INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
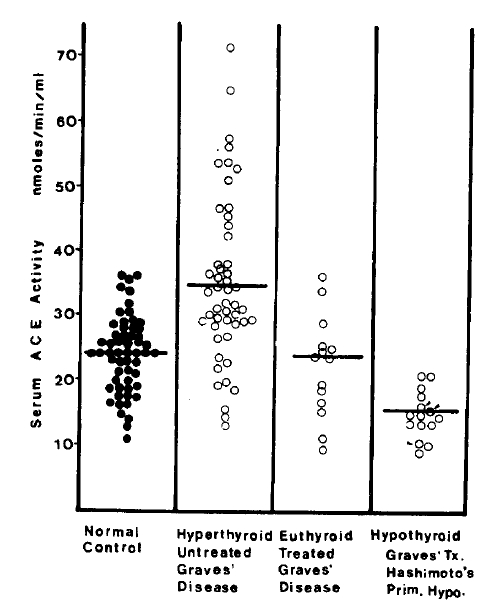
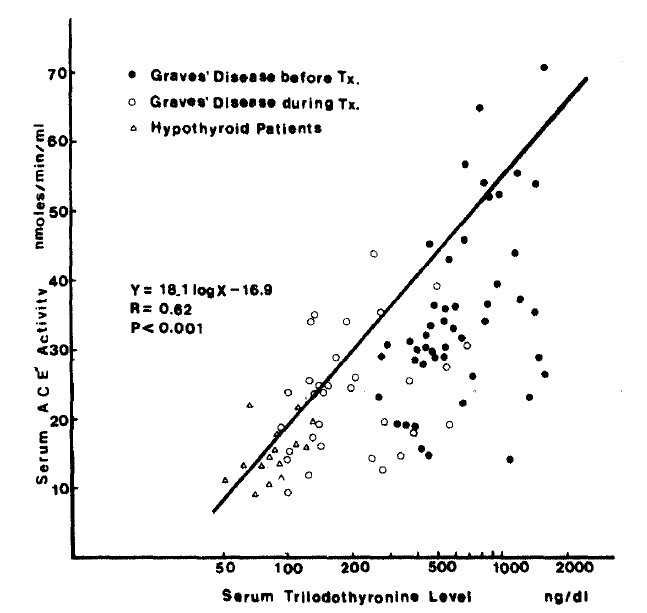
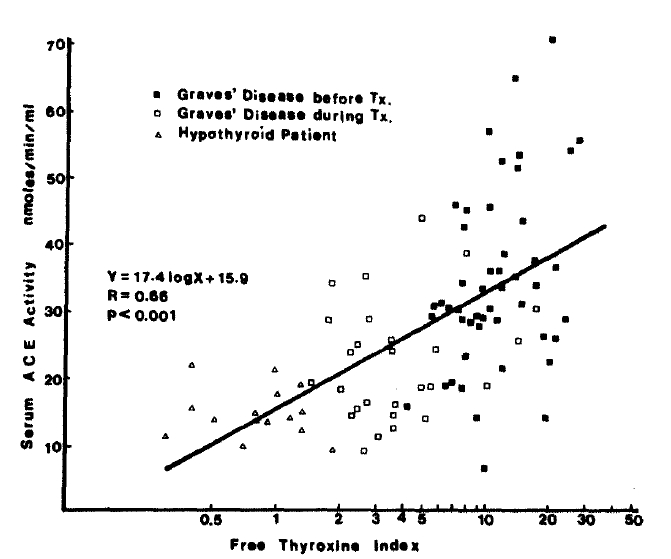
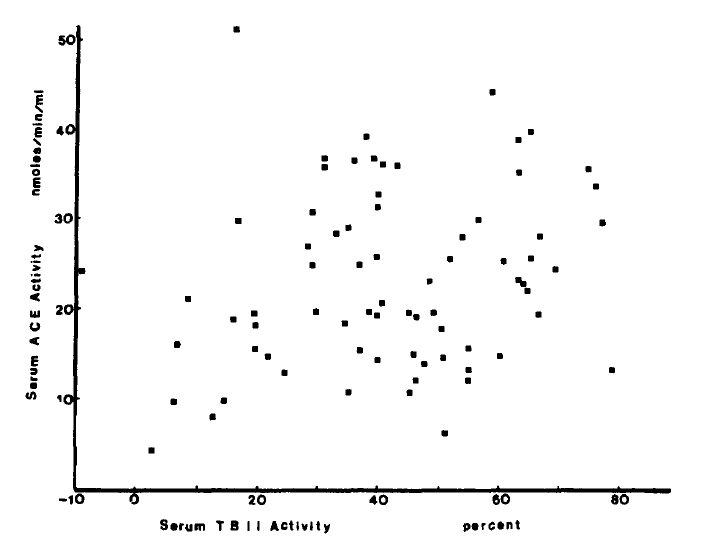
1. Subjects
2. Methods
-
Specimen
The blood of normal persons and the patients were taken and left for appropimately an hour at room temperature. Then, the serum was taken and stored at ŌłÆ70┬░C and the assay was done within 6 months. The assay of serial samples of a patient was done at the same time. -
Measurement of serum ACE activity
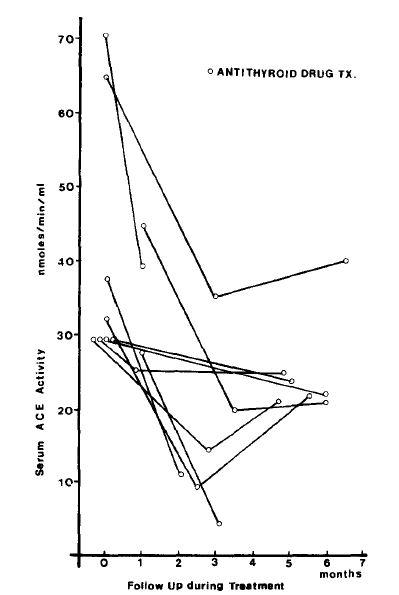
Serum ACE activity was measured by a modification of the method of Cushman and Cheung. Hippuryl-histidyl-leucin (Sigma┬«) was used as a substrate, and phosphate was used as a buffer and hippuric acid produced by ACE activity in patientŌĆÖs sera was measured at 228 nm by spectrophotometry. In the normal control serum and the positive standard serum, the intraassay coefficients of variation were both 4.4%, and the interassay coefficients of variation were 11 % and 6% (Table 1). To observe serial change of ACE activity in a patient, the specimens having been refrigerated at ŌłÆ70┬░C, were measured together at the same time. Accordingly, the measurement error of the assay for the evaluation of the change during treatment was 4.4%. It was not found that the enzyme activity decreased or changed significantly during storage for 6 months. -
Measurement of serum TBII activity
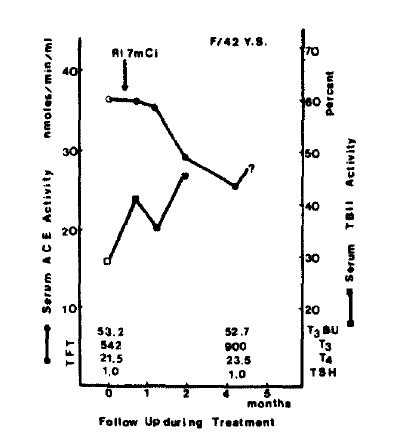
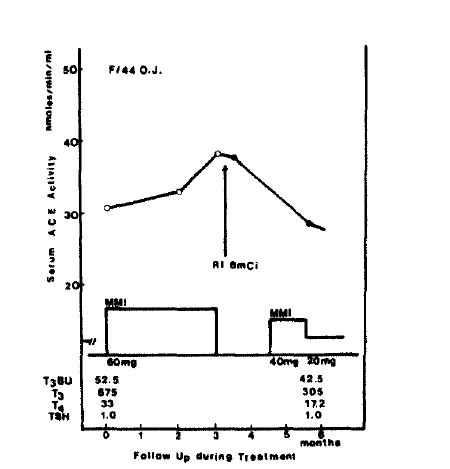
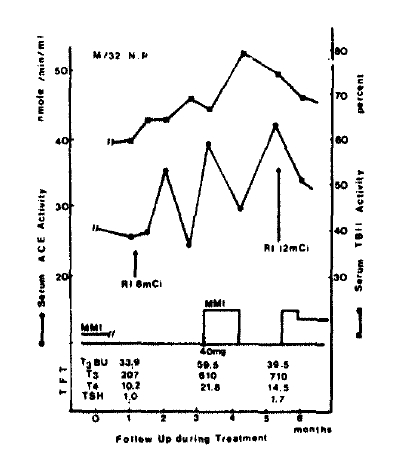
Using the commerical kits, R.S.R.┬« radioreceptor assay, patientŌĆÖs serum TBII activity was measured by the activity to displace radiolabeled TSH from solubilized membrane TSH receptor. The normal range was less than 15%, the intraassay and interassay coefficients of variation were between 4% and 15%. Triiodothyronine (T3), total Thyroxin (T4), and T3 Bead Uptake in serum were measured by radioimmunoassay (Abbott┬«). The normal range of T3 was 99ŌĆō219ng/d1, and that of T4 was 6.6ŌĆō13.8ug/d1. The normal range of T3 Bead Uptake was 22.8ŌĆō33.6%, and that of free T4 index was 1.7ŌĆō4.0.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





