 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 30(2); 2015 > Article |
|
To the Editors,
Staphylococcus aureus is the pathogen most commonly isolated from patients with bone and joint infections; methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) account for 2% to 60% of S. aureus isolates [1,2,3]. There is a growing concern about the increasing rates of MRSA infection in community and nosocomial settings. Oral antibiotics provide an alternative treatment, particularly when long-term therapies are needed, such as when patients have a prosthesis [4]. In culture-negative cases of bone and joint infections, clinicians should select the appropriate oral antibiotics to combat MRSA, based on pathogen susceptibility to locally-prescribed antibiotics. This study was conducted to investigate surgical site isolates of staphylococcal species (S. aureus and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus [CNS]) obtained from patients aged Ōēź 18 years at two university hospitals (Chonbuk National University Hospital and Wonkwang University School of Medicine & Hospital) in the Chonbuk province of Korea, from January 2003 to December 2012. The cases enrolled in this study included patients with bone and joint infections diagnosed via magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography (CT) imaging, and clinical symptoms of infection such as pain or tenderness, or limited movement over the affected bone or joint, as well as fever or chills. The results of the joint fluid analyses were used in the diagnosis of septic arthritis. The bacterial strains were identified and the antimicrobial susceptibility of the clinical isolates was evaluated using the standard Vitek2 (bioMeriux Vitek Inc., Hazelwood, MO, USA) automated system. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 15.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chonbuk National University Hospital. All discharges were identified using the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes for bone infection (M45), septic arthritis (M009), and cellulitis (L03). Healthcare-associated infections were defined according to the modified criteria of Friedman et al. [5], as follows: (1) the patient received intravenous therapy, wound care, or specialized nursing care at home 30 days prior to the infection; (2) the patient attended a hemodialysis clinic or received intravenous chemotherapy 30 days prior to the infection; (3) the patient had been hospitalized for acute care for 2 or more days in an acute care hospital for 90 days preceding the infection; and (4) the patient resided in a nursing home or long-term care facility. If the patient did not fulfill any of the above criteria, the episode was defined as a community-associated infection. A total of 1,080 patients with ICD-10-CM discharge codes were reviewed, and 561 patients were identified as having bone or joint infections. Among them, 228 (40.6%) contained identified bacterial species, some of which were gram-positive and included 151 staphylococcal species (126 S. aureus, 25 CNS), 20 streptococcal species, 12 enterococcal species, and six others that were not specifically identified. Gram-negative species included nine Escherichia coli, seven Pseudomonas aeruginosa, six Klebsiella, four Enterobacter, four Serratia marcescens, one Proteus, one Citrobacter, and five other species that were not specifically identified. Fungal isolates included one Candida albicans, and one Candida parapsilosis. Staphylococcus species comprised 76 (50.3%) methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus species (MSSS; 70 S. aureus, six CNS) and 75 (49.7%) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus species (MRSS; 56 S. aureus, 19 CNS). The mean age of patients with Staphylococcus species was 59.1 ┬▒ 13.9 years, and 95 (62.9%) were male. A total of 101 cases (66.9%) were community-acquired infections and 30 (19.9%) were patients with prostheses. The sources of the isolated cultures were surgical specimens (63.6%), needle wound aspiration (19.9%), CT or ultrasound guided aspiration (14.6%), and blood (2%). The rate of MRSS was higher in patients with prostheses than in patients without (86.7% [26/30] vs. 40.5% [49/121]). The rate of MRSS infection was higher in patients with hospital-acquired infection than in patients with community-acquired infection (70.0% [35/50] vs. 39.6% [40/101]) (Table 1). The antibiotic sensitivity rates of all the staphylococcal species for linezolid, rifampin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) were excellent (100.0%, 93%, and 91.7%, respectively), but those for ciprofloxacin, clindamycin, and fusidic acid were only fair (69.7%, 67.6%, and 58.7%, respectively) (Table 2). There was a significant difference in the sensitivity between MSSS and MRSS. The sensitivity of MSSS to almost all oral antibiotics, except for fusidic acid (57.1%), was excellent. The sensitivity rates of MRSS to erythromycin, clindamycin, ciprofloxacin, fusidic acid, TMP/SMX, rifampin, and linezolid were 32%, 44%, 44%, 54.7%, 84%, 88%, and 100%, respectively. In our study, Staphylococcus species accounted for more than 65% of bacterial isolates and MRSS accounted for 50% of Staphylococcus species. According to expectations, patients with prostheses or hospital-acquired infection showed a higher rate of MRSS (86.7% and 70.0%, respectively). Compared with previous studies, which dealt exclusively with spondylitis, the rate of Staphylococcus species among isolates in our study was noticeably higher (36.6% to 39.8% vs. 66.2%) [1,2]. However, in this study, the number of patients with bone and joint infections of unknown bacterial etiology was 59.4%. This indicates that physicians select antibiotics empirically without culture information in about 60% of bone and joint infections. Based on the results in this study, monotherapy with linezolid or TMP/SMX, and rifampin in combination with TMP/SMX rather than fusidic acid or quinolone, would be an appropriate treatment for patients with bone and joint infections, especially in cases of suspected MRSA.
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by research funds from Chonbuk National University in 2013.
References
1. Kim CJ, Song KH, Park WB, et al. Microbiologically and clinically diagnosed vertebral osteomyelitis: impact of prior antibiotic exposure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012;56:2122ŌĆō2124PMID : 22232286.



2. Kim YI, Kim SE, Jang HC, Jung SI, Song SK, Park KH. Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of infectious spondylitis. Infect Chemother 2011;43:48ŌĆō54.

3. Tice AD, Hoaglund PA, Shoultz DA. Risk factors and treatment outcomes in osteomyelitis. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003;51:1261ŌĆō1268PMID : 12668581.


Table┬Ā1
General characteristics of study populations infected with Staphylococcus species (n = 151)

Table┬Ā2
Antibiogram of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus
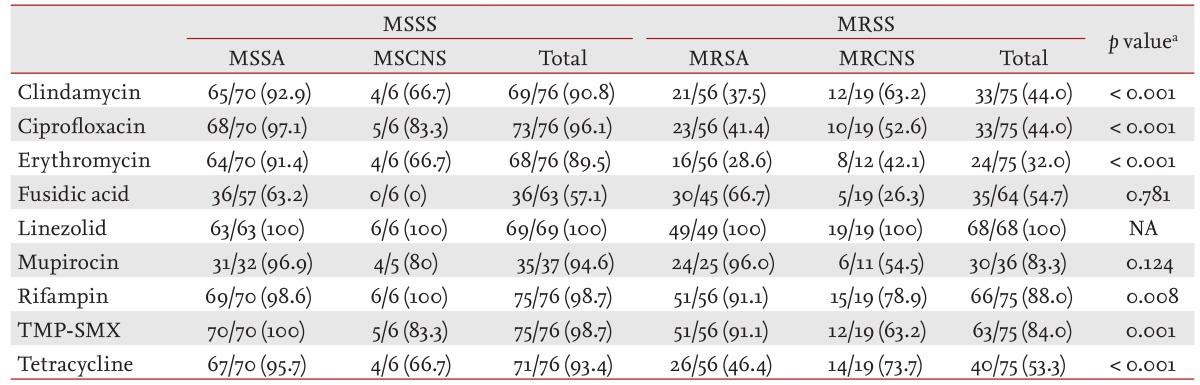
Values are presented as number (%).
MSSS, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus species (S. aureus 70 and CNS 6); MRSS, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus species (S. aureus 56 and CNS 19); MSSA, methicillin-sensitive S. aureus; MSCNS, methicillin-sensitive coagulase negative Staphylococcus; MRSA, methicillin-resistant S. aureus; MRCNS, methicillin-resistant coagulase negative Staphylococcus; NA, not available.
aAnalyzed by chi-square test between MSSS vs. MRSS.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



