 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 21(1); 2006 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
There are contradictory reports concerning hypercapnia as a predictor of a better outcome in COPD. This study examined the clinical implications of hypercapnea in COPD patients (M:F = 59:19) who required mechanical ventilation.
Methods
The clinical parameters at the time of MICU admission, the total ventilation time, the APACHE II score and the pulmonary function testing were retrospectively analyzed between the survivors and nonsurvivors.
Results
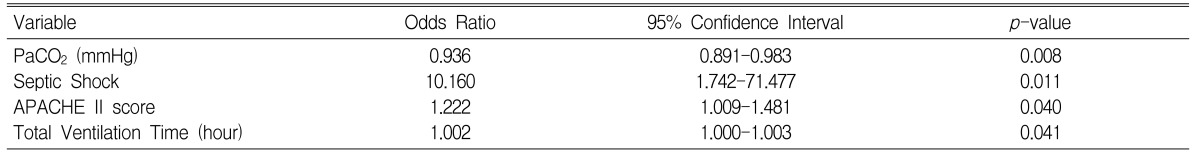
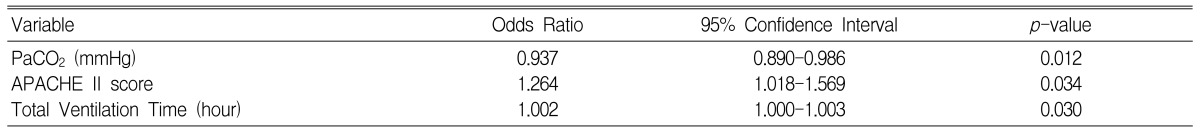
Univariate analysis showed that compared with the nonsurvivors, the survivors had lower AaDO2 values (59.8±53.5 vs. 105.0±73.3 mmHg, p=0.000), higher PaCO2 values (64.9±16.0 vs. 48.9±17.8 mmHg, p=0.000), lower APACHE II scores (19.0±3.8 vs. 24.1±5.1, p=0.002), the more frequent application of initial noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (44.0 vs. 14.3%, p=0.008), and a lower combined rate of septic shock (4.0 vs. 39.3%, p=0.000). Multivariate analysis revealed that a lower PaCO2 (OR: 0.94, p=0.008), the presence of septic shock (OR: 10.16, p=0.011), a higher APACHE II score (OR: 1.22, p=0.040) and a longer ventilation time (OR: 1.002, p=0.041) were the risk factors for mortality. A lower PaCO2 was also verified as the predictor for mortality by multivariate analysis when excluding septic shock.
Deterioration of lung function that leads to progressive acute respiratory failure in the patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) requires the administration of mechanical ventilatory support. The mortality rates that have been reported for these patients range between 19% and 46%1-8). A number of prognostic factors have been reported for COPD patients, including the APACHE (acute physiology and chronic health evaluation) II score, age, the baseline pulmonary function, the oxygenation status, the number of organ failures, the nutritional status, the severity of the underlying disease and the appropriateness of the medical management1-10).
It may be that in COPD patients with hypercapnia, if oxygenation is equally maintained regardless of the serum carbon dioxide, a low minute ventilation is required to maintain the optimal arterial oxygenation, and this reflects the less advanced diffusion disturbances or the less severe ventilation-perfusion mismatch compared to the COPD patients with hypocapnea. The results from experimental models of acute lung injury indicate that hypercapnea can attenuate lung injury via various mechanisms and it may have some therapeutic potential11-18). Depending on the PaCO2 level at admission, these physiological and therapeutic differences may affect survival for the COPD patients suffering with acute respiratory failure. However, there are conflicting reports regarding hypercapnia as a predictor for survival in COPD patients8, 19-22).
The aim of the present study was to determine whether the PaCO2 level at admission was a prognostic indicator for survival in the COPD patients who underwent mechanical ventilatory support.
The study retrospectively examined 78 consecutive COPD patients who underwent mechanical ventilation due to their acute respiratory, and they were treated in the medical intensive care unit (MICU) of a university-affiliated hospital from March 1991 to August 2003. The diagnosis of COPD was determined by the clinical criteria and the previously documented airflow limitation (FEV1 <80% of the predicted value in combination with an FEV1/FVC <70% that was not fully reversible)23-26). We used the clinical criteria, the clinical history with the compatible physical findings and/or evidence of hyperinflation on the chest radiography to support the diagnosis of COPD in the absence of the results for the previous pulmonary function testing23-26). A positive bronchodilator response was defined according to the ATS criteria when there was an increase of either the FVC or FEV1 by 12% or more and an absolute change of 200 mL of either one was documented27). The study excluded patients with COPD combined with a tuberculous-destroyed lung, bronchiectasis, kyphoscliosis, malignancy, preexisting tracheostomy and stroke. The application of invasive or noninvasive ventilation was decided upon based on the judgment of the ICU attending physicians. Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV) was not tried dor the patients who had respiratory arrest, unstable hemodynamics, problems of airway protection, excessive secretion, anatomic abnormalities that interfered with the mask fit and poor cooperation.
We retrospectively analyzed the following data that was collected at the time of MICU admission: the complete blood count and blood chemistry, the radiological findings, the APACHE II scores (first day of MICU), the infection status, the presence of septic shock, the co-existing medical problems and the medication. The blood gas data obtained before the start of mechanical ventilation was also analyzed. In addition, the total ventilation time, the total ICU stay, the total hospital stay and the final outcome (survival or death) during the hospital stay were reviewed. The best results for the pulmonary function testing (PFT) and the baseline arterial blood gas analysis were also obtained when the patient was stable and this was done within the preceding 3 years. For the patients who had a history of frequent mechanical ventilation, the most recent application available was selected. PFT data were available for 64 of the 78 COPD patients, and the baseline arterial blood gas data with the patient in a stable condition were collected for 53 of the 78 COPD patients. The admission route, cor pulmonale, home oxygen therapy and smoking status were noted during the chart review. A detailed smoking history, including the total pack-years of smoking, was obtained for each patient. An ex-smoker was defined as an individual who had stopped smoking for more than one year.
Clinical parameters were analyzed either between the surviving and nonsurviving groups or depending upon the PaCO2 value at admission: the hypercapnic group had ≥50 mm Hg, and the non-hypercapnic group had <50 mmHg. Hypercapnia was defined as a PaCO2 level ≥50 mmHg28). PAO2 (the alveolar oxygen tension) was calculated using the following formula: PAO2=(760-47)×FiO2-PaCO2/R, where R was assumed to be 0.8. The alveolar-arterial PO2 difference was calculated by subtracting the PaO2 from the PAO2. The body mass index (BMI) at the time of admission was calculated as weight (kg) divided by the square of height (m2).
All the data were analyzed using SPSS version 11.0. All the values are expressed as means±standard deviation (SD), or as the numbers of patients and a percentage. Chi-Square and/or Fisher's exact tests were used for comparison of the categorical data. For the continuous data, Student's t-test was used for comparison of the parametric data, and the Mann-Whitney test was used for comparison of the nonparametric data. Multiple logistic regression using the stepwise forward method was used to evaluate the independent risk factors by including all the significant and nearly significant parameters (p<0.1) The results of the logistic regression analysis are reported as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). p-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
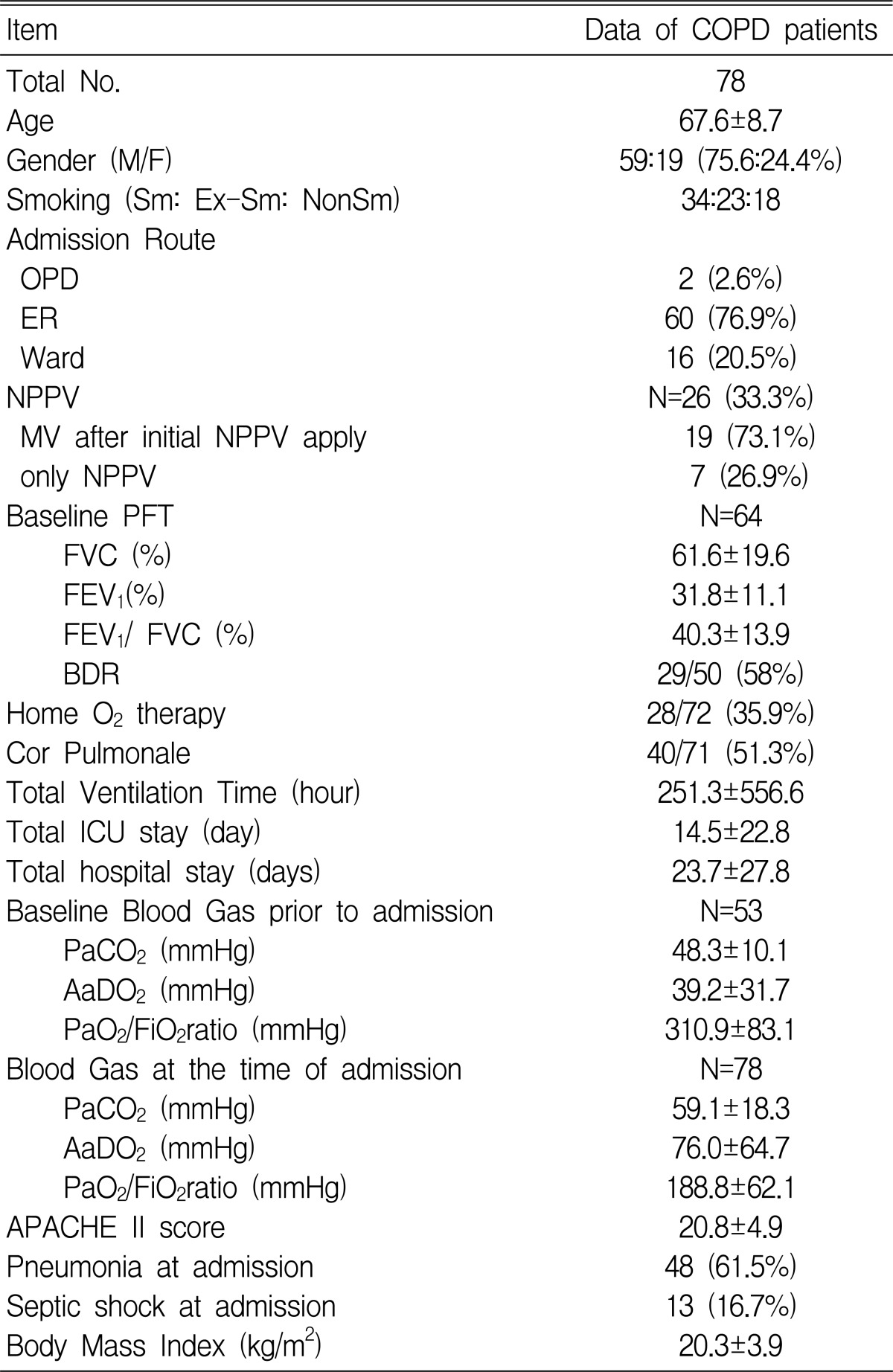
Males comprised 75.6% of the study group. The emergency room was the admission route to the MICU in 76.9% (60) of the cases. NPPV was first applied in 33.3% (26) of the patients, of whom 73.1% (19) had to be intubated during their MICU stay. The baseline FEV1 analysis showed that the patients generally had severe airway obstruction (31.8±11.1%) even when they were in a stable state. The baseline blood gas data in the stable state was available for 53 patients, and it showed that the PaCO2 was 48.3±10.1 mmHg and the PiO2/FiO2 ratio was 310.9±83.1 mmHg. Home O2 therapy was administered in 35.9% of the cases (28 of 72 patients).
At the time of admission, the mean APACHE II score was 20.8±4.9. Septic shock was present in 13 (16.7%) of the patients, and 48 (61.5%) patients had pneumonia.
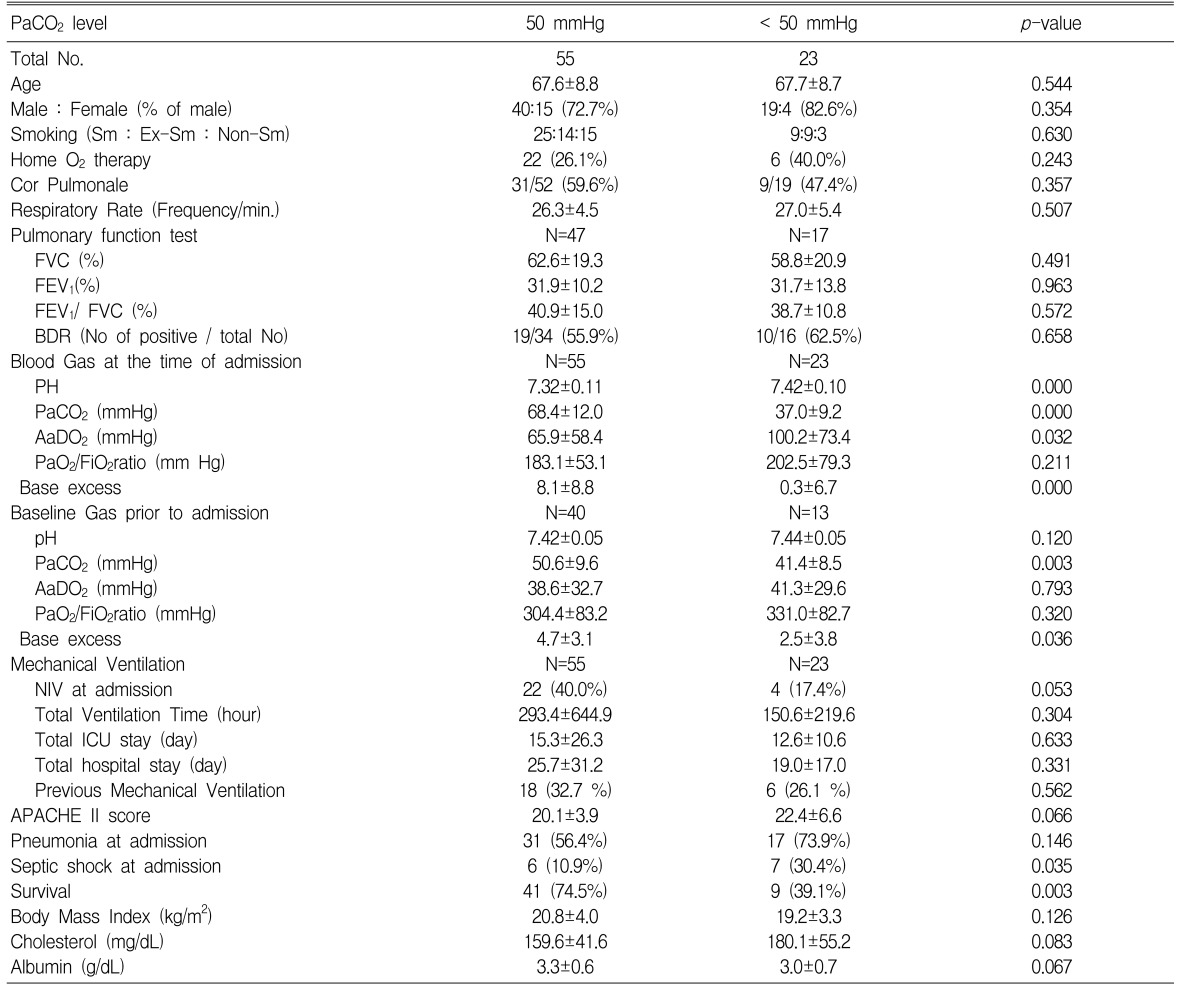
We found that the PaCO2 level was inversely correlated with the APACHE II score (r=-0.313, p=0.005) (Figure 2). Although not statistically significant, the group with higher PaCO2 values (≥50 mmHg) appeared to have lower APACHE II scores (20.1±3.9 vs. 22.4±6.6, p=0.066) and more use of NPPV (40.0 vs. 17.4%, p=0.053) than did the group with the lower PaCO2 values (<50 mm Hg). The higher PaCO2 group had more survivors (74.5% vs. 39.1%, p=0.003) and less cases of septic shock (10.9% vs. 30.4%, p=0.035) as compared to the lower group. There was no difference between the two groups in terms of the baseline pulmonary function test results, the total ventilation time or the BMI.
The mortality rate while receiving mechanical ventilation was 29.5% (28/78 patients). The cause of death was identified in 21 patients: respiratory failure (7 cases, 33.3%), septic shock (6 cases, 28.6%), pneumonia (6 cases, 28.6%) and arrhythmia (2 cases, 9.5%).
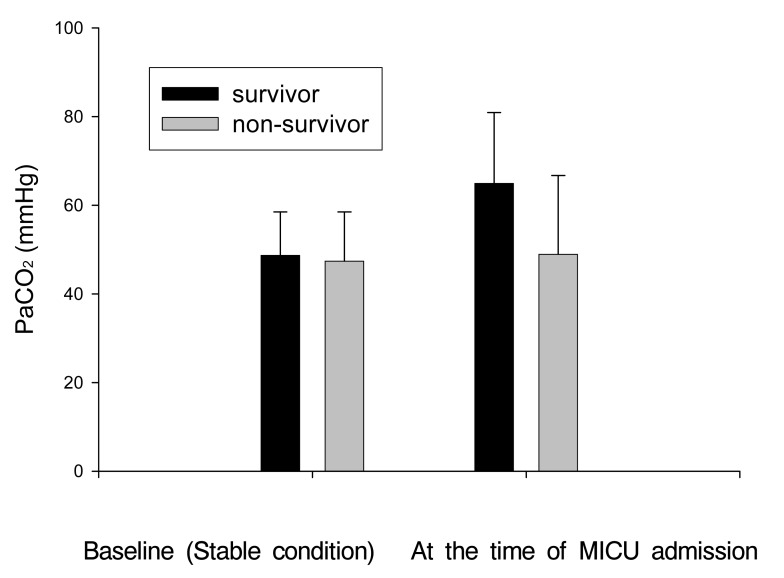
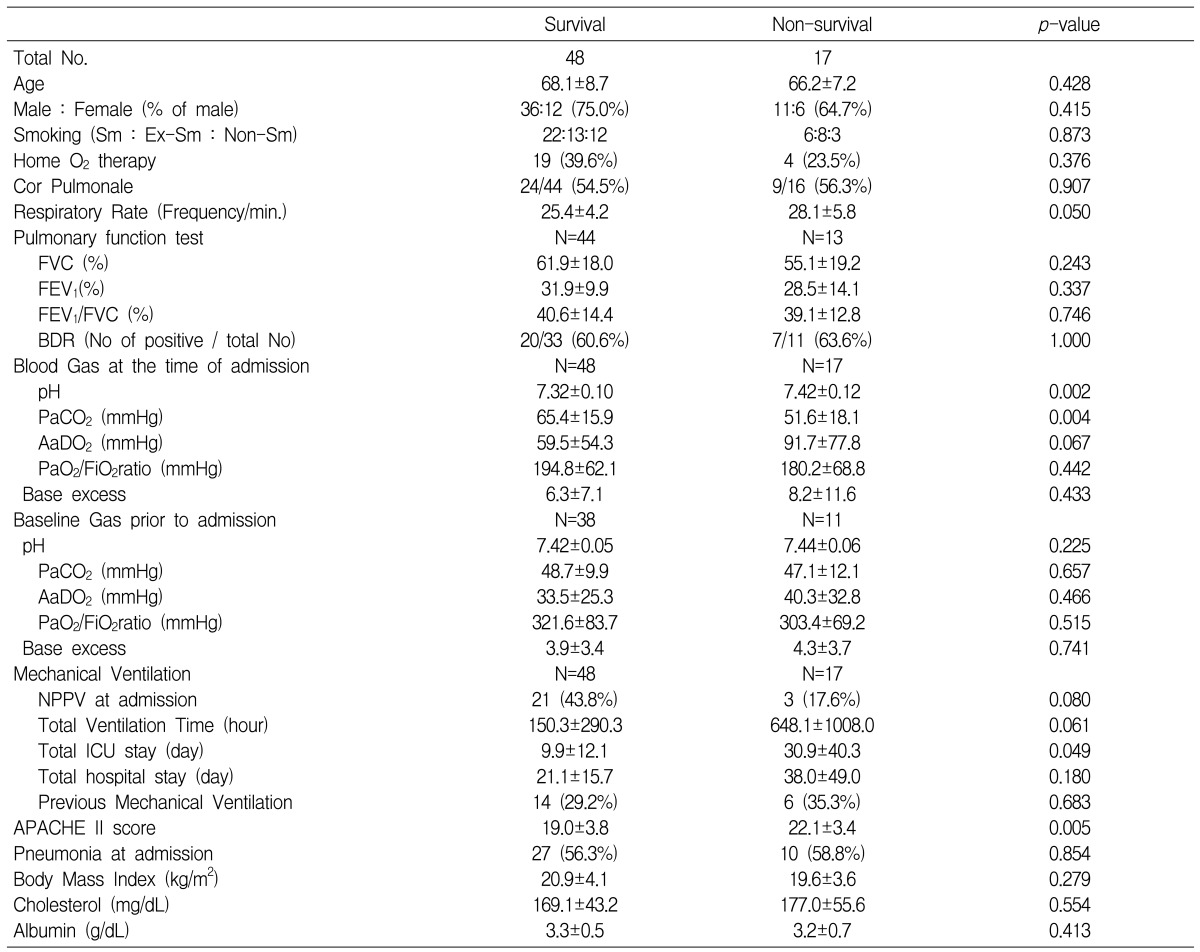
Age and gender did not differ between the survivors and nonsurvivors, and neither did the baseline PFT including the FVC, FEV1 and FEV1/FVC. Although both groups had similar degrees of severe obstructive ventilatory defect (FEV1; 31.7± 9.8% vs. 32.1±14.1%, p=0.901) and identical PaCO2 levels when stable, the survivors had higher PaCO2 values (64.9± 16.0% vs. 48.9±17.8%, p=0.002) and lower AaDO2 (59.8±53.5 vs. 105.0±73.3 mmHg, p=0.000) levels at the time of ICU admission compared to the nonsurvivors (Figure 1). The PaO2/FiO2 ratio was not different between the two groups.
Regarding the parameters of mechanical ventilation, compared to nonsurvivors, the survivors used NPPV more frequently (44.0% vs. 14.3%, p=0.011), and they appeared to have longer ventilation times, although this latter difference was not found to be statistically significant (440.3±823.2 vs. 145.4±285.3 h, p=0.076). There were no significant differences for the ICU stay, the total hospital stay and the number of previous mechanical ventilations between the survivors and nonsurvivors.
The survivors had lower APACHE II scores (19.0±3.8 vs. 24.1±5.1, p=0.000) and fewer cases of septic shock (4.0 vs. 39.3%, p=0.228). Although the BMI appeared to be higher in the survivors, this difference was not statistically significant (20.9±4.0 vs. 19.1±3.4, p=0.058). In the analysis with excluding the patients with septic shock, the survivors had a lower pH, a higher PaCO2 and a longer ICU stay than did the non-survivors.
Multiple logistic regression analysis that included the variables whose p-values were less than p<0.1 showed that a low PaCO2 as well as the presence of septic shock, a high APACHE II score and a long total ventilation time were the independent prognostic factors for a worse outcome in the COPD patients who underwent mechanical ventilation. Multiple logistic regression analysis for the COPD patients without septic shock also demonstrated that not only were a high APACHE II score and a long total ventilation time independent prognostic factors, but a low PaCO2 was also an independent prognostic factor.
This study showed that hypercapnia at admission was an independent predictor for better survival in the COPD patients who underwent mechanical ventilation. In addition, the study found that septic shock, a high APACHE II score and a long ventilation time were independent factors for a worse prognosis.
The PaCO2 levels prior to the start of mechanical ventilation were analyzed in the present study. This approach was taken since the PaCO2 levels can be altered by the tidal volumes from a mechanical ventilator or by other therapeutic measures designed to relieve airway obstruction during the ICU stay, and such PaCO2 level changes are thought to make the carbon dioxide levels less reliable as a prognostic marker.
The principal finding of this study is that elevated systemic carbon dioxide tension at the time of MICU admission was linked to better survival, and this was despite that both the survivors and nonsurvivors had similar pulmonary function and PaCO2 levels during their stable condition. This study also demonstrated that the PaCO2 levels were inversely correlated with the APACHE II scores, and that the higher PaCO2 group had a lower AaDO2 compared to the lower PaCO2 group. Because septic shock that causes hyperventilation and hypocapnia could have been a confounding factor in our study, we analyzed our subjects with excluding the patients without septic shock. This result also showed that hypocapnia was an independent factor for a worse outcome by the multivariate analysis. The findings suggest that high carbon dioxide levels can be an independent marker for survival before mechanical ventilation is applied in the clinical context of a COPD patient with respiratory failure.
There are conflicting data in the literature regarding hypercapnia as a predictor for survival in COPD patients8, 19-22). There is a concern that acidosis and hypercapnia may carry the risk of pulmonary vasoconstriction and pulmonary hypertension 29-33). Many in vivo and in vitro experimental models have demonstrated that hypercapnia causes no harm, and indeed it directly ameliorates lung injury after ischemic-reperfusion, free radical exposure and ventilator-induced lung damage11-18). There are additional reports that hypercapnic acidosis attenuates several aspects of the inflammatory response, and that acidosis per se has a cytoprotective effect34-43). Indeed, hypercapnic acidosis is reported to alleviate ischemia-induced injury, and even in the heart and brain44-49). Elevation of the systemic carbon dioxide tension has been considered as a negligible side-effect that is the consequence of limiting alveolar stress for lung-protective ventilation, and permissive hypercapnia (acceptance of increased concentrations of carbon dioxide in mechanically-ventilated patients) has been found to increase survival50-53). Conversely, hypocapnia, which is related to many acute illnesses, is thought to reflect the underlying hyperventilation. However, we could not say that our results indirectly support the above-mentioned studies. Moreover, the present study was unable to determine whether acidosis or hypercapnia has the greater beneficial effect because the effects of pH and pCO2 were not separately analyzed.
Hypercapnia has been reported in clinical studies to result in a better prognosis for COPD and interstitial fibrosis patients19, 20). We have also observed that a higher PaCO2 level could be an independent parameter of better survival in respiratory failure patients with tuberculosis-destroyed lungs54).
With reference to hypocapnia, it has been suggested that low PaCO2 levels identical to those observed during hypoxia indicate a condition that requires a higher degree of ventilation to maintain the oxygenation, and this suggests the presence of more advanced diffusion disturbances or a more advanced ventilation-perfusion mismatch20, 54). There is also a possibility that some degree of hypoventilation related to hypercapnia could delay respiratory muscle fatigue and improve the survival rate19).
An issue for this study was the classification of COPD into emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Hypercapnia linked to a better COPD prognosis may be attributed to the possibility that late stage emphysema may have played a role, and this was more common in the hypocapnic group19). We were unable to separate the COPD patients into emphysema and chronic bronchitis groups because the HRCT data was not available.
While NPPV is known to reduce mortality in COPD patients55, 56), the application of NPPV in this retrospective study was not randomized and multivariate analysis did not identify the independent benefits of NPPV. In this study, the mortality rate of all the patients who received mechanical ventilation while in MICU was 29.5%. The reported mortality rates for the COPD patients while they received mechanical ventilation due to acute respiratory failure range between 19% and 46%1-9). This wide range in the reported mortality may reflect differences in the severity of organ dysfunction and the different inclusion criteria for each study.
The data for the present study were collected over 10 years. Recent advances in mechanical ventilation strategies may be a confounding factor for the parameters such as the total ventilation time and survival. However, differing mechanical ventilation strategies were not considered in the analysis as the study focused on the initial manifestations at the time of MICU admission.
In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to show data indicating that hypercapnia is an independent predictor for survival in the COPD patients who undergo mechanical ventilation. In addition, the study showed that shock, a high APACHE II score and a long ventilation time were also independent prognostic factors.
References
1. Celli BR, MacNee W. Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD: a summary of the ATS/ERS position paper. Eur Respir J 2004;23:932–946PMID : 15219010.


2. Menzies R, Gibbons W, Goldberg P. Determinants of weaning and survival among patients with COPD who require mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory failure. Chest 1989;95:398–405PMID : 2914493.


3. Spicher JE, White DP. Outcome and function following prolonged mechanical ventilation. Arch Intern Med 1987;147:421–425PMID : 3827415.


4. Stauffer JL, Fayter NA, Graves B, Cromb M, Lynch JC, Goebel P. Survival following mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory failure in adult men. Chest 1993;104:1222–1229PMID : 8404197.


5. Driver AG, McAlevy MT, Smith JL. Nutritional assessment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and acute respiratory failure. Chest 1982;82:568–571PMID : 6813030.


6. Corrado A, Gorini M, Ginanni R, Pelagatti C, Villella G, Buoncristiano U, Guidi F, Pagni E, Peris A, de Paola E. Negative pressure ventilation versus conventional mechanical ventilation in the treatment of acute respiratory failure in COPD patients. Eur Respir J 1998;12:519–525PMID : 9762773.


7. Nevins ML, Epstein SK. Predictors of outcome for patients with COPD requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Chest 2001;119:1840–1849PMID : 11399713.


8. Fuso L, Incalzi RA, Pistelli R, Muzzolon R, Valente S, Pagliari G, Gliozzi F, Ciappi G. Predicting mortality of patients hospitalized for acutely exacerbated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Med 1995;98:272–277PMID : 7872344.


9. Afessa B, Morales IJ, Scanlon PD, Peters SG. Prognostic factors, clinical course, and hospital outcome of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease admitted to an intensive care unit for acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med 2002;30:1610–1615PMID : 12130987.


10. Schols AM, Slangen J, Volovics L, Wouters EF. Weight loss is a reversible factor in the prognosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:1791–1797PMID : 9620907.


11. Shibata K, Cregg N, Engelberts D, Takeuchi A, Fedorko L, Kavanagh BP. Hypercapnic acidosis may attenuate acute lung injury by inhibition of endogenous xanthine oxidase. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;158:1578–1584PMID : 9817711.


12. Laffey JG, Kavanagh BP. Carbon dioxide and the critically ill: too little of a good thing? Lancet 1999;354:1283–1286PMID : 10520649.


13. Laffey JG, Engelberts D, Kavanagh BP. Buffering hypercapnic acidosis worsens acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161:141–146PMID : 10619811.


14. Hickling KG. Lung-protective ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome protection by reduced lung stress or by therapeutic hypercapnia? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:2021–2022PMID : 11112102.


15. Laffey JG, Tanaka M, Engelberts D, Luo X, Yuan S, Tanswell AK, Post M, Lindsay T, Kavanagh BP. Therapeutic hypercapnia reduces pulmonary and systemic injury following in vivo lung reperfusion. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:2287–2294PMID : 11112153.


16. Broccard AF, Hotchkiss JR, Vannay C, Markert M, Sauty A, Feihl F, Schaller MD. Protective effects of hypercapnic acidosis on ventilator induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;164:802–806PMID : 11549536.


17. Sinclair SE, Kregenow DA, Lamm WJ, Starr IR, Chi EY, Hlastala MP. Hypercapnic acidosis is protective in an in vivo model of ventilator induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;166:403–408PMID : 12153979.


18. Laffey JG, Honan D, Hopkins N, Hyvelin JM, Boylan JF, McLoughlin P. Hypercapnic acidosis attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;169:46–56PMID : 12958048.


19. Dubois P, Jamart J, Machiels F, Smeets F, Lulling J. Prognosis of severely hypoxemic patients receiving long-term oxygen therappy. Chest 1994;105:469–474PMID : 8306749.


20. Strom K, Boman G. Long-term oxygen therapy in parenchymal lung disease: an analysis of survival. Eur Respir J 1993;6:1264–1270PMID : 8287941.


21. The Medical Research Council Working Party. Long-term domiciliary oxygen therapy in chronic hypoxic cor pulmonale complicating chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Lancet 1981;1:681–686PMID : 6110912.


22. Emerman CL, Connors AF, Lukens TW, Effron D, May ME. Relationship between arterial blood gases and spirometry in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Emerg Med 1989;18:523–527PMID : 2497664.


23. American Thoracic Society. Standards for the diagnosis and care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 1987;136:225–244PMID : 3605835.


24. American Thoracic Society. Standards for the diagnosis and care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995;152:S77–S121PMID : 7582322.

25. Siafakas NM, Vermeire P, Pride NB, Paoletti P, Gibson J, Howard P, Yernault JC, Decramer M, Higenbottam T, Postma DS, Rees J. Optimal assessment and management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Eur Respir J 1995;8:1398–1420PMID : 7489808.


26. Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;163:1256–1276PMID : 11316667.


27. American Thoracic Society. Lung function testing: selection of reference values and interpretative stratedies. Am Rev Respir Dis 1991;144:1202–1218PMID : 1952453.


28. Calverley PM. Respiratory failure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J 2003;47(Suppl 47):26s–30s.

29. Horsfield K, Segel N, Bishop JM. The pulmonary circulation in chronic bronchitis at rest and during exercise breathing air and 80% oxygen. Clin Sci 1968;34:473–483PMID : 5666876.

30. Aber GM, Bayley TJ, Bishop JM. Inter-relationships between renal and cardiac function and respiratory gas exchange in obstructive airways disease. Clin Sci 1963;25:159–170PMID : 14070901.

31. Durand J, Leroy-Ladurie M, Ransom-Bitker B. Effects of hypoxia and hypercapnea on the repartition of pulmonary blood flow in supine subjects. Prog Respir Res 1970;5:156–165.

32. Enson Y, Giuntini C, Lewis ML, Morris TQ, Ferrer MI, Harvey RM. The influence of hydrogen ion concentration and hypoxia on the pulmonary circulation. J Clin Invest 1964;43:1146–1162PMID : 14171792.



33. Housley E, Clarke SW, Hedworth-Whitty RB, Bishop JM. Effect of acute and chronic acidaemia and associated hypoxia on the pulmonary circulation of patients with chronic bronchitis. Cardiovasc Res 1970;4:482–489PMID : 5533087.


34. Rehncrona S, Hauge HN, Siesj BK. Enhancement of iron-catalyzed free radical formation by acidosis in brain homogenates: difference in effect by lactic acid and CO2. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1989;9:65–70PMID : 2492027.


35. Allen DB, Maguire JJ, Mahdavian M, Wicke C, Marcocci L, Scheuenstuhl H, Chang M, Le AX, Hopf HW, Hunt TK. Wound hypoxia and acidosis limit neutrophil bacterial killing mechanisms. Arch Surg 1997;132:991–996PMID : 9301612.


36. Xu L, Glassford AJ, Giaccia AJ, Giffard RG. Acidosis reduces neuronal apoptosis. Neuroreport 1998;9:875–879PMID : 9579683.


37. Wang H, Harrison-Shostak DC, Lemasters JJ, Herman B. Contribution of pH-dependent group II phospholipase A2 to chemical hypoxic injury in rat hepatocytes. FASEB J 1996;10:1319–1325PMID : 8836046.


38. Serrano CV Jr, Fraticelli A, Paniccia R, Teti A, Noble B, Corda S, Faraggiana T, Ziegelstein RC, Zweier JL, Capogrossi MC. pH dependence of neutrophil-endothelial cell adhesion and adhesion molecule expression. Am J Physiol 1996;271:C962–C970PMID : 8843727.


39. Gewirtz AT, Seetoo KF, Simons ER. Neutrophil degranulation and phospholipase D activation are enhanced if the Na+/H+ antiport is blocked. J Leukoc Biol 1998;64:98–103PMID : 9665282.


40. Yamaguchi K, Takasugi T, Fujita H, Mori M, Oyamada Y, Suzuki K, Miyata A, Aoki T, Suzuki Y. Endothelial modulation of pH-dependent pressor response in isolated perfused rabbit lungs. Am J Physiol 1996;270:H252–H258PMID : 8769759.


41. Parfenova H, Leffler CW. Effects of hypercapnia on prostanoid and cAMP production by cerebral microvascular cell cultures. Am J Physiol 1996;270:C1503–C1510PMID : 8967453.


42. Abu Romeh S, Tannen RL. Amelioration of hypoxia-induced lactic acidosis by superimposed hypercapnea or hypochloride acid infusion. Am J Physiol 1986;250:F702–F709PMID : 3083699.

43. Swallow CJ, Grinstein S, Sudsbury RA, Rotstein OD. Modulation of the macrophage respiratory burst by an acidic environment: the critical role of cytoplasmic pH regulation by proton extrusion pumps. Surgery 1990;108:363–369PMID : 2166358.

44. Kitakaze M, Weisfeldt ML, Marban E. Acidosis during early reperfusion prevents myocardial stunning in perfused ferret hearts. J Clin Invest 1988;82:920–927PMID : 3417873.



45. Kitakaze M, Takashima S, Funaya H, Minamino T, Node K, Shinozaki Y, Mori H, Hori M. Temporary acidosis during reperfusion limits myocardial infarct size in dogs. Am J Physiol 1997;272:H2071–H2078PMID : 9176271.


46. Kitakaze M, Node K, Takashima S, Asanuma H, Asakura M, Sanada S, Shinozaki Y, Mori H, Sato H, Kuzuya T, Hori M. Role of cellular acidosis in production of nitric oxide in canine ischemic myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2001;33:1727–1737PMID : 11549351.


47. Nomura F, Aoki M, Forbess JM, Mayer JE Jr. Effects of hypercarbic acidotic reperfusion on recovery of myocardial function after cardioplegic ischemia in neonatal lambs. Circulation 1994;90:II321–II327PMID : 7955274.

48. Vannucci RC, Towfighi J, Heitjan DF, Brucklacher RM. Carbon dioxide protects the perinatal brain from hypoxicischemic damage: an experimental study in the immature rat. Pediatrics 1995;95:868–874PMID : 7761212.



49. Vannucci RC, Brucklacher RM, Vannucci SJ. Effect of carbon dioxide on cerebral metabolism during hypoxiaischemia in the immature rat. Pediatr Res 1997;42:24–29PMID : 9212033.


50. Hickling KG, Walsh J, Henderson S, Jackson R. Low mortality rate in adult respiratory distress syndrome using low-volume, pressurelimited ventilation with permissive hypercapnia: a prospective study. Crit Care Med 1994;22:1568–1578PMID : 7924367.


51. Milberg JA, Davis DR, Steinberg KP, Hudson LD. Improved survival in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): 1983-1993. JAMA 1995;273:306–309PMID : 7815658.


52. Montgomery AB, Stager MA, Carrico CJ, Hudson LD. Causes of mortality in patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Resp Dis 1985;132:485–489PMID : 4037521.


53. Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, Magaldi RB, Schettino GP, Lorenzi-Filho G, Kairalla RA, Deheinzelin D, Munoz C, Oliveira R, Takagaki TY, Carvalho CR. Effect of a protective ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 1998;338:347–354PMID : 9449727.


54. Park JH, Na JO, Kim EK, Lim CM, Shim TS, Lee SD, Kim WS, Kim DS, Kim WD, Koh Y. The prognosis of respiratory failure in patients with tuberculous destroyed lung. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2001;5:963–967PMID : 11605892.

Figure 2
Correlation between the PaCO2 and the APACHE II score at the time of MICU admission (r=-0.313, p=0.005).
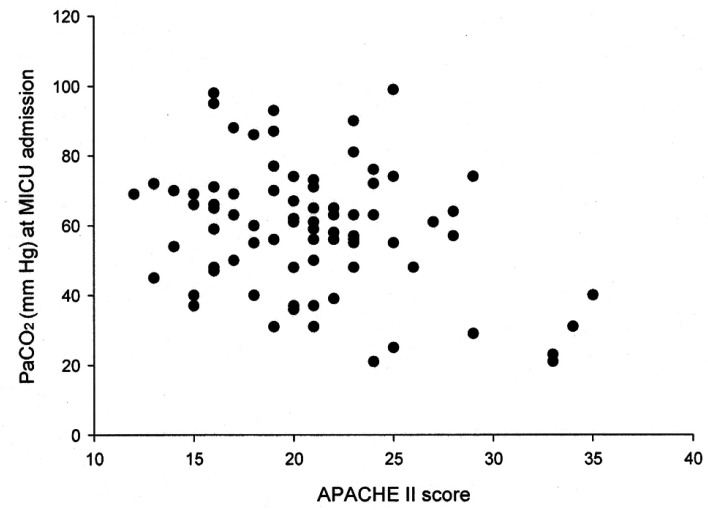
Table 3
Comparison of the parameters at the time of MICU admission between the survivals and non-survivals




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



