a significant proportion of patients with relapsed refractory DLBCL are thought to be resistant to rituximab [6].
Previous studies have demonstrated several potential mechanisms of rituximab resistance: downregulation of CD20 expression, resistance to complement-dependent cytotoxicity, resistance to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and resistance to apoptosis [6-11]. However, the exact mechanism of rituximab resistance has not yet been clearly elucidated, and additional agents for overcoming rituximab resistance have not yet been presented.
Deferasirox, an orally administered iron chelator, showed anticancer effects in various cancers, and our previous study demonstrated that deferasirox induced apoptosis in lymphoma cell lines [12,13].
Based on these results, we attempted to elucidate the mechanism of rituximab resistance using a rituximab-resistant cell model and present candidate substances to overcome rituximab resistance.
This study was conducted using the rituximab-sensitive human activated B-cell-like-DLBCL cell line, NU-DUL-1. The NU-DUL-1 cell line was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were maintained in the Roswell Park Memorial Institute Medium 1,640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin-streptomycin (100 U/mL) at 37┬░C and 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. Human serum, a source of complement, was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Luis, MO, USA).
To develop resistant cell lines, the na├»ve cell line was gradually exposed to an escalating dose of rituximab (0.1ŌĆō128 ╬╝g/mL). After 24 h of incubation with a specific dose of rituximab and human serum, cells were centrifuged and maintained in fresh growth medium for several days. Once the log phase of growth was reached, the same process was repeated with an escalating dose of rituximab 10 times [9].
AntiCD 20 monoclonal antibody, rituximab (Mabthera), was provided by Roche (Basel, Switzerland). Deferasirox and SB 203580 were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. BIRB 796 was purchased from MedChemExpress (Princeton, NJ, USA). Primary antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA; antibodies against Erk1/2, phosphoErk1/2, SAPK/JNK, phosphoSAPK/JNK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase [MAPK], phosphop38 MAPK, phosphoNF-╬║B, antipoly [ADP-ribose] polymerase [PARP], and Bcl-2) and BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA, USA; antibody against ╬▓-actin). The secondary antibodies were purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch (West Grove, PA, USA; anti-mouse immunoglobulin (Ig)G and anti-rabbit IgG).
Cell viability was evaluated using the EZ-cytox Cell Viability Assay Kit (Water water-soluble tetrazolium salt, 4-[3-(4-iodophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2H-5-tetrazolio]-1, 3-benzene disulfonate) (Daeillab service, Seoul, Korea). Cells were seeded in 96-well plates (2.0 ├Ś 104 cells per well), and various concentrations of rituximab (0ŌĆō80 ╬╝g/mL), deferasirox (0ŌĆō25 ╬╝M), or rituximab and deferasirox were administered with 20% human serum. After 48 hours of incubation, 10 ╬╝L of the kit reagent was added to each well, and the cells were further incubated for 4 hours. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a SpectraMax 190 Microplate Reader (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA).
Rituximab-resistant cells were treated with the same concentration of rituximab (10 ╬╝g/mL) and human serum. Treated cells were stained with a FITC-conjugated Annexin V apoptosis detection kit (BD Biosciences) and analyzed through flow cytometry using a Navios EX Flow Cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Pasadena, CA, USA).
Total RNA was extracted from previously collected rituximab-sensitive cell line (RSCL) and RRCL using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The library was constructed using the TruSeq Stranded Total RNA LT Single Prep Kit (Gold) and mapped to the reference genome (GRCh37) using HISAT version 1.10 and Bowtie2 aligner 2.3.4.1. Transcript assembly was performed using StringTie, version 2.1.3b. The fragment counts were measured in units of reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (RPKM). The values of log2(RPKM+1) were calculated for differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis, and DEG was analyzed using DESeq2.
Whole cells were solubilized in mammalian protein extraction reagent (ThermoFicher Scientific, BRIMS, Cambdridge, MA, USA) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail tablets (Roche┬«, Indianapolis, IN, USA). The supernatant was collected after centrifugation (15,000 ├Ś g, 4┬░C, 15 min), and protein concentrations were measured using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). Equal quantities of protein were electrophoresed on a Novex WedgeWell Trisglycine gel (ThermoFicher Scientific, BRIMS) and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Richmond, CA, USA). The membranes were blocked with phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.2% Tween 20 and 5% nonfat dry milk and incubated overnight at 4┬░C with primary antibodies against the following proteins: ERK1/2, phosphoERK1/2, SAPK/JNK, phosphoSAPK/JNK, p38 MAPK, phosphop38 MAPK, phosphoNF-╬║B, PARP, Bcl-2, and ╬▓-actin. The membranes were then incubated with the following horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies: antirabbit IgG and antimouse IgG. The immunoblots were visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence solution (DoGenBio, Seoul, Korea) and exposed to X-ray film.
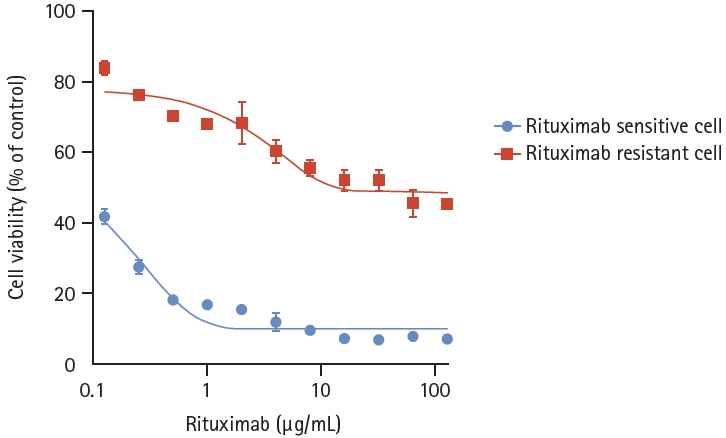
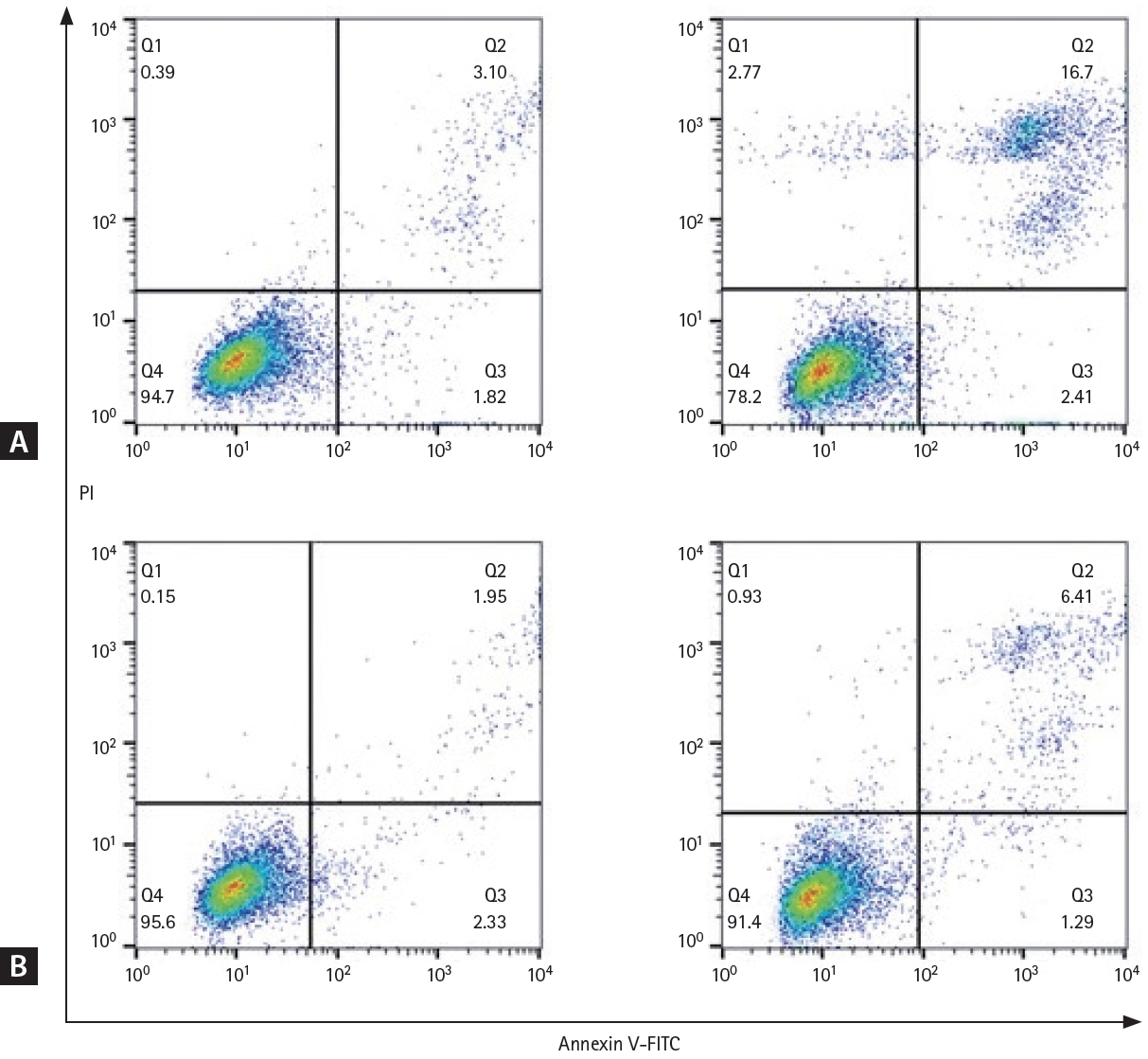
We developed a RRCL by sequential exposure to rituximab in human serum. To determine whether rituximab resistance was obtained, cell viability was confirmed after administration of various concentrations of RSCL and RRCL. Rituximab caused a dose-dependent reduction in the viability of both cell lines. After treatment with rituximab 8 ╬╝g/mL, the viability of RRCL cells was reduced to 60%, whereas that of RSCL cells was reduced to 8.7%. Cell viability was significantly reduced in RSCL compared to RRCL at all concentrations (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 1). Analysis of apoptosis using annexin V/PI staining also showed similar results. Both cell lines were treated with rituximab (10 ╬╝g/mL) and human serum (20%) for 48 hours, and RRCL showed decreased early and late apoptosis compared with RSCL (Fig. 2). These results revealed that the cells that were gradually exposed to an escalating dose of rituximab acquired rituximab resistance.
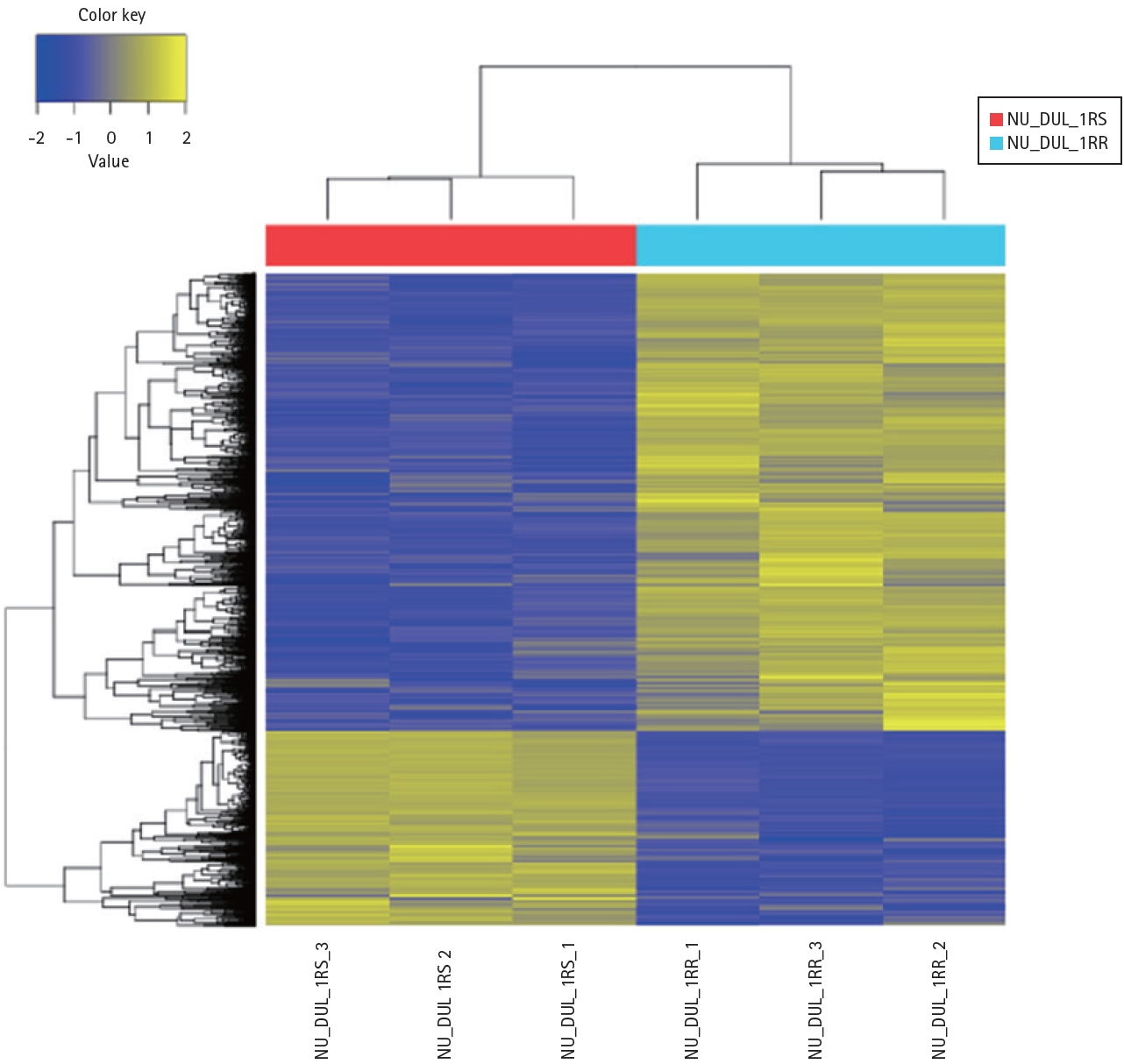
To determine the differences in gene expression between RSCL and RRCL, we performed NGS. A total of 1,879 DEGs were identified in RRCL compared to RSCL (|fold change| Ōēź 2 and p < 0.05) (Fig. 3). Subsequently, we applied ConsensusPathDB (CPDB) to the 1,879 genes to determine which functional signaling pathway was associated with rituximab resistance. In the over-representation analysis of CPDB, 20 pathways showed statistical significance (q-value < 0.1) (Table 1). As the MAPK signaling pathway is known to be associated with cell survival and tumorigenesis, we identified DEGs related to the MAPK signaling pathway (Table 2). MAPK13, which encodes the p38╬┤ protein, was expressed more than four-fold in RRCL.
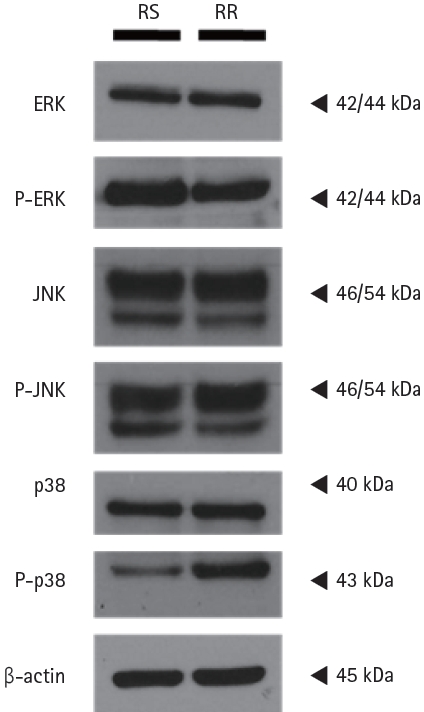
We then performed western blot analysis for the major proteins of the MAPK pathway and found that phosphop38 expression was increased in RRCL (Fig. 4). There were four isoforms of p38 MAPK (╬▒, ╬▓, ╬│, and ╬┤), which are known to be different MAPK subgroups, so we performed western blot analysis after administration of two kinds of p38 inhibitors: SB205380, an ╬▒ and ╬▓ selective p38 inhibitor and BIRB 796, a panp38 inhibitor. When SB205380 was administered, phosphop38 expression slightly decreased compared to that in controls, who were not administered any drugs. However, phosphop38 expression significantly decreased when BIRB 796 was administered (Fig. 5). Therefore, we elucidated that p38 ╬┤ expression was increased in RRCL, and that p38 MAPK activation was associated with rituximab resistance.
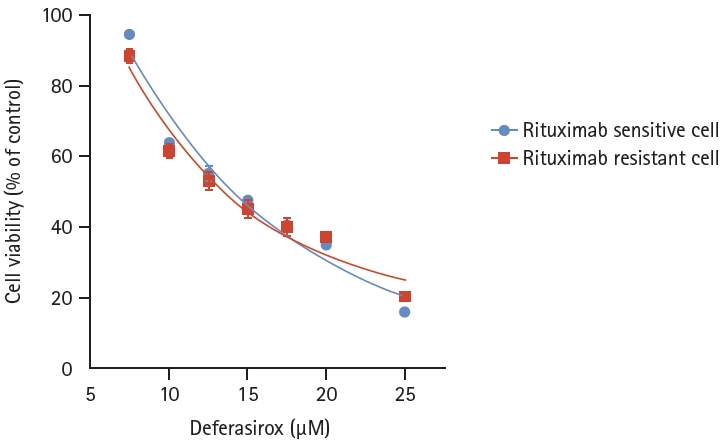
Since deferasirox, an orally administered iron chelator, is also known to suppress phosphorylation of the MAPK pathway and inhibit NF-╬║B activity, we hypothesized that deferasirox could be a candidate for overcoming rituximab resistance. Deferasirox caused a dose-dependent reduction in cell viability in both RSCL and RRCL, and there were no significant differences between the two cell lines (p = 0.4481) (Fig. 6). To determine the combined effects of deferasirox and rituximab, RRCL was treated with gradually increasing concentrations of rituximab (0ŌĆō10 ╬╝g/mL) alone or in combination with 10 ╬╝M deferasirox. When RRCL was treated with 1.25 ╬╝g/mL rituximab only, 56.6% of the cells survived, but when treated with 1.25 ╬╝g/mL rituximab and 10 ╬╝M deferasirox, only 28.3% of the cells survived. Cell viability of RRCL was significantly reduced at all of the combination concentrations when rituximab and deferasirox were coadministered compared to when rituximab was administered alone (p < 0.0001) (Fig. 7).
To determine whether there was a synergistic effect of the two drugs, the ChouŌĆōTalalay combination index (CI) was performed using CompuSyn software. The CI for deferasirox and rituximab was < 1 (0.43ŌĆō0.68) at all combination concentrations, indicating that the combination of deferasirox and rituximab had a synergistic effect.
The acquisition of rituximab resistance is a major unmet medical need in patients with DLBCL. Potential mechanisms of rituximab resistance have been presented, including downregulation of CD20 expression, resistance to complement-dependent cytotoxicity, resistance to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and resistance to apoptosis [6-11]; however, despite its importance, the exact mechanism of resistance to rituximab has not yet been clarified. Several previous studies have attempted to elucidate the mechanisms of rituximab resistance using B-cell lymphoma cells that acquired rituximab resistance. They presented that rituximab resistant cells showed hyperactivation of p38 MAPK, NF-╬║B, ERK 1/2, and AKT pathway and overexpression of antiapoptotic proteins, and that eventually led to rituximab resistance [14,15].
In this study, we developed a RRCL by exposure to gradually increasing concentrations of rituximab and attempted to elucidate the mechanism of rituximab resistance. NGS results showed that gene expression related to the MAPK pathway was activated, and phosphop38 protein expression was increased in RRCL. Phosphop38 protein expression was decreased when the panp38 inhibitor was administered compared to when the ╬▒, ╬▓ selective p38 inhibitor was administered. Therefore, we suggest that acquired rituximab resistance is associated with p38 MAPK pathway activation, especially that of p38╬┤, in vitro.
The MAPK pathway is associated with cell survival, and hyperactivation of the p38 MAPK pathway has been observed in various tumors, including hematological malignancies. Vega et al. [16] demonstrated that rituximab inhibited the p38 MAPK pathway in NHL cell lines, and Pederson et al. [17] also reported that rituximab-induced apoptosis was dependent on p38 MAPK pathway activation in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Several studies have shown that constitutive activation of p38 MAPK in DLBCL cells or tissue biopsy samples is associated with lymphomagenesis [18]. Patients with tumor tissues with high phosphop38 MAPK expression showed poor prognosis, and the expression of phosphop38 was revealed as an independent prognostic risk factor [19].
Vega et al. reported that rituximab inhibited p38 MAPK and NF-╬║B activity, and that the p38 MAPK pathway was related to the activation of NF-╬║B and acted as a chemoresistant factor. They also demonstrated that rituximab inhibits cell survival through the p38 MAPK and NF-╬║B pathways in a xenographic model, suggesting that these pathways are targets for overcoming rituximab resistance. Subsequently, they reported that p38 MAPK inhibitors augmented apoptosis and induced chemosensitization in rituximab-resistant B-NHL cells by the combination of antiCD20-hITN-╬▒ [16,19-21]. Furthermore, sustained NF-╬║B activation was well known to be associated with various hematologic malignancies, including DLBCL, and was related to resistance to chemotherapy [22-24]. These results support our hypothesis that acquired rituximab resistance is associated with p38 MAPK pathway activation and linked to the NF-╬║B pathway.
Previous studies identified that deferasirox, an orally administered iron chelator, inhibit NF-╬║B activity and suppress the phosphorylation of the MAPK pathway [21,22]. Iron is an essential element for DNA synthesis and cell proliferation, and several studies have shown that iron chelators have anticancer effects, and induce hematologic improvement in hematologic diseases, such as myelodysplastic syndrome and myeloid leukemia [12,25-27]. Our previous study showed that deferasirox induced apoptosis in human lymphoma cell lines [13]. Furthermore, in our previous studies, we developed tyrosine kinase resistant chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cell lines by sequential exposure to gradually increasing concentrations of drug, and demonstrated that cotreatment with deferasirox and imatinib downregulated NF-╬║B activity and exerted a synergistic effect in imatinib-resistant CML cell line [28,29].
Deferasirox is widely used to reduce iron overload in hematologic malignancy patients with high transfusion requirements in clinical practice and is easily taken orally and well tolerated. Therefore, we assumed that deferasirox could be used relatively safely in combination with other drugs.
Based on these results, we attempted to confirm the cytotoxic effects of deferasirox in our cell lines. Deferasirox induced dose-dependent cytotoxicity in both RSCL and RRCL, and the combination of deferasirox with rituximab showed a synergistic effect in RRCL at all combination concentrations. Therefore, we suggest that deferasirox may be a candidate for overcoming rituximab resistance. However, although deferasirox showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity in RRCL and a synergistic effect with rituximab, p38 and NF-╬║B expression did not change after the administration of deferasirox, and the exact mechanism was not elucidated.
A limitation of this study is that we did not clearly identify the exact mechanism of synergistic effects of the two drugs. Therefore, further experiments are required to define the detailed up- and downstream signaling pathway components. Since several studies have also suggested that altered iron metabolism leads to modification of the tumor microenvironment, including the anti-tumor immune response, further evaluation of pro-inflammatory markers and oxidative stress associated with iron overload might be considered.
Notes
Figure┬Ā1.
Cell viability analysis of rituximab-sensitive and rituximab- resistant cell lines (treated with rituximab). The rituximab-resistant cell line, which was gradually exposed to an escalating dose of rituximab, showed statistically less decreased cell viability than the rituximab-sensitive cell line at the same concentration of rituximab (p < 0.0001).
Figure┬Ā2.
Early and late apoptosis in rituximab-sensitive and rituximab-resistant cell lines. Cell lines were treated with rituximab (10 ╬╝g/ mL) for 48 hours and annexin V/PI staining was analyzed using flow cytometry. (A) Rituximab-sensitive cell line, before administration of rituximab (left), 48 hours after administration of rituximab (right). (B) Rituximab-resistant cell line, before administration of rituximab (left), and 48 hours after administration of rituximab (right). FITC, fluorescein 5(6)-isothiocyanate; PI, propidium iodide.
Figure┬Ā3.
Heat map of the one-way hierarchical clustering. In total, 1,897 genes satisfied with |fold change| Ōēź 2 and p < 0.05 using z-score for normalized value.
Figure┬Ā4.
The phosphop38 MAPK expression was activated in rituximab-resistant cell line. Western blot analysis revealed that phosphop38 expression was increased in rituximab-resistant cell line. ╬▓-actin was used as the loading control.
Figure┬Ā5.
Western blot analysis of rituximab-resistant cell line treated with p38 inhibitor. (A) When SB205380 was administered, the phosphop38 expression was slightly decreased compared to control, which was not administered with any drugs. (B) The phosphop38 expression was significantly decreased when BIRB 796 was administered, and the Bcl-2 expression was decreased when rituximab-resistant cell line was treated with rituximab and BIRB 796.

Figure┬Ā6.
Cell viability analysis of rituximab-sensitive cell line and rituximab-resistant cell line, treated with deferasirox. Both rituximab- sensitive cell line and rituximab-resistant cell line showed a dose-dependent reduction in cell viability with deferasirox, and there was no significant difference between the two cell lines (p = 0.4481).
Figure┬Ā7.
Cell viability analysis of rituximab-resistant cell line, treated with rituximab and deferasirox. rituximab-resistant cell line was treated with gradually increasing concentrations of rituximab (0ŌĆō10 ╬╝g/mL) with 10 ╬╝M deferasirox. Cell viability of rituximab-resistant cell line was significantly reduced at all of the combination concentrations when rituximab and deferasirox were coadministered than when rituximab was administered alone (p < 0.0001).

Table┬Ā1.
Over representation analysis of ConsensusPathDB
Table┬Ā2.
Differentially expressed genes related to MAPK pathway
REFERENCES
1. Kim JM, Ko YH, Lee SS, et al. WHO classification of malignant lymphomas in Korea: report of the third nationwide study. Korean J Pathol 2011;45:254ŌĆō260.

2. Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2002;346:235ŌĆō242.


3. Colosia A, Njue A, Trask PC, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic literature review. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2014;14:343ŌĆō355.e6.


4. Sarkozy C, Sehn LH. Management of relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:209ŌĆō216.


5. Yi JH. Novel combination immunochemotherapy beyond CD20 for B-cell lymphomas. Blood Res 2021;56(S1):S1ŌĆōS4.



7. P├®rez-Callejo D, Gonz├Īlez-Rinc├│n J, S├Īnchez A, Provencio M, S├Īnchez-Beato M. Action and resistance of monoclonal CD20 antibodies therapy in B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Cancer Treat Rev 2015;41:680ŌĆō689.


8. Tsai PC, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Bangia N, Olejniczak SH, Czuczman MS. Regulation of CD20 in rituximab-resistant cell lines and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2012;18:1039ŌĆō1050.




9. Czuczman MS, Olejniczak S, Gowda A, et al. Acquirement of rituximab resistance in lymphoma cell lines is associated with both global CD20 gene and protein down-regulation regulated at the pretranscriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1561ŌĆō1570.



10. van Meerten T, van Rijn RS, Hol S, Hagenbeek A, Ebeling SB. Complement-induced cell death by rituximab depends on CD20 expression level and acts complementary to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:4027ŌĆō4035.



11. Takei K, Yamazaki T, Sawada U, Ishizuka H, Aizawa S. Analysis of changes in CD20, CD55, and CD59 expression on established rituximab-resistant B-lymphoma cell lines. Leuk Res 2006;30:625ŌĆō631.


12. Bedford MR, Ford SJ, Horniblow RD, Iqbal TH, Tselepis C. Iron chelation in the treatment of cancer: a new role for deferasirox? J Clin Pharmacol 2013;53:885ŌĆō891.



13. Choi JG, Kim JL, Park J, et al. Effects of oral iron chelator deferasirox on human malignant lymphoma cells. Korean J Hematol 2012;47:194ŌĆō201.



14. Bonavida B. Rituximab-induced inhibition of antiapoptotic cell survival pathways: implications in chemo/immunoresistance, rituximab unresponsiveness, prognostic and novel therapeutic interventions. Oncogene 2007;26:3629ŌĆō3636.



15. Jazirehi AR, Vega MI, Bonavida B. Development of rituximab-resistant lymphoma clones with altered cell signaling and cross-resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Res 2007;67:1270ŌĆō1281.



16. Vega MI, Huerta-Yepaz S, Garban H, Jazirehi A, Emmanouilides C, Bonavida B. Rituximab inhibits p38 MAPK activity in 2F7 B NHL and decreases IL-10 transcription: pivotal role of p38 MAPK in drug resistance. Oncogene 2004;23:3530ŌĆō3540.



17. Pedersen IM, Buhl AM, Klausen P, Geisler CH, Jurlander J. The chimeric anti-CD20 antibody rituximab induces apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through a p38 mitogen activated protein-kinase-dependent mechanism. Blood 2002;99:1314ŌĆō1319.



18. Ding H, Gabali AM, Jenson SD, Lim MS, Elenitoba-Johnson KS. P38 mitogen activated protein kinase expression and regulation by interleukin-4 in human B cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. J Hematop 2009;2:195ŌĆō204.




19. Vega GG, Avil├®s-Salas A, Chalapud JR, et al. P38 MAPK expression and activation predicts failure of response to CHOP in patients with diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2015;15:722.




20. Vega GG, Franco-Cea LA, Huerta-Yepez S, et al. Overcoming rituximab drug-resistance by the genetically engineered antiCD20-hIFN-╬▒ fusion protein: direct cytotoxicity and synergy with chemotherapy. Int J Oncol 2015;47:1735ŌĆō1748.



21. Vega GG, Arteaga-Campos M, Martinez-Paniagua M, et al. p38 MAPK and NF-╬║B survival pathways as targets for action of rituximab in vivo in a xenographic model. Blood 2017;130(Supplement 1):5199.
22. Turturro F. Constitutive NF- ╬║B Activation underlines major mechanism of drug resistance in relapsed refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Biomed Res Int 2015;2015:484537.


23. Knittel G, Liedgens P, Korovkina D, Pallasch CP, Reinhardt HC. Rewired NF╬║B signaling as a potentially actionable feature of activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 2016;97:499ŌĆō510.



24. Kennedy R, Klein U. Aberrant activation of NF-╬║B signalling in aggressive lymphoid malignancies. Cells 2018;7:189.



25. Messa E, Carturan S, Maff├© C, et al. Deferasirox is a powerful NF-kappaB inhibitor in myelodysplastic cells and in leukemia cell lines acting independently from cell iron deprivation by chelation and reactive oxygen species scavenging. Haematologica 2010;95:1308ŌĆō1316.



26. Al-Rousan RM, Paturi S, Laurino JP, et al. Deferasirox removes cardiac iron and attenuates oxidative stress in the iron-overloaded gerbil. Am J Hematol 2009;84:565ŌĆō570.


27. Ohyashiki JH, Kobayashi C, Hamamura R, Okabe S, Tauchi T, Ohyashiki K. The oral iron chelator deferasirox represses signaling through the mTOR in myeloid leukemia cells by enhancing expression of REDD1. Cancer Sci 2009;100:970ŌĆō977.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



