 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 25(1); 2010 > Article |
|
Abstract
References
Table┬Ā1
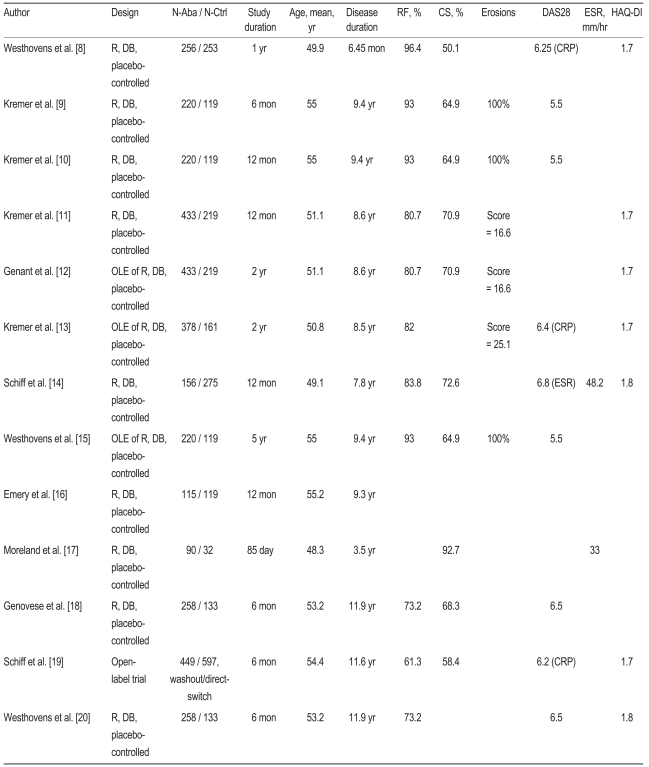
N-Aba, number-abatacept; N-Ctrl, number-control; RF, rheumatoid factor; CS, corticosteroid; DAS28, 28 joint disease activity score; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index; R, random; DB, double-blind; CRP, C-reactive protein; OLE, open label extension.
Table┬Ā4

ACR20, 20% response on the American College of Rheumatology criteria; DAS28, 28 joint disease activity score; R, random; DB, double-blind; MTX, methotrexate; TS, total score; OLE, open label extension; CRP, C-reactive protein; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; SF-36, short form 36.
Table┬Ā6
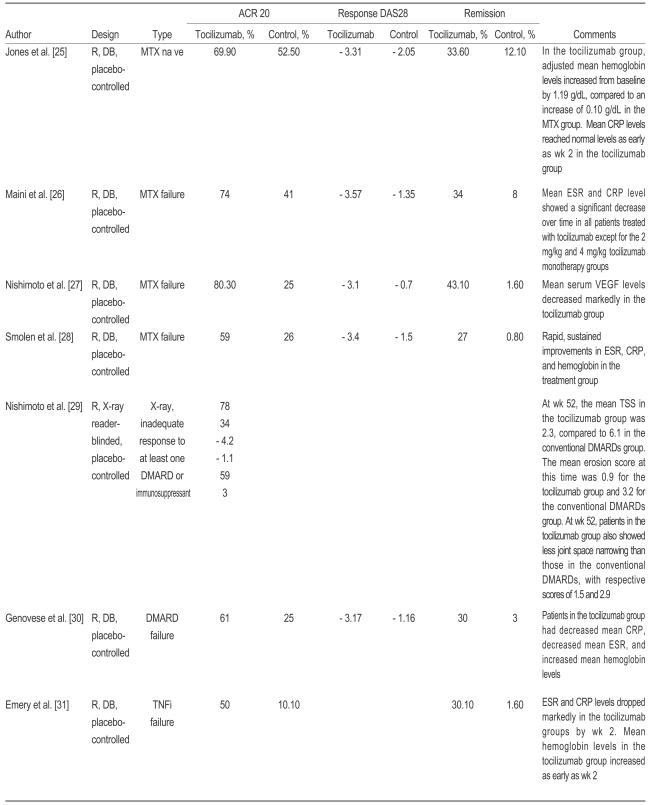
ACR20, 20% response on the American College of Rheumatology criteria; DAS 28, 28 joint disease activity score; R, random; DB, double-blind; MTX, methotrexate; CRP, C-reactive protein; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; TSS, total modified Sharp score; DMARDs, disease-modifyinganti-rheumatic drugs; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
Table┬Ā7

DMARD, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug; N/A, not available; CA, carcinoma; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; CVS, cardiovascular syndrome; CHF, congestive heart failure; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
aExcept where indicated otherwise, values are total number of patients and range of percent of patients.
bDosage of abatacept administered ranged from 2 to 10 mg/kg. Some patients were taking background non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids.
cDMARDs, including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, azathioprine, penicillamine, gold, hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, leflunomide, anakinra.
dControl groups included placebo groups and DMARDs.
eInfections were nasopharyngitis, influenza, urinary tract infection, upper respiratory tract infection, sinusitis, bronchitis.
fSerious infections were infections requiring intravenous antibiotics, hospitalizations, death.
gOther serious infections included bursitis, osteomyelitis, pseudomonas lung infection, postoperative wound infection, bacterial arthritis, bronchopulmonary aspergilliosis, acute pyelonephritis.
hSmall cell CA, squamous cell CA, adeno CA, metastatic lung CA, and malignant lung neoplasms.
iOther malignancies included pancreatic cancer, uterine cancer, endometrial cancer, ovarian CA, myelodysplastic syndrome.
jCVS events include myocardial infarction, CHF, angina, hypertension, and cardiac arrest.
kOther autoimmune diseases like vasculitis of any type, SLE, sjorgrens, sicca syndrome, atrophic gastritis, erythema nodosum, thyroiditis, multiple sclerosis but not including posriasis.
lMusculoskeletal disorders include back pain, rheumatoid arthritis worsening, arthralgias, connective tissue disorders.
mAuto antibodies to the whole molecule or the CTLA-4T portion of the drug.
Table┬Ā8
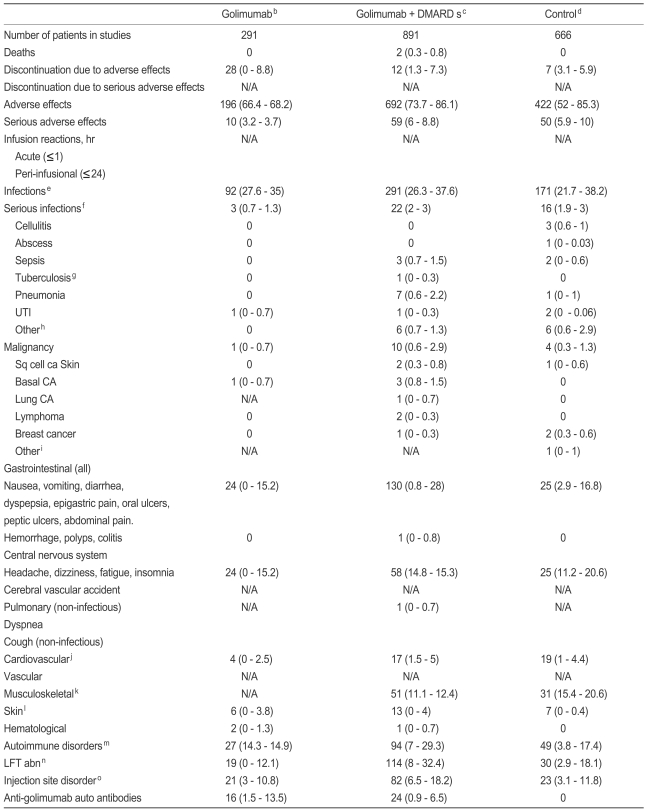
DMARD, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug; N/A, not available; UTI, urinary tract infection; CA, carcinoma; LFT, liver function test; COX, cyclooxygenase; ANA, anti-nuclear antibody; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.
aExcept where indicated otherwise, values are total number of patients and range of percent of patients (range, %).
bDosage of golimumab administered ranged from 2 to 8 mg/kg. Some patients were taking background non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including COX2 inhibitors and corticosteroids.
cDMARDs, including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, azathioprine, penicillamine, gold, hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, leflunomide, anakinra, salazosulfapyridine, and bucillamine, mizoribine.
dControl groups included placebo groups and DMARDs.
eInfections were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, cough, sinusitis, and bacterial infections not otherwise specified.
fSerious infections were infections requiring intravenous antibiotics, hospitalizations, or death.
gPatients with tuberculosis at baseline were not included.
hOther serious infections included, osteomyelitis, bacterial arthritis, infective arthritis, lower respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, urosepsis, infected cystic lymphangioma, gasterointeritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and sinusitis.
iOther malignancies included pancreatic cancer.
jCardiovascular events included myocardial infarction, angina, congestive heart failure, hypertension, and cardiac arrest.
kMusculosketal disorders included back pain, worsening rheumatoid arthritis, arthralgia, and a fractured coccyx.
lSkin manifestations included rash.
mIncludes ANA positivity, anti double strained DNA positivity. None of the patients developed systemic lupus erythematosus or erthyma.
nLiver function test abnormalities including elevations in ALT, AST and bilirubin levels. Most were unconjugated bilirubinemias (four people were on Tb prophylaxis i.e. isoniazid).
oInjection site reactions included erythema, bruising, warmth, pruritus, pain, induration, burning, hemorrhaging, stinging, urticaria, and swelling.
Table┬Ā9
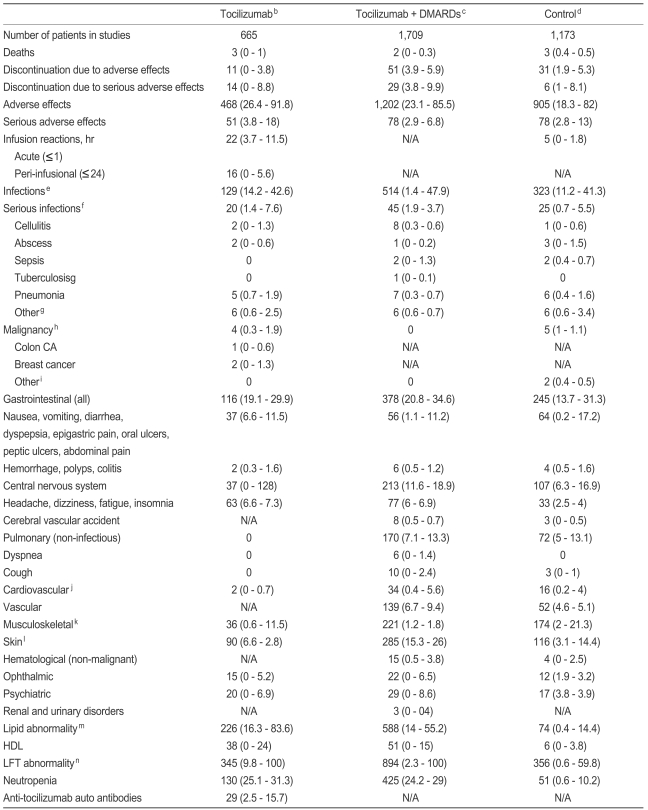
DMARD, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug; N/A, not available; CA, carcinoma; HDL, high density lipoprotein; LFT, liver function test; COX, cyclooxygenase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.
aExcept where indicated otherwise, values are total number of patients and ranges of the percent of patients (range, %).
bDosages of tocilizumab ranged from 2 to 8 mg/kg. Some patients were taking background non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including COX2 inhibitors and corticosteroids.
cDMARDs including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, azathioprine, penicillamine, gold, hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, leflunomide, anakinra, salazosulfapyridine, bucillamine, and mizoribine.
dControl groups included placebo groups and DMARDs.
eInfections were nasopharyngitis, somatitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and bacterial infections not otherwise specified.
fSerious infections were infections requiring intravenous antibiotics, hospitalizations, or death.
gOther serious infections included osteomyelitis, bacterial arthritis, infective arthritis, lower respiratory tract infection, pleural effusion, viral herpes zoster, herpes simplex, gastroenteritis, staphylococcal polyarthritis, urosepsis, empyema, and unidentified infections.
hMalignancies included the below mentioned malignancies and others not otherwise specified.
iOther malignancies included pancreatic cancer, uterine cancer, endometrial cancer, ovarian carcinoma, myelodysplastic syndrome, squamous cell cancer of the skin, and lung cancer.
jCardiovascular events included myocardial infarction, angina, congestive heart failure, hypertension, and cardiac arrest.
kMusculosketal disorders included back pain, rheumatoid arthritis worsening, arthralgias, connective tissue disorders, and compression fractures.
lSkin manifestations included rash, eczema, pruritus, and paronychia.
mLiver function test abnormalities included elevations in ALT, AST and bilirubin levels. Most were unconjugated bilirubinemias, and a simultaneous rise in ALT and bilirubin levels were not frequently seen.
nIncrease in low density lipoprotein, total cholesterol, and triglycerides (values may be combined or an individual number depending upon the study data available).




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



