INTRODUCTION
Background and purpose
Scope and subjects
Method of development
DEFINITIONS
Influenza-like illness
High risk groups
Persons at high risk for severe or complicated influenza
Children aged less than 2 years and adults aged 65 years or older
Persons with chronic pulmonary diseases, cardiovascular disorders (except controlled hypertension), chronic renal diseases, chronic hepatic diseases, chronic metabolic disorders, hemoglobinopathies, neurologic disorders (including neuromuscular diseases, epilepsy, cerebral infarction, cerebral palsy, etc.), and malignancies
Persons with immunosuppression, including that caused by immunosuppressants or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
Women who are pregnant or postpartum (within 2 weeks after delivery)
Children receiving chronic aspirin therapy
Persons with obesity
Residents of long-term care facilities
Healthcare workers
INFLUENZA OVERVIEW
Epidemiology
Transmission
Clinical course
Diagnosis
Treatment
PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF INFLUENZA IN A MEDICAL INSTITUTION
Vaccination
Priority subjects for vaccination
-
Persons at high risk for severe or complicated influenza
- Children aged less than 2 years and adults aged 65 years or older
- Persons with chronic pulmonary diseases, cardiovascular disorders (except controlled hypertension), chronic renal diseases, chronic hepatic diseases, chronic metabolic disorders, hemoglobinopathies, neurologic disorders (including neuromuscular diseases, epilepsy, cerebral infarction, cerebral palsy, etc.), and malignancies
- Persons with immunosuppression, including that caused by immunosuppressants or HIV infection
- Women who are pregnant or postpartum (within 2 weeks after delivery)
- Children receiving chronic aspirin therapy
- Persons with obesity
- Residents of long-term care facilities
Healthcare workers
Vaccination for hospitalized patients
Vaccination for healthcare workers
Adherence to precautions
Adherence to standard precautions
Adherence to droplet precautions
Precautions when performing aerosol-generating procedures
Influenza surveillance
Surveillance during influenza season
Surveillance in patients with contact to influenza
Surveillance during an outbreak in a medical institution
Infection control according to the environment and facilities of the institution
The entrance of a medical institution
Outpatient clinic
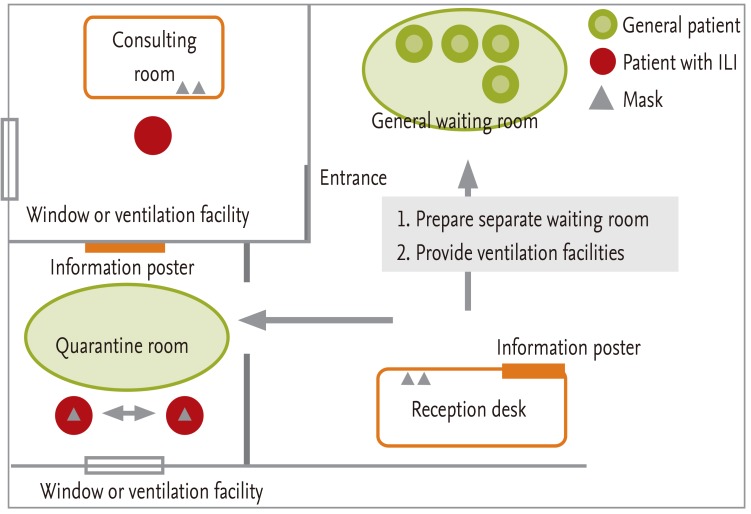
When installation of a quarantine waiting room is possible
When installation of a quarantine waiting room is difficult
Emergency room
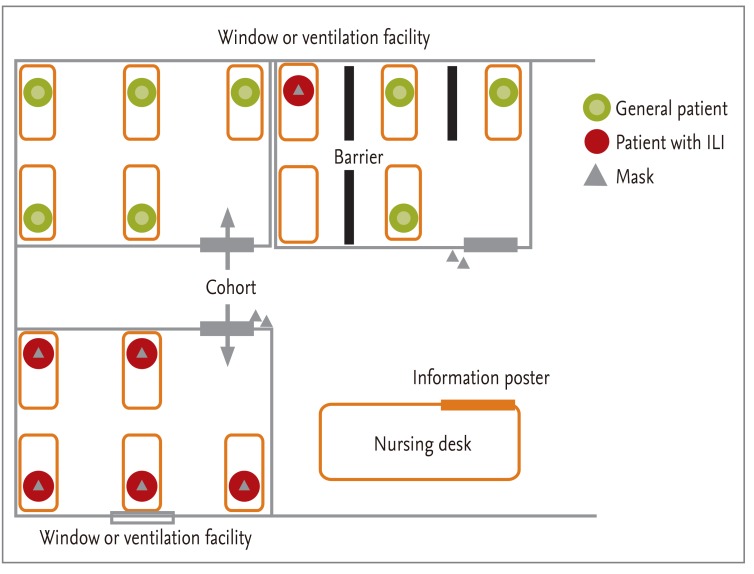
Ward
Infection control according to different situations
Sporadic cases of influenza in hospitalized patients
Laboratory diagnosis when patients suspected of influenza occur
Patient management
1) Adherence to precautions
2) Restriction of movement
3) Administration of antiviral agents for treatment
4) Surveillance and early treatment for influenza in patients exposed to influenza
5) Duration of isolation
Management of high risk patients exposed to influenza
Definition of exposure
Definition of high risk group
Persons at high risk for severe or complicated influenza
Children aged less than 2 years and elderly aged 65 years or older
Patients with chronic respiratory disease, cardiovascular disorders (excluding isolated hypertension), chronic renal disease, chronic liver disease, metabolic disorders, hemoglobinopathy, neurologic disorders (neuromuscular diseases, epilepsy, cerebral infarction, cerebral palsy, etc.), and malignancy
Patients taking immunosuppressants or who are at immunodeficiency conditions such as HIV infection
Pregnant women and mothers who gave birth within 2 weeks
Children with long-term aspirin therapy, obesity, residents of long-term care facilities
Prophylactic use of antiviral agents for high risk patients with influenza exposure
Outbreak
Definition of an outbreak
Management
2) Restriction of movement
3) Vaccination
4) Administration of antiviral agents
5) Active surveillance
Management and education of subjects excluding patients
Management of visitors
Management of caregivers
Management of healthcare workers
Healthcare workers with suspected or confirmed influenza
Medical staffs who contact with patients requiring a protected environment
Environment management
Cleaning and disinfection
Cleaners should wear masks and gloves.
Surfaces that are frequently touched by patients (doorknobs, bedrails, tables, mattresses, phones, call bells) should be thoroughly disinfected every day and after patient discharge using environmental disinfectant (e.g., degree 4 ammonium agent, chloride based disinfectant [bleach diluted to 1:100]).
Surfaces such as floors and table tops should be cleaned regularly.
Walls, blinds, and window curtains are only cleaned when contamination is visible.
Disinfectant should be not sprayed when cleaning.
When blood or other potential infective material is spilled, contaminants should be removed immediately using a spill kit.
Used instruments should be disinfected with disinfectant before using with other patients.
Management of linen
It can be washed together with other laundry but take precautions that workers moving the laundry do not contact with the contaminated linen and do not shake the laundry.
Put into a separate bag and seal it within the room.
Wear gloves when moving linen.
Wear gloves and a gown when coming in direct contact with contaminated laundry.
Perform hand sanitation after laundry.








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





