 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 26(4); 2011 > Article |
|
Abstract
Airway remodeling in asthma is a result of persistent inflammation and epithelial damage in response to repetitive injury. Recent studies have identified several important mediators associated with airway remodeling in asthma, including transforming growth factor-╬▓, interleukin (IL)-5, basic fibroblast growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, LIGHT, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-╬▒, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, IL-33, and IL-25. In addition, the epithelium mesenchymal transformation (EMT) induced by environmental factors may play an important role in initiating this process. Diagnostic methods using sputum and blood biomarkers as well as radiological interventions have been developed to distinguish between asthma sub-phenotypes. Human clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate biological therapies that target individual inflammatory cells or mediators including anti IgE, anti IL-5, and anti TNF-╬▒. Furthermore, new drugs such as c-kit/platelet-derived growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors, endothelin-1 receptor antagonists, calcium channel inhibitors, and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have been developed to treat asthma-related symptoms. In addition to targeting specific inflammatory cells or mediators, preventing the initiation of EMT may be important for targeted treatment. Interestingly, bronchial thermoplasty reduces smooth muscle mass in patients with severe asthma and improves asthma-specific quality of life, particularly by reducing severe exacerbation and healthcare use. A wide range of different therapeutic approaches has been developed to address the immunological processes of asthma and to treat this complex chronic illness. An important future direction may be to investigate the role of mediators involved in the development of airway remodeling to enhance asthma therapy.
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airway that is characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells and structural changes that are referred to as "airway remodeling." Classically, airway remodeling in patients with asthma constitutes subepithelial fibrosis, increased deposition of extracellular matrix protein, goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus gland hypertrophy, smooth muscle hypertrophy and hyperplasia, and epithelial damage [1-3]. Candidate cells involved in airway remodeling are eosinophils, T-lymphocytes, mast cells, epithelia, macrophages, airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells, and fibroblasts. Immune cells provide mediators that are involved in the process of airway remodeling [4-6]. Several mediators such as transforming growth factor-╬▓ (TGF-╬▓), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), ADAM metallopeptidase domain 33 (ADAM-33), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and Th2 cytokines (interleukin [IL]-5, IL-13, IL-4, and IL-9) are linked to remodeling [4-6]. Additional mediators have recently been identified including LIGHT (TNFSF14), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-╬▒, and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) [7-10]. Epithelial cells are also important in the initiation of allergic inflammation. Epithelial injury results in the persistent activation of epithelial mesenchymal transforming unit (EMTU), which promotes airway remodeling, leading to persistent asthma [10,11]. Epithelial injury increases the expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-33, and IL-25, which induce Th2 memory cell expansion and cytokine secretion [12]. Clinicians seek additional options other than the currently available conventional treatments to improve the condition of patients with severe asthma and to spare systemic corticosteroid administration. This review presents recent advances in the mechanism, diagnosis, and treatment of asthma, focusing on the use of mediators for airway remodeling therapy, as well as procedures that assess asthma severity. Animal research and human studies have enabled clinicians to better evaluate the extent of airway remodeling and to design specific treatment strategies appropriate for each patient.
Animal studies using models of airway remodeling and human studies both support the finding that immune or inflammatory cells and mediators are important in the pathogenesis of airway remodeling (Fig. 1). For example, recent studies have demonstrated that environmental factors cause a defect in the epithelia, inducing an innate immune response by activating dendritic cells and Th2 memory cells to release mediators linked to remodeling [13]. In addition, eosinophils are immune cells that express TGF-╬▓, which acts as a key mediator during airway remodeling. Studies using anti IL-5 antibody to deplete eosinophils have reported a link between eosinophilic depletion and decreased TGF-╬▓ expression. Other cell types such as bronchial epithelial cells and macrophages may also express TGF-╬▓ in the lung. It is essential to understand the link between cells and mediators during remodeling to enhance current biological therapies for asthma.
Allergen-induced murine models of airway remodeling have highlighted the importance of eosinophils during airway remodeling. IL-5 transgenic mice exhibit an increase in eosinophils in the lung, accumulation of peribronchial eosinophils, goblet cell hyperplasia, epithelial hypertrophy, and focal collagen deposition. They also show airway hyper-responsiveness (AHR) to methacholine in the absence of an aerosolized antigen challenge [4]. IL-5, chemokine receptor (CCR)-3, and siglec-8(F) are critical molecules associated with eosinophilic trafficking in target organs.
IL-5 is a key cytokine that regulates the proliferation and differentiation of eosinophils, as well as the trafficking of eosinophils from the bone marrow to the lung [14,15]. A remarkable reduction in TGF-╬▓-expressing eosinophils occurs in the remodeled airways of IL-5-deficient mice. Anti IL-5 treatment significantly reduces levels of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) eosinophils and remodeling, as assessed by reduced deposition of the extracellular matrix-associated remodeling proteins procollagen and tenascin [16]. Furthermore, the anti IL-5 antibody mepolizumab decreases airway thickness and wall area in patients with refractory asthma [17]. Several anti IL-5 antibodies including mepolizumab, reslizumab, and enralizumab (MEDI563) are now in clinical trials. However, blocking IL-5 alone only reduces 50-60% of tissue eosinophils; therefore, additional blocking of eosinophil trafficking may be required to completely block eosinophils.
CCR-3 is a chemokine receptor expressed by eosinophils that mediates chemotaxis in response to chemokines including eotaxin and RANTES. CCR-3-deficient mice and eotaxin-deficient mice show decreased levels of airway eosinophilia and mucus production [6]. Reduced subepithelial fibrosis and goblet cell hyperplasia are observed in a mouse model of airway remodeling subjected to low-molecular-weight CCR-3 antagonists [18]. A recent study administered a CCR-3 receptor antagonist (Ki19003) to an ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma model and found that Ki19003 inhibits airway eosinophilic inflammation and peribonchial fibrosis, and increases levels of TGF-╬▓ in BAL [19]. An oral CCR-3 antagonist (GW766944) is now on clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01160224).
Siglec-8 is highly expressed on human eosinophils and is a candidate molecule that may be targeted to alleviate eosinophilic inflammation. The siglec-8 receptor crosslinks with eosinophils to induce an apoptotic signal. Mouse siglec-F shares many properties with human siglec-8, including predominant expression on eosinophils and unique ligand specificity. Thus, mouse siglec-F has provided insight into the potential role of siglec-8 in human allergic disease [20,21]. A recent study used a chronic OVA-challenged murine model to demonstrate that siglec-F plays a role in airway remodeling by modulating eosinophilic apoptosis in lung and bone marrow; furthermore, treatments using anti siglec-F antibody significantly reduced the number of peribronchial TGF-╬▓-expressing eosinophils and the level of peribronchial fibrosis [22]. A significant increase in mucus production, peribronchial fibrosis, and smooth muscle thickness occurs in chronic OVA-challenged mice deficient in siglec-F; IL-4 or IL-13 significantly increase the level of siglec-F ligand expression in bronchial epithelium. Thus, human siglec-8 may be an additional target to modulate eosinophil recruiting during human airway remodeling [23].
The TNF superfamily (TNFSFs) consists of many membrane-bound and soluble proteins that act as key mediators of asthmatic inflammation such as the OX40 ligand (TNFSF4) and TNF itself. The TNF family ligand LIGHT (TNFSF14) is expressed on B and T cells but not on macrophages and granulocytes [7]. LIGHT binds the herpesvirus entry mediator (TNFRSF14). It also acts as a ligand for membrane lymphotoxin (LT╬▒╬▓). Lymphotoxin ╬▓ receptor (LT╬▓R) is strongly expressed on macrophages [7]. A recent study reported an increase in soluble LIGHT in the sputum of patients with asthma, highlighting the role of LIGHT (TNFSF14) in asthma. LIGHT levels in BAL fluid are higher in patients with pulmonary fibrosis [24]. Pharmacological inhibition of LIGHT using the IgG Fc domain and LT╬▓R reduces lung fibrosis, smooth muscle hyperplasia, and AHR in mouse models of chronic asthma. LIGHT-deficient mice also show a similar disruption of fibrosis and smooth muscle hyperplasia, whereas exogenous administration of LIGHT induces fibrosis and smooth muscle hyperplasia. Thus, LIGHT may be a potential target to prevent and/or treat airway remodeling [24].
TGF-╬▓ is a profibrotic cytokine, another key airway remodeling mediator in asthma [25]. TGF-╬▓ is produced by several cell types, including epithelial cells, eosinophils, macrophages, and fibroblasts. It is involved in epithelial changes, subepithelial fibrosis, ASM remodeling, microvascular changes, and increased mucus production. Subepithelial fibrosis is mediated by the induction of TGF-╬▓ expression and the consequent activation of myofibroblasts, which produce extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen and fibronectin. TGF-╬▓ enhances the migration of ASM and produces antiapoptotic effects that stimulate ASM proliferation. Microvascular congestion by secretion of proangiogenic factors such as VEGF and upregulation of mucus production may be induced by TGF-╬▓ stimulation [26,27]. Furthermore, TGF-╬▓ decreases the production of enzymes that degrade the extracellular matrix (collagenase) and increases the production of proteins that inhibit enzymes that degrade the extracellular matrix (tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease, TIMP) [28]. Smad3 is a TGF-╬▓ signaling molecule. Smad3-deficient mice chronically challenged with allergen show reduced numbers of peribronchial myofibroblasts and decreased peribronchial fibrosis [29]. Neutralizing TGF-╬▓ expression either by blocking TGF-╬▓ signaling in the Smad-3 pathway or administering anti activin-A significantly reduces peribronchial fibrosis, ASM proliferation, and mucus production [30]. Increased levels of TGF-╬▓ have been reported in BAL and biopsy specimens of patients with asthma [31,32]. TGF-╬▓ expression correlates with the degree of subepithelial fibrosis. Levels of TGF-╬▓ increase significantly in patients with severe asthma and prominent airway eosinophilic inflammation. TGF-╬▓ levels in the lungs of patients with asthma decrease by depleting eosinophils through anti IL-5 antibody treatment. Surprisingly, very few preclinical experiments using TGF-╬▓ inhibitors have been published [33]. Currently, a monoclonal anti TGF-╬▓ antibody (GC1008) is being tested in a phase I study to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (NCT00125385).
bFGF is a cytokine that is mitogenic to fibroblasts and smooth muscle [34-36], and has proangiogenic properties related to angiogenesis during airway remodeling. Cellular sources of bFGF include macrophages, endothelial cells, mast cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts [37]. bFGF binds to 1-4 high-affinity FGF receptors [38]. A study using chronic OVA-induced airway remodeling demonstrated that bFGF is expressed by peribronchial macrophages and epithelium. Furthermore, bFGF and TGF-╬▓1 are coexpressed on peribronchial macrophages, implying an association between these molecules during airway remodeling. The synergistic effects of bFGF and TGF-╬▓1 have also been found in other cell types [39]. Mast cell-derived activin A, an activator of Smad2/3/4 and a potent inducer of human ASM cell proliferation, could be the main TGF-╬▓ superfamily member that synergizes with bFGF to induce ASM hyperplasia [40]. Interestingly, bFGF administration reduces airway inflammation and AHR in an acute OVA-challenged murine model of asthma [41]. Clinical studies have found an increase in the presence of bFGF immunoreactive cells and levels of bFGF protein in the sputum and BAL fluid of patients with asthma compared to non-asthmatic controls [42,43]. Further studies are needed to clarify the role of bFGF during airway remodeling.
VEGF is a critical multifunctional angiogenic regulator that stimulates epithelial cell proliferation, blood vessel formation, and endothelial cell survival [44]. VEGF has been postulated to contribute to asthmatic tissue edema through its effects on vascular permeability [45,46]. Lung-targeted VEGF165 transgenic mice have an asthma-like phenotype that includes not only vascular remodeling but also inflammation, edema, mucus metaplasia, myocyte hyperplasia, and AHR [47]. Recent studies that investigated the mechanism of VEGF in a murine model of asthma have shown that nitric oxide is an important mediator of the extravascular VEGF remodeling effects [48]. VEGF is elevated in induced sputum, BAL fluid, and bronchial biopsies of patients with asthma [49]. A comparative study of two angiogenic factors, VEGF and angiogenin, demonstrated that children with asthma have significantly higher levels of VEGF and angiogenin than non-asthmatic children, and that the increased levels of VEGF and angiogenin are correlated to asthma severity [50]. In addition, sputum VEGF levels in smoking patients with asthma are significantly lower than those in nonsmoking patients with asthma but remain higher than those in control subjects [51]. Based on these findings, VEGF may be involved in vascular and airway remodeling in patients with asthma.
TNF-╬▒ is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that increases in the airways of patients with asthma. TNF was initially believed to be produced primarily by macrophages but has been shown to be expressed by a broad range of cell types including mast cells and eosinophils [52,53]. Allergen-challenged TNFp55/p75 receptor-deficient mice have significantly reduced levels of peribronchial eosinophils and fibrosis [8]. Studies on mast cell function-deficient mice have demonstrated that mast cells play an important role in eosinophilic lung inflammation, cytokine production, AHR, and production of adhesion molecules, including intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM-1) by liberating TNF-╬▒ [53,54]. Increased TNF-╬▒ levels in BAL are associated with increased levels of remodeling in patients with asthma. Inhibiting TNF-╬▒ reduces asthma exacerbation, further suggesting that TNF-╬▒ may be related to airway remodeling. A study using etanercept, a fusion protein consisting of the type II TNF receptor that binds both TNF-╬▒ and ╬▓, found that patients with refractory asthma have increased expression of membrane-bound TNF-╬▒, TNF-╬▒ receptor 1, and TNF-╬▒ converting enzyme [55]. These findings collectively suggest that TNF-╬▒ may be involved in asthma airway remodeling through eosinophils and mast cells.
MMP-9 belongs to a family of extracellular proteases that are responsible for degrading the extracellular matrix during tissue remodeling. An example of MMP-9 activity is the broad-spectrum MMPI inhibitor R 94128, which reduces the development of allergic airway inflammation [56]. An MMP-9-deficient murine asthma model showed reduced peribronchial fibrosis and total lung collagen compared to wild-type mice, yet no difference was detected in mucus expression, smooth muscle thickness, or airway responsiveness [57]. Moreover, human studies have shown that levels of MMP-9 (gelatinase B) increase significantly in BAL fluid, blood, and sputum of patients with allergic asthma [58]. Thus, therapies targeting MMP-9 may not only decrease airway inflammation but also reduce the levels of peribronchial fibrosis during airway remodeling.
ADAM-33 is a disintegrin and a metalloprotease expressed in patients with asthma [59]. Allergen-challenged ADAM-33-deficient mice show no significant differences in airway hyper-reactivity, IgE production, mucus metaplasia, or airway inflammation compared to wild type mice [1]. However, ADAM-33 mRNA expression is significantly enhanced in the lung tissue of OVA-challenged mice [60]. A genetic polymorphism in ADAM-33 is a novel asthma-associated gene, which results in an accelerated decline in lung function over time. Furthermore, ADAM-33 mRNA expression is higher in patients with severe asthma than in patients with mild asthma or without asthma [61]. ADAM-33 may be a key molecule that contributes to ASM and vascular remodeling.
The epithelium plays an important role initiating allergic inflammation. Epithelial injury results in persistent activation of the EMTU [11], an attenuated fibroblast sheath that is in contact with bronchial epithelium and coordinates airway remodeling following epithelial injury. Epithelial injury caused by viruses, fungus, double-stranded RNA, and protease allergens increase TSLP, IL-33, and IL-25 expression, which induces Th2 memory cell expansion and Th2 cytokine secretion [62].
TSLP, a distant paralog of IL-7, is a type I cytokine and a member of the IL-2 cytokine family. TSLP is expressed by the epithelium, keratinocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and mast cells. A recent study demonstrated that TNF-╬▒ induces TSLP in human ASM as well [63]. Transgenic mice that overexpress TSLP show increased levels of allergic inflammation similar to that in human asthma. Allergen-challenged mice deficient in TSLP-receptor knockdown exhibit suppressed airway inflammation [64]. Zhang et al. [65] demonstrated that a soluble TSLP antagonist, TSLPR-immunoglobulin, reduces the severity of allergic disease. House dust mite protease upregulates epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent protease activated receptor-2 and thymus and activates activation-regulated chemokine and TSLP, which results in epithelium mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and, ultimately, airway remodeling [66,67]. In humans, increased levels of TSLP have been found in airway epithelium and other inflammatory cells of patients suffering from asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder [68,69]. TSLP expression in the airways of patients with asthma is correlated with expression of Th2 cytokines and disease severity [70]. Thus, TSLP may play an important role in asthma airway remodeling by inducing EMT.
IL-25 (IL-17E) is a member of the IL-17 cytokine family that evokes TH2 cell-mediated immunity to parasitic infections [71]. Its upregulation induces a robust expansion of TH2 memory cells by TSLP-activated dendritic cells [12]. IL-25 is not only expressed by lung epithelial cells but also by mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils and is considered part of the innate immune response [72,73]. Moreover, IL-25R is also found on eosinophils, monocytes, ASM cells, and fibroblasts [12]; the expression of IL-25R on these inflammatory and structural cells suggests that it may be involved in airway remodeling. Transgenic overexpression of IL-25 leads to mucus production and airway infiltration by macrophages and eosinophils, whereas IL-25 blockade reduces airway inflammation and TH2 cytokine production in a murine allergen-induced asthma model [72]. Furthermore, studies on IL-25-deficient mice were unable to induce a Th2 response upon Trichuris muris infection, and repeated nasal administration of IL-25 resulted in IL-5 and IL-13 expression in the lung [71,74]. In human studies, IL-25+, IL-25R, and CD31+/IL-25R+ cells are significantly elevated in the bronchial mucosa of patients with asthma, and the number of IL-25+ cells correlate inversely with FEV1, suggesting that IL-25 may contribute to angiogenesis by increasing VEGF/VEGF receptor expression in patients with asthma [75]. Taken together, IL-25 may be involved in airway remodeling by inducing Th2 cytokines such as IL-5 and IL-13 or by directly inducing angiogenesis.
IL-33 is a member of the IL-1 family, associated with promoting a systemic Th2 response [76]. IL-33 expression occurs in a variety of cells, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, cardiac myocytes, keratinocytes, adipocytes, and alveolar macrophages [77-79]. The IL-33 receptor (ST2) is also expressed on Th2 cells, innate lymphoid cells, mast cells, eosinophils, macrophages, and basophils. IL-33 stimulates Th2 cytokine secretion such as IL-5 and IL-13 from these cells types. In animal studies, administering IL-33 into the lung induces AHR and goblet cell hyperplasia and upregulates IL-5, IL-4, and IL-13 in the lung [80,81]. IL-33 transgenic mice spontaneously develop eosinophilic inflammation [82]. Administering the anti IL-33 also abrogates Th2 cytokine secretion and eosinophilic recruitment [83]. IL-33-deficient mice are resistant to allergen-induced AHR [84]. The subcutaneous administration of IL-33 results in ST2-dependent recruitment of eosinophils, CD3+ lymphocytes, F4/80 macrophages, increased IL-13 mRNA, and the development of cutaneous fibrosis [85]. In human studies, IL-33 expression in epithelial cells increases in patients with asthma compared to healthy individuals and increases more dramatically in patients with severe asthma [86]. IL-33 and ST2 gene polymorphisms have been linked to asthma [87]. Higher IL-33 expression is also found in other allergic diseases, including allergic conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis. It is difficult to make a direct correlation between IL-33 and airway remodeling. However, previous findings suggest that IL-33 may be an important factor during airway remodeling.
Non-invasive methods such as the pulmonary function test (PFT), high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), and magnetic resonance image (MRI) are utilized to measure airway function and the pathology of the lung to assess the degree of airway remodeling. Invasive methods such as sputum induction are utilized for a closer examination of airway remodeling to assess inflammatory cells, determine blood eosinophil numbers, and measure levels of inflammatory mediators. Furthermore, bronchoscopic biopsy or BAL, and endobronchial ultrasonography (EBUS) may also be used to assess the level of airway remodeling (Fig. 2).
PFTs using methacholine or exercise provocation have been a traditional diagnostic tool for assessing AHR in patients with asthma. Studies have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of PFT as an airway-remodeling assessment method. A longitudinal population study of asthma from childhood to adulthood demonstrated that a low postbronchodilator ratio of FEV1 to vital capacity is useful as an airway remodeling marker, which, in turn, was associated with an accelerated decline in lung function and reversibility [88]. Many studies have shown that computed tomography scans may be useful for assessing airway remodeling by measuring bronchial wall thickness [89]. A recent retrospective quantitative analysis of HRCT scans in 99 patients with severe asthma versus 16 healthy controls demonstrated that the right upper apical segmental bronchus (RB1) wall area (WA) % increases in patients with severe asthma, whereas the ratio of lumen area to body surface area decreases. Moreover, increased WA% of RB1 in patients with severe asthma was associated with impaired lung function and neutrophilic inflammation in a sputum study [90]. Quantitative densitometry of computed tomography (CT) images serves as an additional tool for non-invasively studying airway remodeling in patients with asthma [91]. Hyperpolarized gas MRIs of patients with asthma commonly exhibit ventilation defects; the size and the extent of the ventilation defects are correlated with the severity of regional airway closure and narrowing. A recent study demonstrated that the ventilation defects on MRI images of patients with moderate to severe asthma are significantly greater than those of patients with mild asthma [92]. Another study using hyperpolarized helium-3 MRI found a moderate correlation between the number of ventilation defects and predicted FEV1%. However, no significant correlation was found between the total number of ventilation defects and whole lung inflammation markers in BAL analysis [93]. CT and MRI have been and will continue to be instrumental for assessing airway remodeling to provide treatments for asthma in the future.
Sputum induction is another useful tool that assesses the degree of inflammation by measuring the levels of mediators in patients with asthma. Because the levels of lung inflammation correlate with airway remodeling severity, the absolute numbers of inflammatory cells, including eosinophils, neutrophils, and macrophages, are used to help assess the development of airway remodeling. In a study that examined osteopontin in patients with severe refractory asthma, the levels of sputum supernatant cysteinyl leukotrienes IL-13, TGF-╬▓1, and eosinophilic cationic protein (ECP) were higher in patients with severe asthma than in healthy subjects [94]. Another study, which focused on persistent remodeling and eosinophil activation, showed that histamine and ECP levels from patients with asthma in complete remission are significantly lower than those in patients who continue to suffer from severe asthma [95]. A study of the effects of formoterol-budesonide on airway remodeling in patients with asthma demonstrated a significant decrease in the levels of MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TGF-╬▓1 after treatment [96].
Blood eosinophil number, serum IgE level, and other biomarkers may also indicate the level of airway remodeling. A study of occupational asthma biomarkers demonstrated that serum VEGF, MMP-9, and other markers could be measured in three diisocyanate-induced patients with occupational asthma (TDI-OA) and found that serum MMP-9 level is elevated in patients with TDI-OA compared to that in healthy control subjects [97]. Thus, measuring sputum and serum eosinophil biomarker levels could be useful for assessing the degree of asthmatic airway remodeling.
EBUS has been used to assess bronchial wall remodeling in patients with asthma [98]. This method correlates asthma severity parameters to bronchial wall layers. Furthermore, a bronchial biopsy with specific immunohistochemical stains and analysis of BAL fluid by bronchoscopy can help determine the degree of remodeling and inflammatory cell involvement.
Conventional treatments do not adequately control some severe cases of asthma. This has been a major clinical challenge, which is becoming an important healthcare issue. In the last decade, this dilemma has fostered the development of several biological and pharmacological agents to provide possible mechanical treatments for ASM. Phenotyping each patient will be very important to specifically tailor treatment for patients with severe asthma.
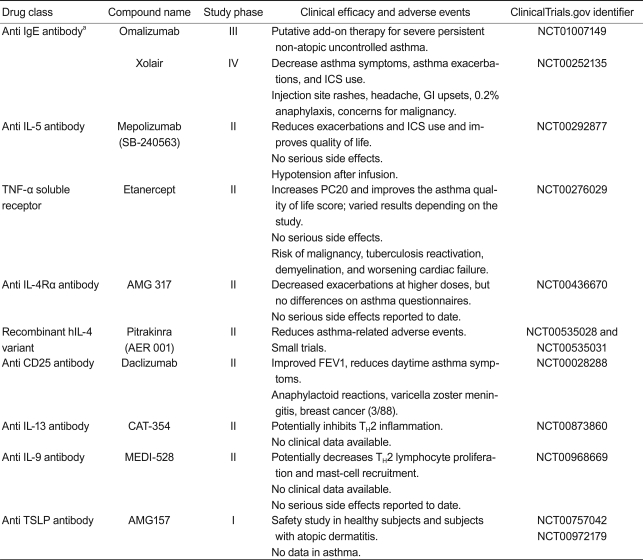
Monoclonal antibodies against IgE or cytokines including anti IgE (omalizumab), anti IL-5 (mepilozumab), and anti TNF-╬▒ (etanercept) have been investigated in patients with asthma. Other candidates for antibody treatment include anti IL-4, anti IL-4/13, anti IL-9, anti CD25, and anti TSLP, which are currently under clinical trial.
Omalizumab and Xolair are humanized anti IgE antibodies that prevent IgE from interacting with the high-affinity portion of the IgE receptor [99]. These drugs prevent degranulation of allergen-bound mast cells, which results in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which are associated with airway remodeling [100]. anti IgE therapy decreases the level of IgE in patients with allergic asthma. It also decreases the number of inflammatory cells, including mast cells, eosinophils, FceRI positive cells, IL-4+ cells, CD3, CD4, and CD8 T cells in the asthmatic bronchus [101]. Furthermore, anti IgE therapy prevents the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors such as TGF-╬▓ [102]. Markers of inflammation and features of airway remodeling are currently being investigated in patients with moderate to severe persistent allergic asthma by treatment with omalizumab (Clinical Trials.gov identifier: NCT00670930). An anti IgE antibody (omalizumab) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2003 to treat patients of greater than 12 years of age with moderate to severe persistent allergic asthma. In a recent study on a murine model of chronic asthma, anti IgE therapy decreased airway inflammation and remodeling features, including lung collagen, hydroxyproline, and ╬▒-smooth muscle actin but did not affect levels of IL-10, TGF-╬▓, or activin A [103]. Clinical studies and a few animal studies have shown that anti IgE therapy may be a good candidate for relieving airway remodeling but may only be applicable to patients who suffer from severe allergic asthma correlated with a high IgE level.
Mepolizumab is a high-affinity, anti IL-5, humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that blocks IL-5 binding to eosinophils. Based on animal studies, blocking IL-5 may be related to improving airway remodeling via eosinophil regulation of TGF-╬▓ during the remodeling process. This antibody was initially evaluated in a group of patients with mild to moderate asthma and was demonstrated to significantly reduce blood eosinophils but did not result in a significant improvement in clinical parameters [16]. A study on 61 patients found that mepolizumab decreases blood and sputum eosinophil levels, prevents further asthma exacerbation, and improves asthma-related quality-of-life scores [104]. For example, a clinical trial in which mepolizumab was given to patients with asthma for 6 months showed reduced exacerbation frequency and steroid requirements [104,105]. Gruenberg and Busse's study [106] suggested that patients who are being treated with steroid therapy and continue to have persistent sputum eosinophilia may benefit from an agent that can specifically target and reduce eosinophils. Clinical trials with other anti IL-5 antibodies, including reslizumab and enralizumab, are currently in progress.
Etanercept (a soluble form of the recombinant TNF-╬▒ human receptor) has been used to improve FEV1 scores and the quality of life of patients with severe refractory asthma [55]. However, a recent phase II clinical study of 132 patients with moderate to severe asthma who used etanercept for 12 weeks reported no significant difference in clinical outcomes between the placebo and treatment groups [107]. Even though etanercept is well tolerated, doctors and patients should consider the risk/benefit ratio before administration. Some studies have shown that the anti TNF-╬▒ antibody infliximab significantly reduces asthma exacerbation [108]; however, other studies that evaluated golimumab, another type of anti TNF-╬▒ antibody, on 309 patients with severe asthma demonstrated no measurable changes in lung function, symptoms, or exacerbation rates in the treatment group [109]. Serious adverse events such as infections and malignancy occurred and resulted in early discontinuation. Although TNF-╬▒ blocking has resulted in promising early results for treating airway remodeling, its clinical application to asthma has been unsuccessful and requires further research to continue.
IL-4 contributes to the development of asthma by inducing B-cells to switch from the production of IgM to IgE, and promotes the aggregation of eosinophils, lymphocytes, basophils, and monocytes in target tissues. In addition, IL-4 mediates differentiation of naïve T-cells into Th2 cells capable of producing IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. Nuvance, a soluble IL-4 receptor antagonist, improves asthma symptoms and reduces FEV1 in patients with moderate to severe asthma. However, subsequent studies with a larger number of patients did not reproduce the good clinical response [110]. Pascolizumab, an anti IL-4 antibody, also initially showed promising results, but clinical studies did not show favorable results [111]. These negative results suggest that IL-4 blocking alone may not be sufficient to resolve the allergic inflammation process.
Receptors for IL-4 and IL-13 are regulated by similar signaling pathways. Pitrakinra, a recombinant human IL-4 variant, binds to the IL-4 R╬▒ complex and prevents binding of both IL-4 and IL-13 [112]. Subcutaneous administration of pitrakinra significantly reduces asthma-related symptoms. In addition, a 12-week study by Corren et al. [113] showed that AMG 317, an anti IL-4R╬▒ antibody, inhibits the effects of IL-4 and IL-13. They demonstrated that the number of asthma exacerbations decreased in the higher-dose groups without significant clinical efficacy. Therefore, targeting IL-4 and IL-13 together shows a better clinical response than IL-4 blocking alone, but larger placebo-controlled trials may be needed to demonstrate its clinical significance.
CD25 is an IL-2 receptor related to antigen-dependent T-cell proliferation and secretion of Th1 and Th2 cytokines by activated lymphocytes. Daclizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to the CD25 ╬▒-subunit. A 12-week study on 115 patients with moderate to severe asthma who received daclizumab demonstrated improvement in FEV1, a decrease in daytime asthma symptoms, and a decrease in short-acting ╬▓-agonist use [114]. However, side effects including an anaphylatoid reaction, varicella zoster meningitis, and breast cancer were reported. New cytokine targets such as anti IL-9 antibody (Med-528), anti CD23 antibody (lumiliximab), and anti TSLP antibody (AMG 157) have emerged and are now in clinical trials.
Smooth muscle hypertrophy, hyperplasia, and deposition of extracellular matrix have been treatment targets for airway remodeling. Clinical studies related to new drugs, including a c-kit/platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (mastinib), an endothelin (ET)-1 receptor antagonist (sitaxentan), a calcium channel inhibitor (gallopamil), and statins are now being conducted.
The c-kit/PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate decreases peribronchial collagen deposition and ASM thickening in a murine model of asthma [115]. Based on these animal study results, a clinical study evaluated the effects of mastinib in a small group of patients with severe persistent asthma [116]. Mastinib lowered the asthma control questionnaire score and reduced the frequency of asthma exacerbations. However, no significant improvement in lung function was observed in the treatment group. Further studies on a larger number of patients are needed to determine its efficacy.
ET-1 induces bronchoconstriction, mediates eosinophil recruitment during allergic inflammation, and contributes to airway remodeling by inducing fibroblast and smooth muscle cell differentiation and proliferation [117]. Increased ET-1 expression on ASM areas is strongly correlated with airway obstruction (measured by FEV1) in patients with asthma [118]. Another study reported that an ET-1 receptor polymorphism is strongly associated with the degree of airway obstruction in a population of patients with asthma [119]. These data suggest that inhibiting the ET-1 pathway could be a potential therapeutic option in patients with steroid-refractory asthma or an irreversible airway obstruction. The ET-1 receptor antagonist sitaxentan is now in clinical trials on patients with severe persistent asthma.
Airway remodeling mainly involves increased ASM mass, which is related to increased smooth muscle cell proliferation. Calcium influx in smooth muscle cells activates calcium-calmodulin kinase IV (CamK-IV). CamK-IV then enhances mitochondrial biogenesis through subsequent activation of various transcription factors. In vitro studies show that ASM cell proliferation in patients with severe asthma is mainly mitochondria-dependent, whereas that of controls is virtually mitochondria-independent [120]. Gallopamil administration induces a reduction in mitochondrial mass and subsequent ASM cell proliferation and is now in clinical trials on patients with severe persistent asthma.
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) are well-known cholesterol-lowering agents. Interestingly, they also have pleiotropic effects, which include inhibiting ASM cell proliferation and promoting ASM cell apoptosis. Despite promising in vitro results, two clinical trials have demonstrated that neither simbastatin [121] nor atrovastatin [122] improve inflammatory outcomes and lung function in patients with allergic asthma. Lovastatin administration in patients with severe persistent asthma is now being evaluated for its effects on airway remodeling in clinical trials.
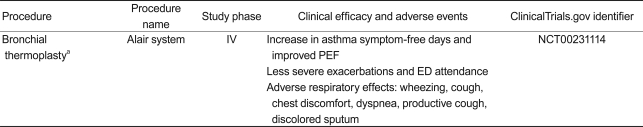
BT is a bronchoscopic procedure for patients with severe persistent asthma; it delivers thermal energy to the airway wall to reduce excess ASM. Preclinical studies have shown that BT results in a reduction in ASM and AHR in an animal model [123,124]. Initially, a clinical study with 16 patients confirmed that BT increases the number of mild to moderate asthma symptom-free days and the peak expiratory flow rate (PEF) at 3 months, in addition to reducing AHR for 2 years [125]. In a study of patients with moderate to severe asthma, BT significantly alleviated mild exacerbations, reduced the use of reliever medicine, and improved morning PEF, resulting in improved asthma-related questionnaires scores [126]. The recently conducted Asthma Intervention Research (AIR) study demonstrated that BT improves asthma-specific quality of life with a reduction in severe exacerbation and healthcare use during the post-treatment period in patients with severe asthma [127,128]. A long-term (5-year) safety study of BT (AIR trial) reported that clinical complications did not increase over time, based on the rate of adverse respiratory events. It also determined that lung function (FVC and FEV1) had not deteriorated over a 5-year period post-BT in patients with moderate to severe asthma. These findings suggest that BT treatment is a safe procedure with effects that last at least 5 years [129]. BT was approved by the FDA in April 2010 for patients with severe asthma.
Asthma is a complex disease derived from the interaction between inhaled environmental agents and the airway. This review focused on recent advances in mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of airway remodeling in patients with asthma during the last decade. Numerous animal studies and clinical trials using biological therapy, drugs, and mechanical disruption of airway remodeling have been conducted. Acquiring detailed information on asthma subtypes for individual patients will help develop more specific and effective target treatments for severe asthma. Anti IL-5 and anti IgE therapy effectively reduce asthma exacerbation in patients with severe asthma. However, human clinical trials with biological therapy targeting individual inflammatory cells and mediators, including anti TNF-╬▒ and anti IL-4 therapy, have demonstrated disappointing results during clinical application. Therefore, larger studies targeting specific asthma subtypes are needed to determine the benefits of each cytokine antagonist. Because recent studies have demonstrated that the epithelium plays an important role in the initiation of airway remodeling, preventing the EMT may be an important target for the development of more effective treatments, in addition to targeting each cell or mediator. Another candidate for severe asthma treatment is to reduce excessive ASM with BT. As mechanical disruption of ASM by thermal energy may result in adverse respiratory effects such as wheezing, chest discomfort, dyspnea, productive cough, and discolored sputum, long-term safety after treatment has been an issue. Since recent studies have shown that clinical complications did not increase overtime, BT may be a safe procedure for severe asthma patients. Over the last decade, animal and human studies have provided valuable insight into asthma airway remodeling. However, many aspects of asthma airway remodeling still remain elusive; thus, it is important to further explore the mechanisms of airway remodeling and investigate mediators that have the potential to be used as clinical treatments.
Acknowledgements
I thank Alexa Pham for helpful discussions and advice during the preparation of this review.
References
1. Broide DH. Immunologic and inflammatory mechanisms that drive asthma progression to remodeling. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008;121:560ŌĆō570PMID : 18328887.



2. Mauad T, Bel EH, Sterk PJ. Asthma therapy and airway remodeling. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;120:997ŌĆō1009PMID : 17681364.


3. Pascual RM, Peters SP. Airway remodeling contributes to the progressive loss of lung function in asthma: an overview. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;116:477ŌĆō486PMID : 16159612.


4. Cho JY, Miller M, Baek KJ, et al. Inhibition of airway remodeling in IL-5-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 2004;113:551ŌĆō560PMID : 14966564.



5. Humbles AA, Lloyd CM, McMillan SJ, et al. A critical role for eosinophils in allergic airways remodeling. Science 2004;305:1776ŌĆō1779PMID : 15375268.


6. Fulkerson PC, Fischetti CA, McBride ML, Hassman LM, Hogan SP, Rothenberg ME. A central regulatory role for eosinophils and the eotaxin/CCR3 axis in chronic experimental allergic airway inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:16418ŌĆō16423PMID : 17060636.



7. Doherty TA, Soroosh P, Khorram N, et al. The tumor necrosis factor family member LIGHT is a target for asthmatic airway remodeling. Nat Med 2011;17:596ŌĆō603PMID : 21499267.



8. Cho JY, Pham A, Rosenthal P, Miller M, Doherty T, Broide DH. Chronic OVA allergen challenged TNF p55/p75 receptor deficient mice have reduced airway remodeling. Int Immunopharmacol 2011;11:1038ŌĆō1044PMID : 21382533.



9. Yum HY, Cho JY, Miller M, Broide DH. Allergen-induced coexpression of bFGF and TGF-╬▓1 by macrophages in a mouse model of airway remodeling: bFGF induces macrophage TGF-╬▓1 expression in vitro. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2011;155:12ŌĆō22PMID : 21109744.



10. Holgate ST, Davies DE, Lackie PM, Wilson SJ, Puddicombe SM, Lordan JL. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000;105(2 Pt 1):193ŌĆō204PMID : 10669837.


11. Holgate ST, Arshad HS, Roberts GC, Howarth PH, Thurner P, Davies DE. A new look at the pathogenesis of asthma. Clin Sci (Lond) 2009;118:439ŌĆō450PMID : 20025610.



12. Wang YH, Liu YJ. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, OX40-ligand, and interleukin-25 in allergic responses. Clin Exp Allergy 2009;39:798ŌĆō806PMID : 19400908.



13. Jacquet A. Interactions of airway epithelium with protease allergens in the allergic response. Clin Exp Allergy 2011;41:305ŌĆō311PMID : 21121984.


15. Lopez AF, Sanderson CJ, Gamble JR, Campbell HD, Young IG, Vadas MA. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is a selective activator of human eosinophil function. J Exp Med 1988;167:219ŌĆō224PMID : 2826636.



16. Flood-Page P, Menzies-Gow A, Phipps S, et al. Anti-IL-5 treatment reduces deposition of ECM proteins in the bronchial subepithelial basement membrane of mild atopic asthmatics. J Clin Invest 2003;112:1029ŌĆō1036PMID : 14523040.



17. Haldar P, Brightling CE, Hargadon B, et al. Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med 2009;360:973ŌĆō984PMID : 19264686.



18. Wegmann M, Goggel R, Sel S, et al. Effects of a low-molecular-weight CCR-3 antagonist on chronic experimental asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2007;36:61ŌĆō67PMID : 16917075.


19. Komai M, Tanaka H, Nagao K, et al. A novel CC-chemokine receptor 3 antagonist, Ki19003, inhibits airway eosinophilia and subepithelial/peribronchial fibrosis induced by repeated antigen challenge in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 2010;112:203ŌĆō213PMID : 20134116.


20. Tateno H, Crocker PR, Paulson JC. Mouse Siglec-F and human Siglec-8 are functionally convergent paralogs that are selectively expressed on eosinophils and recognize 6'-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a preferred glycan ligand. Glycobiology 2005;15:1125ŌĆō1135PMID : 15972893.


21. Bochner BS, Alvarez RA, Mehta P, et al. Glycan array screening reveals a candidate ligand for Siglec-8. J Biol Chem 2005;280:4307ŌĆō4312PMID : 15563466.


22. Song DJ, Cho JY, Lee SY, et al. Anti-Siglec-F antibody reduces allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation and airway remodeling. J Immunol 2009;183:5333ŌĆō5341PMID : 19783675.



23. Cho JY, Song DJ, Pham A, et al. Chronic OVA allergen challenged Siglec-F deficient mice have increased mucus, remodeling, and epithelial Siglec-F ligands which are up-regulated by IL-4 and IL-13. Respir Res 2010;11:154. PMID : 21040544.



24. Luzina IG, Atamas SP, Wise R, et al. Occurrence of an activated, profibrotic pattern of gene expression in lung CD8+ T cells from scleroderma patients. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:2262ŌĆō2274PMID : 12905481.


25. Halwani R, Al-Muhsen S, Al-Jahdali H, Hamid Q. Role of transforming growth factor-╬▓ in airway remodeling in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2011;44:127ŌĆō133PMID : 20525803.


26. Yanai M, Sekizawa K, Ohrui T, Sasaki H, Takishima T. Site of airway obstruction in pulmonary disease: direct measurement of intrabronchial pressure. J Appl Physiol 1992;72:1016ŌĆō1023PMID : 1568955.


27. McMillan SJ, Xanthou G, Lloyd CM. Manipulation of allergen-induced airway remodeling by treatment with anti-TGF-beta antibody: effect on the Smad signaling pathway. J Immunol 2005;174:5774ŌĆō5780PMID : 15843580.


28. Wynn TA. Common and unique mechanisms regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. J Clin Invest 2007;117:524ŌĆō529PMID : 17332879.



29. Le AV, Cho JY, Miller M, McElwain S, Golgotiu K, Broide DH. Inhibition of allergen-induced airway remodeling in Smad 3-deficient mice. J Immunol 2007;178:7310ŌĆō7316PMID : 17513781.


30. Gregory LG, Mathie SA, Walker SA, Pegorier S, Jones CP, Lloyd CM. Overexpression of Smad2 drives house dust mite-mediated airway remodeling and airway hyperresponsiveness via activin and IL-25. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;182:143ŌĆō154PMID : 20339149.



31. Redington AE, Madden J, Frew AJ, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 in asthma: measurement in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997;156:642ŌĆō647PMID : 9279252.


32. Chakir J, Shannon J, Molet S, et al. Airway remodeling-associated mediators in moderate to severe asthma: effect of steroids on TGF-beta, IL-11, IL-17, and type I and type III collagen expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;111:1293ŌĆō1298PMID : 12789232.


33. Girodet PO, Ozier A, Bara I, Tunon de Lara JM, Marthan R, Berger P. Airway remodeling in asthma: new mechanisms and potential for pharmacological intervention. Pharmacol Ther 2011;130:325ŌĆō337PMID : 21334378.


34. Bosse Y, Rola-Pleszczynski M. FGF2 in asthmatic airway-smooth-muscle-cell hyperplasia. Trends Mol Med 2008;14:3ŌĆō11PMID : 18055262.


35. Bosse Y, Thompson C, Stankova J, Rola-Pleszczynski M. Fibroblast growth factor 2 and transforming growth factor beta1 synergism in human bronchial smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006;34:746ŌĆō753PMID : 16439802.


36. Strutz F, Zeisberg M, Renziehausen A, et al. TGF-beta 1 induces proliferation in human renal fibroblasts via induction of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2). Kidney Int 2001;59:579ŌĆō592PMID : 11168939.


37. Qu Z, Kayton RJ, Ahmadi P, et al. Ultrastructural immunolocalization of basic fibroblast growth factor in mast cell secretory granules: morphological evidence for bfgf release through degranulation. J Histochem Cytochem 1998;46:1119ŌĆō1128PMID : 9742068.


38. Powers CJ, McLeskey SW, Wellstein A. Fibroblast growth factors, their receptors and signaling. Endocr Relat Cancer 2000;7:165ŌĆō197PMID : 11021964.


39. Bosse Y, Stankova J, Rola-Pleszczynski M. Transforming growth factor-beta1 in asthmatic airway smooth muscle enlargement: is fibroblast growth factor-2 required? Clin Exp Allergy 2010;40:710ŌĆō724PMID : 20447083.


40. Cho SH, Yao Z, Wang SW, et al. Regulation of activin A expression in mast cells and asthma: its effect on the proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells. J Immunol 2003;170:4045ŌĆō4052PMID : 12682233.


41. Jeon SG, Lee CG, Oh MH, et al. Recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits the airway hyperresponsiveness, mucus production, and lung inflammation induced by an allergen challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;119:831ŌĆō837PMID : 17289133.


42. Kanazawa H, Yoshikawa T. Up-regulation of thrombin activity induced by vascular endothelial growth factor in asthmatic airways. Chest 2007;132:1169ŌĆō1174PMID : 17934112.


43. Redington AE, Roche WR, Madden J, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor in asthma: measurement in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid basally and following allergen challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;107:384ŌĆō387PMID : 11174209.


44. Clauss M. Functions of the VEGF receptor-1 (FLT-1) in the vasculature. Trends Cardiovasc Med 1998;8:241ŌĆō245PMID : 14987558.


45. Charan NB, Baile EM, Pare PD. Bronchial vascular congestion and angiogenesis. Eur Respir J 1997;10:1173ŌĆō1180PMID : 9163664.


46. Antony AB, Tepper RS, Mohammed KA. Cockroach extract antigen increases bronchial airway epithelial permeability. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;110:589ŌĆō595PMID : 12373266.


47. Lee CG, Link H, Baluk P, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces remodeling and enhances TH2-mediated sensitization and inflammation in the lung. Nat Med 2004;10:1095ŌĆō1103PMID : 15378055.



48. Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Chapoval SP, et al. Essential role of nitric oxide in VEGF-induced, asthma-like angiogenic, inflammatory, mucus, and physiologic responses in the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:11021ŌĆō11026PMID : 16832062.



49. Asai K, Kanazawa H, Otani K, Shiraishi S, Hirata K, Yoshikawa J. Imbalance between vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin levels in induced sputum from asthmatic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;110:571ŌĆō575PMID : 12373263.


50. Abdel-Rahman AM, el-Sahrigy SA, Bakr SI. A comparative study of two angiogenic factors: vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenin in induced sputum from asthmatic children in acute attack. Chest 2006;129:266ŌĆō271PMID : 16478840.


51. Bae YJ, Kim TB, Moon KA, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in induced sputum and emphysematous changes in smoking asthmatic patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2009;103:51ŌĆō56PMID : 19663127.


52. Costa JJ, Matossian K, Resnick MB, et al. Human eosinophils can express the cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha. J Clin Invest 1993;91:2673ŌĆō2684PMID : 8514874.



53. Reuter S, Heinz A, Sieren M, et al. Mast cell-derived tumour necrosis factor is essential for allergic airway disease. Eur Respir J 2008;31:773ŌĆō782PMID : 18094004.


54. Nakae S, Ho LH, Yu M, et al. Mast cell-derived TNF contributes to airway hyperreactivity, inflammation, and TH2 cytokine production in an asthma model in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;120:48ŌĆō55PMID : 17482668.


55. Berry MA, Hargadon B, Shelley M, et al. Evidence of a role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in refractory asthma. N Engl J Med 2006;354:697ŌĆō708PMID : 16481637.


56. Vandenbroucke RE, Dejonckheere E, Libert C. A therapeutic role for MMP inhibitors in lung diseases? Eur Respir J 2011;38:1200ŌĆō1214PMID : 21659416.


57. Lim DH, Cho JY, Miller M, McElwain K, McElwain S, Broide DH. Reduced peribronchial fibrosis in allergen-challenged MMP-9-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2006;291:L265ŌĆōL271PMID : 16825657.


58. Lee YC, Lee HB, Rhee YK, Song CH. The involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in airway inflammation of patients with acute asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 2001;31:1623ŌĆō1630PMID : 11678864.


59. Van Eerdewegh P, Little RD, Dupuis J, et al. Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Nature 2002;418:426ŌĆō430PMID : 12110844.


60. Jie Z, Jin M, Cai Y, et al. The effects of Th2 cytokines on the expression of ADAM33 in allergen-induced chronic airway inflammation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 2009;168:289ŌĆō294PMID : 19635592.


61. Foley SC, Mogas AK, Olivenstein R, et al. Increased expression of ADAM33 and ADAM8 with disease progression in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;119:863ŌĆō871PMID : 17339047.


62. Lloyd CM. IL-33 family members and asthma - bridging innate and adaptive immune responses. Curr Opin Immunol 2010;22:800ŌĆō806PMID : 21071194.



63. Shan L, Redhu NS, Saleh A, Halayko AJ, Chakir J, Gounni AS. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor-mediated IL-6 and CC/CXC chemokines expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: role of MAPKs (ERK1/2, p38, and JNK) and STAT3 pathways. J Immunol 2010;184:7134ŌĆō7143PMID : 20483734.


64. Al-Shami A, Spolski R, Kelly J, Keane-Myers A, Leonard WJ. A role for TSLP in the development of inflammation in an asthma model. J Exp Med 2005;202:829ŌĆō839PMID : 16172260.



65. Zhang F, Huang G, Hu B, Song Y, Shi Y. A soluble thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) antagonist, TSLPR-immunoglobulin, reduces the severity of allergic disease by regulating pulmonary dendritic cells. Clin Exp Immunol 2011;164:256ŌĆō264PMID : 21352203.



66. Heijink IH, Postma DS, Noordhoek JA, Broekema M, Kapus A. House dust mite-promoted epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2010;42:69ŌĆō79PMID : 19372245.


67. Heijink IH, van Oosterhout A, Kapus A. Epidermal growth factor receptor signalling contributes to house dust mite-induced epithelial barrier dysfunction. Eur Respir J 2010;36:1016ŌĆō1026PMID : 20351035.


68. Ying S, O'Connor B, Ratoff J, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in asthmatic airways and correlates with expression of Th2-attracting chemokines and disease severity. J Immunol 2005;174:8183ŌĆō8190PMID : 15944327.


69. Ying S, O'Connor B, Ratoff J, et al. Expression and cellular provenance of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and chemokines in patients with severe asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Immunol 2008;181:2790ŌĆō2798PMID : 18684970.


70. Zhou B, Comeau MR, De Smedt T, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a key initiator of allergic airway inflammation in mice. Nat Immunol 2005;6:1047ŌĆō1053PMID : 16142237.


71. Owyang AM, Zaph C, Wilson EH, et al. Interleukin 25 regulates type 2 cytokine-dependent immunity and limits chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. J Exp Med 2006;203:843ŌĆō849PMID : 16606667.



72. Angkasekwinai P, Park H, Wang YH, et al. Interleukin 25 promotes the initiation of proallergic type 2 responses. J Exp Med 2007;204:1509ŌĆō1517PMID : 17562814.



73. Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, et al. IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity 2001;15:985ŌĆō995PMID : 11754819.


74. Hurst SD, Muchamuel T, Gorman DM, et al. New IL-17 family members promote Th1 or Th2 responses in the lung: in vivo function of the novel cytokine IL-25. J Immunol 2002;169:443ŌĆō453PMID : 12077275.


75. Corrigan CJ, Wang W, Meng Q, et al. T-helper cell type 2 (Th2) memory T cell-potentiating cytokine IL-25 has the potential to promote angiogenesis in asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011;108:1579ŌĆō1584PMID : 21205894.



76. Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005;23:479ŌĆō490PMID : 16286016.


77. Sanada S, Hakuno D, Higgins LJ, Schreiter ER, McKenzie AN, Lee RT. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J Clin Invest 2007;117:1538ŌĆō1549PMID : 17492053.



78. Moussion C, Ortega N, Girard JP. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: a novel 'alarmin'? PLoS One 2008;3:e3331. PMID : 18836528.



79. Wood IS, Wang B, Trayhurn P. IL-33, a recently identified interleukin-1 gene family member, is expressed in human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009;384:105ŌĆō109PMID : 19393621.


80. Kurowska-Stolarska M, Stolarski B, Kewin P, et al. IL-33 amplifies the polarization of alternatively activated macrophages that contribute to airway inflammation. J Immunol 2009;183:6469ŌĆō6477PMID : 19841166.


81. Kondo Y, Yoshimoto T, Yasuda K, et al. Administration of IL-33 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and goblet cell hyperplasia in the lungs in the absence of adaptive immune system. Int Immunol 2008;20:791ŌĆō800PMID : 18448455.


82. Zhiguang X, Wei C, Steven R, et al. Over-expression of IL-33 leads to spontaneous pulmonary inflammation in mIL-33 transgenic mice. Immunol Lett 2010;131:159ŌĆō165PMID : 20412815.


83. Liu X, Li M, Wu Y, Zhou Y, Zeng L, Huang T. Anti-IL-33 antibody treatment inhibits airway inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009;386:181ŌĆō185PMID : 19508862.


84. Coyle AJ, Lloyd C, Tian J, et al. Crucial role of the interleukin 1 receptor family member T1/ST2 in T helper cell type 2-mediated lung mucosal immune responses. J Exp Med 1999;190:895ŌĆō902PMID : 10510079.



85. Rankin AL, Mumm JB, Murphy E, et al. IL-33 induces IL-13-dependent cutaneous fibrosis. J Immunol 2010;184:1526ŌĆō1535PMID : 20042577.


86. Prefontaine D, Nadigel J, Chouiali F, et al. Increased IL-33 expression by epithelial cells in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125:752ŌĆō754PMID : 20153038.


87. Smith DE. IL-33: a tissue derived cytokine pathway involved in allergic inf lammation and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 2010;40:200ŌĆō208PMID : 19906013.


88. Rasmussen F, Taylor DR, Flannery EM, et al. Risk factors for airway remodeling in asthma manifested by a low postbronchodilator FEV1/vital capacity ratio: a longitudinal population study from childhood to adulthood. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:1480ŌĆō1488PMID : 12045120.


89. Mitsunobu F, Tanizaki Y. The use of computed tomography to assess asthma severity. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;5:85ŌĆō90PMID : 15643349.


90. Gupta S, Siddiqui S, Haldar P, et al. Quantitative analysis of high-resolution computed tomography scans in severe asthma subphenotypes. Thorax 2010;65:775ŌĆō781PMID : 20805170.



91. Aysola R, de Lange EE, Castro M, Altes TA. Demonstration of the heterogeneous distribution of asthma in the lungs using CT and hyperpolarized helium-3 MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010;32:1379ŌĆō1387PMID : 21105142.


92. de Lange EE, Altes TA, Patrie JT, et al. Evaluation of asthma with hyperpolarized helium-3 MRI: correlation with clinical severity and spirometry. Chest 2006;130:1055ŌĆō1062PMID : 17035438.


93. Fain SB, Gonzalez-Fernandez G, Peterson ET, et al. Evaluation of structure-function relationships in asthma using multidetector CT and hyperpolarized He-3 MRI. Acad Radiol 2008;15:753ŌĆō762PMID : 18486011.



94. Delimpoura V, Bakakos P, Tseliou E, et al. Increased levels of osteopontin in sputum supernatant in severe refractory asthma. Thorax 2010;65:782ŌĆō786PMID : 20805171.


95. Broekema M, Timens W, Vonk JM, et al. Persisting remodeling and less airway wall eosinophil activation in complete remission of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;183:310ŌĆō316PMID : 20813885.


96. Wang K, Liu CT, Wu YH, et al. Effects of formoterol-budesonide on airway remodeling in patients with moderate asthma. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2011;32:126ŌĆō132PMID : 21170080.



97. Palikhe NS, Kim JH, Park HS. Biomarkers predicting isocyanate-induced asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 2011;3:21ŌĆō26PMID : 21217921.



98. Soja J, Grzanka P, Sladek K, et al. The use of endobronchial ultrasonography in assessment of bronchial wall remodeling in patients with asthma. Chest 2009;136:797ŌĆō804PMID : 19429721.


99. Holgate S, Casale T, Wenzel S, Bousquet J, Deniz Y, Reisner C. The anti-inflammatory effects of omalizumab confirm the central role of IgE in allergic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;115:459ŌĆō465PMID : 15753888.


100. Rabe KF, Calhoun WJ, Smith N, Jimenez P. Can anti-IgE therapy prevent airway remodeling in allergic asthma? Allergy 2011;66:1142ŌĆō1151PMID : 21645010.


101. van Rensen EL, Evertse CE, van Schadewijk WA, et al. Eosinophils in bronchial mucosa of asthmatics after allergen challenge: effect of anti-IgE treatment. Allergy 2009;64:72ŌĆō80PMID : 19076931.


102. Holgate S, Smith N, Massanari M, Jimenez P. Effects of omalizumab on markers of inflammation in patients with allergic asthma. Allergy 2009;64:1728ŌĆō1736PMID : 19839977.


103. Kang JY, Kim JW, Kim JS, et al. Inhibitory effects of anti-immunoglobulin E antibodies on airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. J Asthma 2010;47:374ŌĆō380PMID : 20528589.


104. Corren J. Cytokine inhibition in severe asthma: current knowledge and future directions. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2011;17:29ŌĆō33PMID : 21330823.


105. Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med 2009;360:985ŌĆō993PMID : 19264687.


106. Gruenberg D, Busse W. Biologic therapies for asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2010;16:19ŌĆō24PMID : 19797955.


107. Holgate ST, Noonan M, Chanez P, et al. Efficacy and safety of etanercept in moderate-to-severe asthma: a randomised, controlled trial. Eur Respir J 2011;37:1352ŌĆō1359PMID : 21109557.


108. Erin EM, Leaker BR, Nicholson GC, et al. The effects of a monoclonal antibody directed against tumor necrosis factor-alpha in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;174:753ŌĆō762PMID : 16840747.


109. Wenzel SE, Barnes PJ, Bleecker ER, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade in severe persistent asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009;179:549ŌĆō558PMID : 19136369.


110. Borish LC, Nelson HS, Corren J, et al. Efficacy of soluble IL-4 receptor for the treatment of adults with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;107:963ŌĆō970PMID : 11398072.


111. Hart TK, Blackburn MN, Brigham-Burke M, et al. Preclinical efficacy and safety of pascolizumab (SB 240683): a humanized anti-interleukin-4 antibody with therapeutic potential in asthma. Clin Exp Immunol 2002;130:93ŌĆō100PMID : 12296858.



112. Wenzel S, Wilbraham D, Fuller R, Getz EB, Longphre M. Effect of an interleukin-4 variant on late phase asthmatic response to allergen challenge in asthmatic patients: results of two phase 2a studies. Lancet 2007;370:1422ŌĆō1431PMID : 17950857.


113. Corren J, Busse W, Meltzer EO, et al. A randomized, controlled, phase 2 study of AMG 317, an IL-4Ralpha antagonist, in patients with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;181:788ŌĆō796PMID : 20056900.


114. Busse WW, Israel E, Nelson HS, et al. Daclizumab improves asthma control in patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma: a randomized, controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;178:1002ŌĆō1008PMID : 18787222.


115. Berlin AA, Hogaboam CM, Lukacs NW. Inhibition of SCF attenuates peribronchial remodeling in chronic cockroach allergen-induced asthma. Lab Invest 2006;86:557ŌĆō565PMID : 16607380.


116. Humbert M, de Blay F, Garcia G, et al. Masitinib, a c-kit/PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, improves disease control in severe corticosteroid-dependent asthmatics. Allergy 2009;64:1194ŌĆō1201PMID : 19614621.


117. Dube J, Chakir J, Dube C, Grimard Y, Laviolette M, Boulet LP. Synergistic action of endothelin (ET)-1 on the activation of bronchial fibroblast isolated from normal and asthmatic subjects. Int J Exp Pathol 2000;81:429ŌĆō437PMID : 11298190.



118. Taille C, Guenegou A, Almolki A, et al. ETB receptor polymorphism is associated with airway obstruction. BMC Pulm Med 2007;7:5. PMID : 17470272.



119. Zhu G, Carlsen K, Carlsen KH, et al. Polymorphisms in the endothelin-1 (EDN1) are associated with asthma in two populations. Genes Immun 2008;9:23ŌĆō29PMID : 17960156.


120. Trian T, Benard G, Begueret H, et al. Bronchial smooth muscle remodeling involves calcium-dependent enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis in asthma. J Exp Med 2007;204:3173ŌĆō3181PMID : 18056286.



121. Menzies D, Nair A, Meldrum KT, Fleming D, Barnes M, Lipworth BJ. Simvastatin does not exhibit therapeutic anti-inflammatory effects in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;119:328ŌĆō335PMID : 17141851.


122. Hothersall EJ, Chaudhuri R, McSharry C, et al. Effects of atorvastatin added to inhaled corticosteroids on lung function and sputum cell counts in atopic asthma. Thorax 2008;63:1070ŌĆō1075PMID : 18757458.


123. Danek CJ, Lombard CM, Dungworth DL, et al. Reduction in airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine by the application of RF energy in dogs. J Appl Physiol 2004;97:1946ŌĆō1953PMID : 15258133.


124. Miller JD, Cox G, Vincic L, Lombard CM, Loomas BE, Danek CJ. A prospective feasibility study of bronchial thermoplasty in the human airway. Chest 2005;127:1999ŌĆō2006PMID : 15947312.


125. Cox G, Miller JD, McWilliams A, Fitzgerald JM, Lam S. Bronchial thermoplasty for asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;173:965ŌĆō969PMID : 16456145.


126. Cox G, Thomson NC, Rubin AS, et al. Asthma control during the year after bronchial thermoplasty. N Engl J Med 2007;356:1327ŌĆō1337PMID : 17392302.


127. Castro M, Rubin AS, Laviolette M, et al. Effectiveness and safety of bronchial thermoplasty in the treatment of severe asthma: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;181:116ŌĆō124PMID : 19815809.



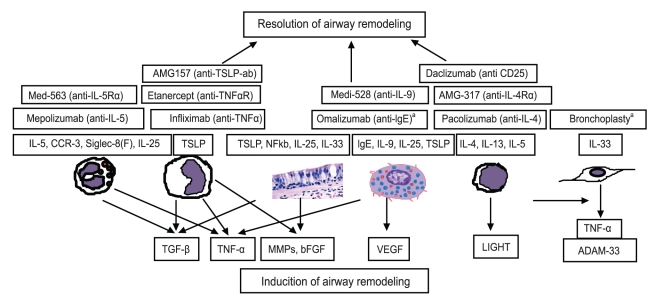
Figure┬Ā1
Inflammatory cells and mediators related to induction of airway remodeling and biological therapy targeting specific cells and mediators. Airway remodeling is a result of persistent inflammation and epithelial damage by repetitive injuries. Several important mediators including transforming growth factor (TGF)-╬▓, interleukin (IL)-5, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), LIGHT, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-╬▒, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-33, and IL-25 are associated with airway remodeling in asthma. Biological therapy targeting specific cells or mediators are now in clinical trial. CCR-3, chemokine receptor type 3; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase. aBronchoscopic procedure which delivers thermal energy to the airway wall to reduce excess airway smooth muscle.
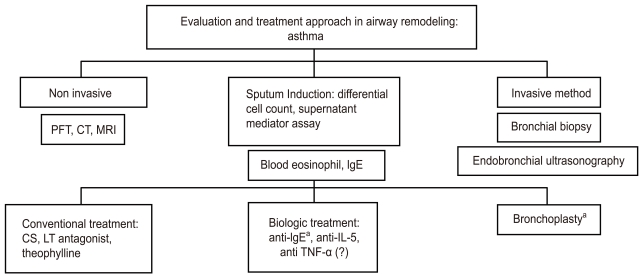
Figure┬Ā2
Evaluation and treatment approach during asthmatic airway remodeling. Non-invasive methods such as the pulmonary function test (PFT), high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are utilized first to assess the degree of airway remodeling. Invasive methods such as sputum induction for inflammatory cells and biological markers, blood eosinophils and IgE, bronchoscopic biopsy or bronchoalveolar lavage, and endobronchial ultrasonography may be applied for a more detailed determination of airway remodeling. Additional treatment including biological therapy and bronchial thermoplasty can then be used as a more mechanical approach to treatment based on asthma subtype. CT, computed tomography; CS, corticosteroid; LT, leukotriene; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. aFDA-approved for patients with severe asthma.




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



