To the Editor,
The association between sarcoidosis and lymphoma was first suggested by Bichel and Brincker in the 1960s, and this association was described as ŌĆ£sarcoidosis-lymphoma syndromeŌĆØ (SLS) by Brincker [1] in the 1980s. Typical SLS is characterized by sarcoidosis that precedes the diagnosis of lymphoproliferative disease. However, in a small number of patients with SLS, lymphoma precedes the diagnosis of sarcoidosis [2]. We herein describe a patient who was diagnosed with sarcoidosis 2 years after achieving a complete response (CR) from non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
A 55-year-old woman underwent a regular health examination in April 2012, and a left ovarian mass was detected on abdominal ultrasonography. Subsequent computed tomography (CT) scans of the abdomen and pelvis revealed a 7-cm left ovarian mass without lymph node enlargement that was suspicious for ovarian cancer. The patient underwent a total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy with pelvic and para-aortic lymph node dissection. Specimens obtained during surgery demonstrated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in the left ovary and salpinx, right mesosalpinx, and fallopian tube, without lymph node involvement.
Repeated postoperative CT scans of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis showed multifocal lymphoceles in the para-aortic space and left pelvic wall. No lymphoma involvement was noted in the neck or thorax. Bone marrow biopsies and aspirates were negative for lymphoma. Positron emission tomography (PET) scans showed abnormal fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in the left para-aortic lymph node. The patient was diagnosed with stage IV disease and treated with six cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) from May to September 2012. The patient achieved a CR and underwent regular follow-up examinations. Chest, neck, and abdominopelvic CT scans were performed every 3 months.
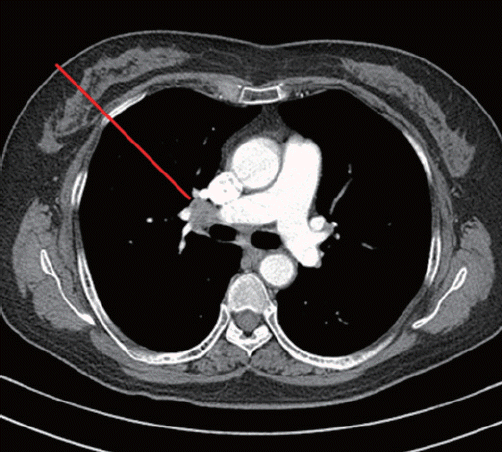
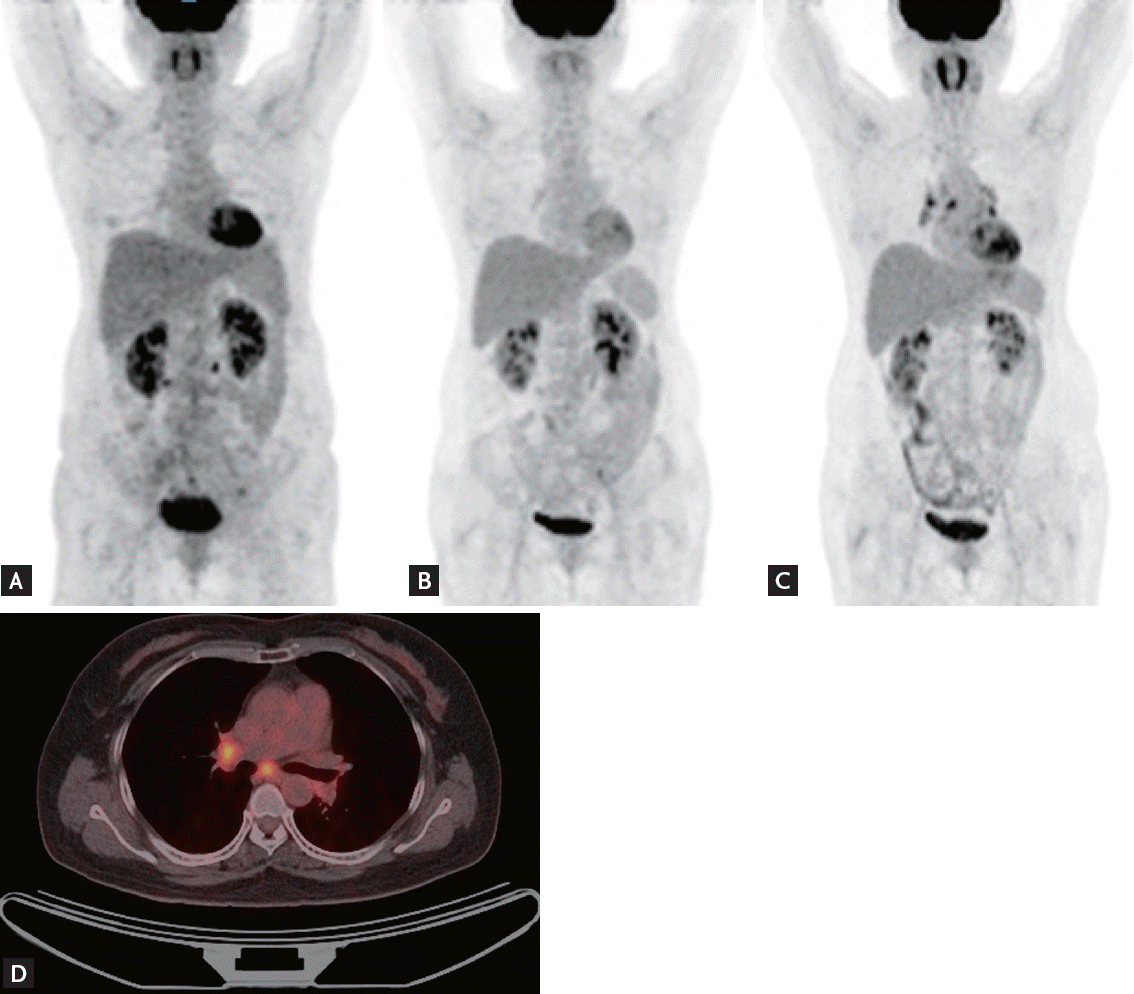
Follow-up CT performed 2 years after CR revealed new enlarged subcarinal lymph nodes (both hilar and subpleural in the right middle and lower lung, maximum standardized uptake value [SUV] ranging from 4.6 to 5.2, and Deauville score of 5) (Fig. 1). However, the patient had no symptoms, and there was no sign of lymphoma recurrence on neck or abdominopelvic CT scans. A subsequent PET scan revealed new hypermetabolic lymph nodes in both the hilar and interlobar areas and the right upper paraesophageal area that were suggestive of lymphoma recurrence (Fig. 2). Salvage chemotherapy was planned with consideration of DLBCL recurrence.
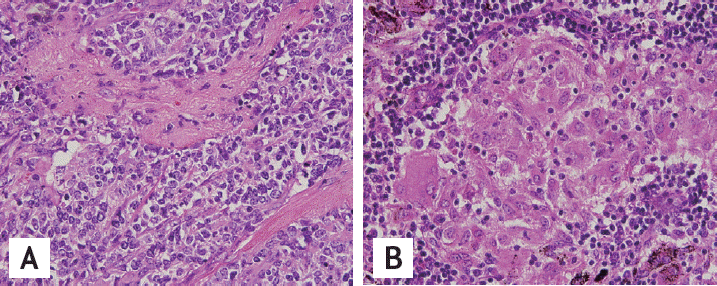
To confirm the diagnosis, excisional biopsies of the right hilar, paratracheal, and subcarinal lymph nodes were obtained via video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. The specimens were identified as non-necrotizing, non-malignant granulomas (Fig. 3). Ziehl-Neelsen and GomoriŌĆÖs methenamine silver stains were negative for mycobacteria and fungi, and sarcoidosis was subsequently diagnosed. The patientŌĆÖs pulmonary function test was normal, and she was receiving regular follow-up examinations without specific treatment at the time of this writing. Her last follow-up exam was conducted in August 2014, and she was symptom-free at that time.
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that is characterized pathologically by non-caseating granulomas. Although the lungs are most commonly affected, any organ can be involved. The term SLS was first suggested by Brinkcker [1], who described 46 patients with sarcoidosis that coexisted with lymphoma, identified from the Danish cancer and sarcoid registries. Patients with sarcoidosis demonstrated a relative risk of developing lymphoma that was 5.5 times higher than expected, and this association was also observed in the data presented by Mellemkjaer et al. [3]. The three proposed features of SLS are lymphoproliferative disease that always develops after sarcoidosis, median age at sarcoidosis onset that is 10 years older than other patients with sarcoidosis, and Hodgkin lymphoma as the most common histology associated with sarcoidosis.
To our knowledge, SLS has only been reported in 85 patients to date. Sarcoidosis preceded lymphoma in the majority of these cases. However, lymphoma developed first in a small number of cases [2]. Our patient is the first reported case of SLS in Korea and, unlike most reported cases, lymphoma preceded the diagnosis of sarcoidosis by 2 years in our case.
Treatment options for relapsed DLBCL include salvage chemotherapy and chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation. These therapies are potentially toxic, but no treatment is usually needed for asymptomatic sarcoidosis. Thus, a definitive diagnosis must be made before administering any salvage treatment. While max SUV values of >10 are considered to indicate aggressive lymphoma [4], the max SUV of sarcoidosis ranges from 2.0 to 15.8 [5], making it difficult to discriminate between lymphoma and sarcoidosis just by PET scan results [2]. Thus, a tissue biopsy and a pathological diagnosis are essential before new therapies are administered to patients where relapsed lymphoma is suspected.
In conclusion, we have reported a case of SLS wherein sarcoidosis was diagnosed after CR from lymphoma, thereby demonstrating the importance of histological confirmation when relapsed lymphoma is suspected.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





