 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 39(2); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Mucoprotective agents, such as eupatilin, are often prescribed to prevent gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding in addition to an acid suppressant despite the absence of a large-scale study. We evaluated the additional effect of eupatilin on the prevention of GI bleeding in both the upper and lower GI tract in concomitant aspirin and acid suppressant users using the nationwide database of national claims data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS).
Methods
An aspirin cohort was constructed using the NHIS claims data from 2013 to 2020. Patients who manifested with hematemesis, melena, or hematochezia were considered to have GI bleeding. A Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to determine the risk factors for GI bleeding associated with the concomitant use of GI drugs and other covariates among aspirin users.
Results
Overall, a total of 432,208 aspirin users were included. The concurrent use of an acid suppressant and eupatilin (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.85, p = 0.016, vs. acid suppressant only) was a statistically significant preventive factor for GI bleeding. Moreover, a more than 3-month duration (HR = 0.88, p = 0.030) of acid suppressant and eupatilin prescription (vs. acid suppressant only) was a statistically significant preventive factor for GI bleeding.
Conclusions
Eupatilin administration for Ōēź 3 months showed additional preventive effect on GI bleeding in concomitant aspirin and acid suppressant users. Thus, cotreatment with eupatilin with a duration of 3 months or longer is recommended for reducing GI bleeding among aspirin plus acid suppressant users.
In the United States, cardiovascular disease (CVD), specifically acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and stroke, is the leading cause of disability and mortality [1]. Aspirin is widely accepted as a secondary CVD prevention after AMI or stroke [2]. Moreover, in large surveys, use rates for primary CVD prevention in the population increased steadily in both men and women from 1980 to 2009, reaching approximately 21% of men and 12% of women aged 25 to 74 years [3].
However, the conflict between the benefits and harm of aspirin usage persists. Low doses of aspirin can inflict injury to the gastrointestinal (GI) mucosa, with the potential for considerable morbidity and mortality [4]. The primary adverse effect of aspirin is major bleeding, typically defined as bleeding from the GI tract or other sites that require hospitalization or transfusion. In most patients who are on aspirin, bleeding most commonly occurs in the GI tract [5].
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are useful for the prevention of ulcers secondary to low-dose aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use [6ŌĆō8]. Additionally, a previous study showed that mucoprotective agents (MPAs) such as misoprostol can decrease the risk of upper GI bleeding in aspirin or NSAID users [9]. Therefore, MPAs are often prescribed in clinical practice to prevent or treat upper GI bleeding in addition to PPI or histamine-2 receptor antagonist (H2RA). However, relevant evidence for MPAs except misoprostol is limited, and no large-scale studies have been conducted. In addition to upper GI bleeding, the treatment and prevention of aspirin-associated lower GI bleeding remain unclear and difficult, because the pathogenic mechanisms are different and poorly understood. The national claims data could be considered as a real-world evidence in a large population. Thus, we aimed to investigate the additional effect of MPA, especially eupatilin, on total GI bleeding prevention including lower GI bleeding in concomitant users of aspirin and acid suppressants such as PPI and H2RA using the nationwide database of national claims data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS).
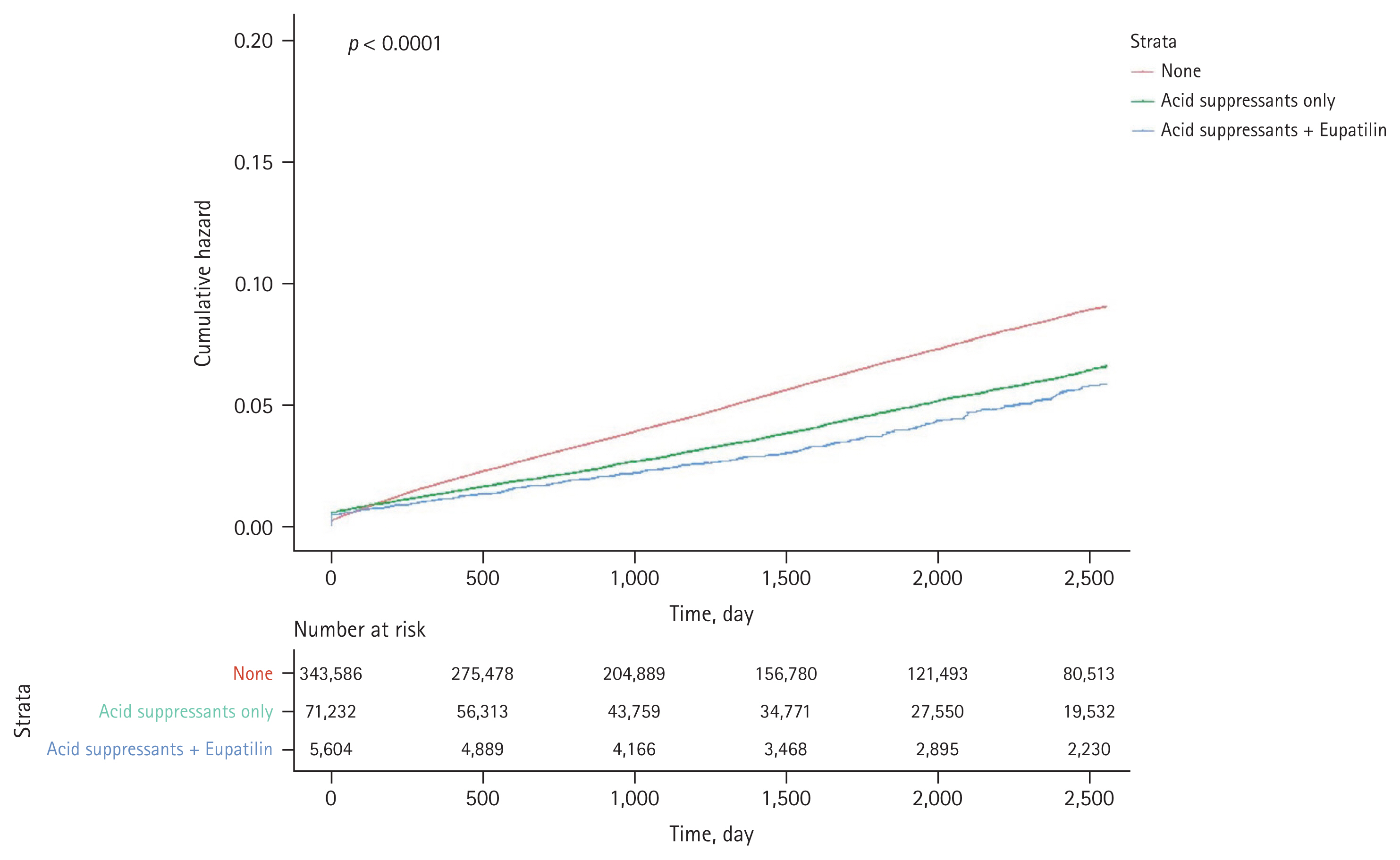
This study utilized the cohort data from the Korean nationwide cohort database (NHIS). Since 2002, the NHIS database has been an invaluable resource for patient data regarding the residence, income levels (based on salary and property), medical diagnosis, disability or death-related data, and claims data under insurance coverage. We constructed a cohort of 5,261,222 aspirin/NSAID users between 2013 and 2020 using the South Korea NHIS database to assess aspirin-induced GI bleeding. To ensure exclusive focus on aspirin usage, 507,344 patients who were prescribed with aspirin for over 28 days were selected from 5,261,222 aspirin/NSAID users. Patients who died during 2013ŌĆō2020 were excluded. Individuals with missing values for age or sex and those who were prescribed with MPAs only without PPI or H2RA were excluded. If one person discontinued aspirin for more than 6 months and resumed again, the resumption was considered an additional case, resulting in 432,208 cases of aspirin users in total (Fig. 1).
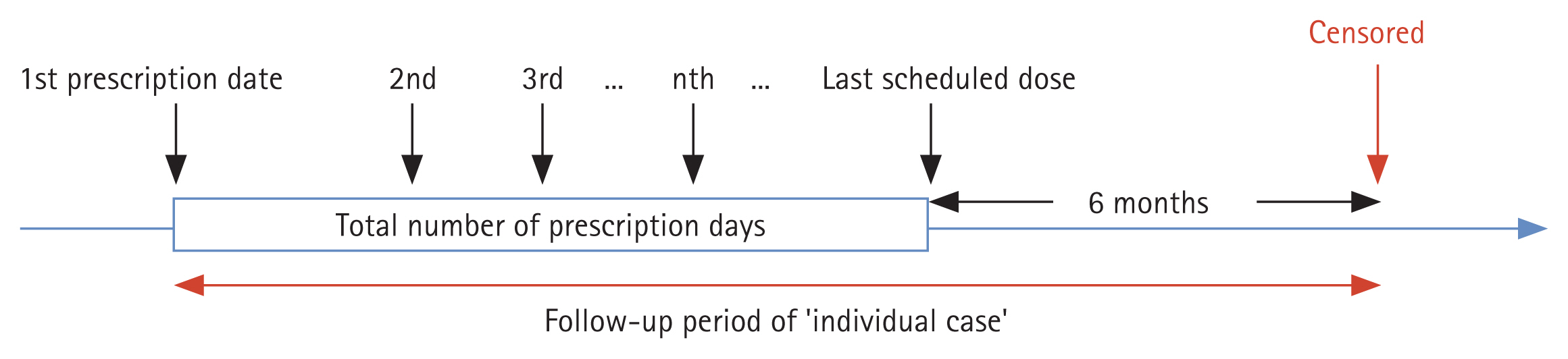
The follow-up period of the case was from the date of the first dose of aspirin to 6 months after the scheduled dose of the last aspirin administration (Fig. 2). The event was measured based on hospital visits due to GI bleeding and censored at the end of the follow-up period. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital (DUIH 2020-05-010-002), which waived the requirement for informed consent.
The relevant diseases were identified using the International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision codes for hematemesis (K920), melena or hematochezia (K921), or GI hemorrhage (including upper GI bleeding and lower GI bleeding) (K922) in the NHIS data. Patients with hematemesis, melena or hematochezia, or GI hemorrhage who had an emergency room consult were defined to have GI bleeding.
The use of aspirin corresponded to the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) code B01AC06 (acetylsalicylic acid). The concomitant anticoagulant use (warfarin, clopidogrel, cilostazol, prasugrel, ticagrelor, dipyridamole, nonvitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants, and combination drugs containing these ingredients) was also identified in ATC. The concurrent prescription of GI drugs such as PPIs, H2RAs, and MPAs (eupatilin, rebamipide, teprenone, irsogladine, ecabet sodium, polaprezinc, troxipide, sodium alginate, sucralfate, bismuth, sulglycotide, misoprostol, and their combinations) was also investigated. Other covariates included age, sex, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI). The CCI was calculated by scoring the comorbid conditions that could affect the patientsŌĆÖ health outcomes and categorizing them into three groups: 0, 1, 2, 3, or more.
Categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages, while continuous variables were presented as mean ┬▒ standard deviation. The endpoint was GI bleeding during the follow-up period. A chi-square test was performed to compare the occurrences of GI bleeding associated with the intake of specific GI drugs and other covariates. A Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs), and 95% confidence intervals were used to determine the risk factors for GI bleeding associated with the concomitant use of GI drugs and other covariates. Multiple models were adjusted for sex, age, CCI score, peptic ulcer history, concurrent anticoagulant use, acid suppressants (PPIs and H2RAs), and eupatilin as covariates. The cumulative incidence rates of GI bleeding were calculated using the KaplanŌĆōMeier method for different classifications of GI drugs. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. All the statistical analyses were performed using SAS 9.4 version (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) and R version 4.0.3 (R studio, PBC).
Overall, 432,208 eligible aspirin users were included in this study (Table 1). The mean duration of aspirin prescription was 990.7 days. Total aspirin users were classified as the no GI bleeding group and GI bleeding group. GI bleeding was identified in 21,912 patients (5.1%), with a median aspirin prescription duration of 1,150.2 days. The proportion of patients with a CCI score Ōēź 3 was higher with 52.4% (11,478/21,912) in the GI bleeding group than with 37.6% (154,338/410,296) in the no GI bleeding group. In the GI bleeding group, the proportion of patients with a previous peptic ulcer disease history was significantly higher than that in the no GI bleeding group (24.6% [5,389/21,912] vs. 16.5% [67,611/410,296], p < 0.001). In the GI bleeding group, the concomitant use of anticoagulants was significantly higher with 57.9% (12,681/21,912) than that with 33.5% (137,436/410,296) in the no GI bleeding group (p < 0.001). The GI drug prescription rates among the total baseline aspirin users were 12.3% (53,298/432,208), 8.9% (38,617/432,208), and 1.5% (6,479/432,208) for PPI, H2RA, and eupatilin, respectively. The proportion of patients who are on combination GI drugs among the total baseline aspirin users was 16.5% (71,232/432,208) and 1.3% (5,604/432,208) for acid-suppressant (PPI or H2RA) only and the concurrent prescription of an acid suppressant and eupatilin, respectively.
Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted for factors associated with GI bleeding in aspirin users (Table 2). Univariate analysis showed that age Ōēź 65 years, male sex, high CCI scores, peptic ulcer disease history, and anticoagulant use were statistically significant, whereas the concurrent use of acid suppressant only and the concurrent use of acid suppressant and eupatilin were inversely associated with GI bleeding. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that age Ōēź 65 years (HR = 1.26, p < 0.001), male sex (HR = 1.08, p < 0.001), high CCI scores (HR = 1.51, p < 0.001 in CCI score Ōēź 3), peptic ulcer disease history (HR = 1.21, p < 0.001), and anticoagulant use (HR = 2.39, p < 0.001) were statistically significant. Conversely, the concurrent use of acid suppressant only (HR = 0.57, p < 0.001) and the concurrent use of acid suppressant and eupatilin (HR = 0.49, p < 0.001) were preventive factors, in which factors were based on patients with no GI drugs as a reference.
In addition to these initial results, univariate and multivariate analyses were separately performed for factors associated with GI bleeding, which were based on patients on a concurrent use of acid suppressant only as a reference (Table 3). Univariate analysis revealed that age Ōēź 65 years, high CCI scores, peptic ulcer disease history, and anticoagulant use were statistically significant, whereas the concurrent use of acid suppressant and eupatilin were inversely associated with GI bleeding. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that age Ōēź 65 years (HR = 1.36, p < 0.001), high CCI scores (HR = 4.06, p < 0.001 in CCI score Ōēź 3), peptic ulcer disease history (HR = 1.38, p < 0.001), and anticoagulant use (HR = 1.69, p < 0.001) were statistically significant. In contrast, the concurrent use of acid suppressant and eupatilin (HR = 0.85, p = 0.016) was a preventive factor, which was based on patients with the concurrent use of acid suppressant only as a reference.
Moreover, univariate and multivariate analyses were separately performed for factors associated with GI bleeding, particularly, the prescription duration of acid suppressant and eupatilin, which were based on patients with the concurrent use of acid suppressant only as a reference (Table 4). In the multivariate analysis, a more than 3-month duration (HR = 0.88, p = 0.030) of acid suppressant and eupatilin prescription (vs. acid suppressant only) was a statistically significant preventive factor, which was based on patients with the concurrent use of acid suppressant only.
Figure 3 illustrates the KaplanŌĆōMeier curve showing the cumulative incidence rates of GI bleeding according to the concurrent use of acid suppressants and eupatilin in aspirin users. GI bleeding was observed less frequently in aspirin users with a concurrent use of acid suppressants only (without eupatilin) compared to those without the GI drug prescriptions (i.e., aspirin users only). Additionally, GI bleeding was observed less frequently in aspirin users who are using a combination of acid suppressants and eupatilin compared to those with a concurrent use of acid suppressants only (without eupatilin).
To the best of our knowledge, using the nationwide database of national claims data, this is the first study to investigate the additional effect of eupatilin as an MPA on total GI bleeding prevention including the upper and lower GI tracts of aspirin plus concomitant acid suppressant users such as PPI or H2RA. This study is representative of the general population, as data were collated from the Korean NHIS database, which encompasses the entire nation. Other possible risk factors for GI bleeding, such as concomitant anticoagulant use and other comorbidities, were statistically analyzed. Our study findings reveal that the concurrent use of acid suppressants only (without eupatilin) in aspirin users showed a decreased GI bleeding incidence compared to aspirin use without GI drugs. Moreover, the use of eupatilin in addition to acid suppressants demonstrated a significantly lower incidence of GI bleeding in aspirin users compared to concurrent users of aspirin and acid suppressants or aspirin-only users. Also, a 3-month or longer use of eupatilin was deemed more effective.
A major adverse clinical outcome associated with the use of aspirin is GI bleeding. Current evidence shows that aspirin increases the risk of lower GI bleeding to a similar extent as that in the upper GI [10,11]. Lower GI bleeding secondary to aspirin use has become an important medical issue because the number of aspirin users has increased recently, and older age is an important risk factor for lower GI bleeding [12]. Acid suppressants such as PPIs and H2RAs are typically associated with a reduced risk of upper GI bleeding in aspirin users [13]. However, these do not confer protective effects against aspirin-induced lower GI injury. Some studies have shown that PPIs and H2RAs are associated with an increased risk of lower GI bleeding [14ŌĆō16]. In a previous study with a small sample size, misoprostol has shown efficacy in the treatment of aspirin-induced intestinal injury [17]. However, frequent misoprostol side effects are dose-dependent cramping, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. In many patients, these side effects interfere with compliance [18]. Moreover, effective medications to prevent aspirin-induced lower GI bleeding is not yet available.
PPIs and H2RAs are well-known, effective agents for treating or preventing upper GI bleeding in aspirin users [19,20]. Despite the wide use of PPIs, long-term PPI use has been associated with several safety concerns. Previous studies have reported that PPI use has been associated with an increased risk of mineral malabsorption, bone fracture, and enteric infections [21ŌĆō24]. The pathophysiologic mechanism involved in the increased risk of infection remains unclear, although the mechanism of action of PPIs is to block the gastric acid secretion in the stomach. Because of the concerns regarding the long-term safety of PPIs, clinicians consider alternative medications such as MPAs. MPAs, including eupatilin, rebamipide, and misoprostol, do not inhibit gastric acid secretion. Eupatilin is the standardized extract of Artemisia asiatica and has been widely prescribed for treating or preventing gastric mucosal lesions in Asia. Eupatilin has been found to have anti-inflammatory and protective effects against GI lesions in both animal models and humans, which were small sample-sized studies [25ŌĆō28]. A recent large-scale retrospective observational study has found that eupatilin did not reduce the risk of occult GI bleeding in NSAID users [29]. The study used a Ōēź 2 g/dL drop in hemoglobin level to define occult GI bleeding and included participants who underwent routine asymptomatic laboratory follow-ups, which were not conducted on patients with overt GI bleeding and could be a study limitation. Conversely, the present study evaluated the overt GI bleeding risk in aspirin users with the concomitant use of MPA, especially eupatilin. Our results revealed that the use of eupatilin in addition to acid suppressants showed a reduced incidence of GI bleeding in aspirin users compared to concurrent users of aspirin and acid suppressants or aspirin-only users.
A previous small bowel capsule endoscopy (CE) registry-based Korean study, including data from 4,650 CE examinations, revealed that patients in whom the indication for CE was overt, obscure GI bleeding accounted for 53.1% of those who had taken NSAIDs, and the rate of CE diagnosis of NSAID enteropathy was 5.9%. Although the study was limited by a small cohort, the number of diagnoses of NSAID enteropathy had increased, and this increase could be attributed to the aging population [30]. Our study group, using the nationwide database of claims data from the NHIS, found that MPAs had a protective effect against small bowel bleeding in patients using aspirin [31]. In that study, patients with anemia, melena, or hematochezia that occurred within 4 weeks before and after CE were suspected to have small bowel bleeding. Overall, 15,542 patients taking aspirin were included in the study, and small bowel bleeding was confirmed in 126 (0.8%). In that study, PPI use (HR, 2.85) was significantly associated with small bowel bleeding, whereas eupatilin use (HR, 0.35) appeared to be preventive. Small bowel bleeding occurred more frequently in patients who used acid suppressants concurrently with PPIs than in those who did not use acid suppressants concurrently with PPIs (1.3 vs. 0.5%). Subgroup analysis revealed that eupatilin significantly reduced the risk of small bowel bleeding in patients using aspirin concurrently with acid suppressants (HR, 0.23 vs. 2.55) [31]. However, the numbers of patients taking aspirin and those with small bowel bleeding were relatively small. Because the CE findings could not be identified from the claims data, a proportion of CE examinations may not have revealed any bleeding origins in the small bowel. To overcome the study limitations, such as a small number of participants and only patients with small bowel bleeding found on CE examinations, we tried to obtain information from adequate number of patients with total GI bleeding using large-scale nationwide population data.
Because CE is now available to detect small intestinal lesions, small intestinal mucosal injuries have been recognized as a common complication associated with NSAIDs. Small intestinal injury does not occur via an acid-dependent mechanism but because of various factors, such as enteric bacteria; bile acids; prostaglandin deficiency; and topical factors, such as abnormal intestinal mucosal permeability, mitochondrial dysfunction, reactive oxygen species, and stress on the endoplasmic reticulum [32]. Several experimental and clinical studies have revealed the effectiveness of MPAs, such as eupatilin in preventing GI lesions [28,33,34]. In a recent meta-analysis based on 12 studies with 341,063 participants, PPI use was associated with an increased risk of lower GI bleeding, particularly in the small bowel. This association was particularly pronounced among patients taking aspirin or NSAIDs [35]. In a previous study, the following strategies against NSAID-induced GI injuries were recommended [32]. In patients at high risk of upper GI disease, such as peptic ulcer, a PPI for upper GI disease and an MPA for the small intestine should be simultaneously administered to prevent NSAID-induced GI injury. In other patients, an effective MPA is adequate to protect the entire digestive tract, from the esophagus to the small intestine [32]. Our results are the first to demonstrate the positive effects of eupatilin as an MPA on the prevention of total GI bleeding based on large population data in a real-world setting, outside the strictly controlled limits of a clinical trial.
This study has limitations. First, because the esophagogastroduodenoscopy, colonoscopy, and abdominal computed tomography findings could not be identified from the claims data, we considered that the bleeding symptoms such as melena and hematochezia were sufficient measures for overt GI bleeding. The causes and locations of GI bleeding were not identified in detail. Nevertheless, our results included an analysis of the risk for total GI bleeding; however, differentiating between upper and lower GI bleeding was not conducted, which is a limitation. Second, we could not distinguish between the patients who took PPIs and those who took H2RAs, although these drugs have different levels of potency and different effects on acid suppression. These acid suppressants can be prescribed in different amounts, such as PPIs in half or full doses and H2RAs once or twice a day; however, such regimens could not be identified and analyzed in detail from the claims data. Despite these limitations, we believe that the present study has value because the protective effect of eupatilin as an MPA on total GI bleeding in aspirin plus acid suppressant users were evaluated based on the nationwide database of claims data.
In conclusion, eupatilin showed an additional preventive effect for GI bleeding occurrence in aspirin users with concomitant use of an acid suppressant. Moreover, overt GI bleeding reduction was more effective with a 3-month or longer eupatilin use. While acid suppressants are widely used for the prevention of GI bleeding in aspirin uses, the coadministration of eupatilin could be expected to decrease GI bleeding risk. A 3-month or longer-term cotreatment of eupatilin could be recommended for reducing GI bleeding in aspirin plus acid suppressant users.
1. We evaluated the additional effect of eupatilin on the prevention of GI bleeding in both the upper and lower GI tract in concomitant aspirin and acid suppressant users using the nationwide database of national claims data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service.
2. Eupatilin with a duration of 3 months or longer showed additional preventive effect on GI bleeding in concomitant aspirin and acid suppressant users.
Notes
CRedit authorship contributions
Hyun Seok Lee: conceptualization, methodology, writing - original draft, writing - review & editing, visualization, project administration; Ji Hyung Nam: conceptualization, methodology, project administration; Dong Jun Oh: conceptualization, methodology, project administration; Yeo Rae Moon: methodology, data curation, formal analysis, validation; Yun Jeong Lim: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing - review & editing, visualization, project administration, funding acquisition
Figure┬Ā1
Study flow diagram summarizing the approach for the general population-based aspirin/NSAID cohort construction to investigate aspirin-induced gastrointestinal bleeding. H2RA, histamine- 2 receptor antagonist; MPA, mucoprotective agent; NHIS, National Health Insurance Service; NSAID, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; PPI, proton pump inhibitor.
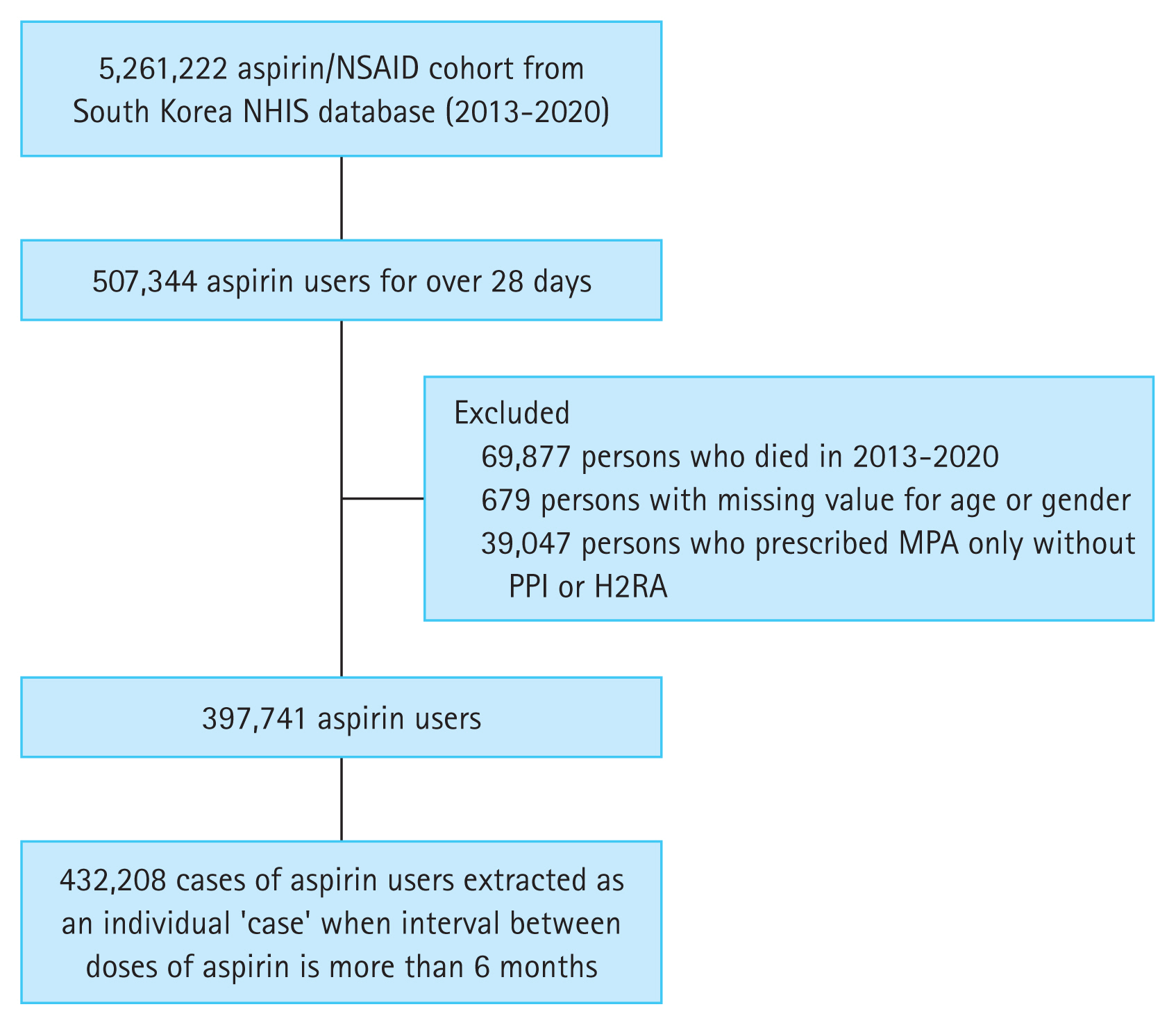
Figure┬Ā3
The KaplanŌĆōMeier curve demonstrating the cumulative incidence rates of gastrointestinal bleeding according to the concurrent use of acid suppressants (proton pump inhibitor or histamine-2 receptor antagonist) and eupatilin in aspirin users. None, only aspirin users without any concurrent use of gastrointestinal drugs; Acid suppressants only, aspirin plus acid suppressants; Acid suppressants + Eupatilin, aspirin plus acid suppressants and eupatilin.
Table┬Ā1
Baseline characteristics of aspirin users and a comparison of those with and without GI bleeding during the follow-up period
Table┬Ā2
Univariate and multivariate analyses of factors for GI bleeding in aspirin users including variables based on patients with no intake of GI drugs as a reference
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | |
| Age, Ōēź 65 yr | 1.42 | 1.39ŌĆō1.47 | < 0.001 | 1.26 | 1.23ŌĆō1.30 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Male | 1.08 | 1.05ŌĆō1.11 | < 0.001 | 1.08 | 1.05ŌĆō1.11 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| CCI scorea) | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆā1 | 1.07 | 1.01ŌĆō1.12 | 0.012 | 1.00 | 0.95ŌĆō1.05 | 0.960 |
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆā2 | 1.25 | 1.19ŌĆō1.31 | < 0.001 | 2.00 | 1.05ŌĆō1.16 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆāŌēź 3 | 1.92 | 1.84ŌĆō2.01 | < 0.001 | 1.51 | 1.44ŌĆō1.58 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Peptic ulcer history | 1.47 | 1.42ŌĆō1.51 | < 0.001 | 1.21 | 1.17ŌĆō1.25 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Anticoagulant | 2.47 | 2.40ŌĆō2.53 | < 0.001 | 2.39 | 2.32ŌĆō2.46 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Acid suppressant only vs. no GI drugs | 0.72 | 0.69ŌĆō0.74 | < 0.001 | 0.57 | 0.55ŌĆō0.59 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Acid suppressant and eupatilin vs. no GI drugs | 0.62 | 0.55ŌĆō0.71 | < 0.001 | 0.49 | 0.43ŌĆō0.56 | < 0.001 |
Table┬Ā3
Univariate and multivariate analyses of factors for gastrointestinal bleeding in aspirin users including variables based on patients with concurrent use of acid suppressant only as a reference
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | |
| Age, Ōēź 65 yr | 1.54 | 1.44ŌĆō1.65 | < 0.001 | 1.36 | 1.26ŌĆō1.47 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Male | 1.05 | 0.98ŌĆō1.12 | 0.159 | 1.07 | 0.99ŌĆō1.15 | 0.071 |
|
|
||||||
| CCI scorea) | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆā1 | 1.95 | 1.59ŌĆō2.40 | < 0.001 | 1.70 | 136ŌĆō2.11 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆā2 | 2.79 | 2.28ŌĆō3.41 | < 0.001 | 2.29 | 1.85ŌĆō2.82 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆāŌēź 3 | 5.50 | 4.56ŌĆō6.62 | < 0.001 | 4.06 | 3.34ŌĆō4.95 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Peptic ulcer history | 1.87 | 1.74ŌĆō2.00 | < 0.001 | 1.38 | 1.28ŌĆō1.49 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Anticoagulant | 1.92 | 1.79ŌĆō2.06 | < 0.001 | 1.69 | 1.57ŌĆō1.83 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Acid suppressant and eupatilin vs. acid suppressant only | 0.87 | 0.76ŌĆō0.99 | 0.041 | 0.85 | 0.74ŌĆō0.97 | 0.016 |
Table┬Ā4
Univariate and multivariate analyses of factors for gastrointestinal bleeding in aspirin users including variables based on patients with the duration of prescription of acid suppressants and eupatilin
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | |
| Age, Ōēź 65 yr | 1.54 | 1.44ŌĆō1.65 | < 0.001 | 1.35 | 1.26ŌĆō1.45 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Male | 1.05 | 0.98ŌĆō1.12 | 0.159 | 1.10 | 1.03ŌĆō1.17 | 0.006 |
|
|
||||||
| CCI scorea) | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆā1 | 1.95 | 1.59ŌĆō2.40 | < 0.001 | 1.83 | 1.49ŌĆō2.25 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆā2 | 2.79 | 2.28ŌĆō3.41 | < 0.001 | 2.45 | 2.01ŌĆō3.00 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| ŌĆāŌēź 3 | 5.50 | 4.56ŌĆō6.62 | < 0.001 | 4.35 | 3.60ŌĆō5.25 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Peptic ulcer history | 1.87 | 1.74ŌĆō2.00 | < 0.001 | 1.38 | 1.29ŌĆō1.48 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Anticoagulant | 1.92 | 1.79ŌĆō2.06 | < 0.001 | 1.71 | 1.59ŌĆō1.83 | < 0.001 |
|
|
||||||
| Acid suppressant and eupatilin < 3 months vs. acid suppressant only | 0.83 | 0.70ŌĆō0.99 | 0.033 | 1.04 | 0.94ŌĆō1.14 | 0.492 |
|
|
||||||
| Acid suppressant and eupatilin Ōēź 3 months vs. acid suppressant only | 0.94 | 0.75ŌĆō1.16 | 0.552 | 0.88 | 0.78ŌĆō0.99 | 0.030 |
REFERENCES
1. Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al.; American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013;127:e6ŌĆōe245.

2. Antithrombotic TrialistsŌĆÖ (ATT) Collaboration; Baigent C, Blackwell L, et al.; Collins R. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 2009;373:1849ŌĆō1860.



3. Luepker RV, Steffen LM, Duval S, Zantek ND, Zhou X, Hirsch AT. Population trends in aspirin use for cardiovascular disease prevention 1980ŌĆō2009: the Minnesota Heart Survey. J Am Heart Assoc 2015;4:e002320.



4. Kang DO, An H, Park GU, et al. Cardiovascular and bleeding risks associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;76:518ŌĆō529.


5. Selak V, Kerr A, Poppe K, et al. Annual risk of major bleeding among persons without cardiovascular disease not receiving antiplatelet therapy. JAMA 2018;319:2507ŌĆō2520.



6. Lin KJ, Hern├Īndez-D├Łaz S, Garc├Ła Rodr├Łguez LA. Acid suppressants reduce risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients on antithrombotic or anti-inflammatory therapy. Gastroenterology 2011;141:71ŌĆō79.


7. Lai KC, Lam SK, Chu KM, et al. Lansoprazole for the prevention of recurrences of ulcer complications from long-term low-dose aspirin use. N Engl J Med 2002;346:2033ŌĆō2038.


8. Graham DY, Agrawal NM, Campbell DR, et al.; NSAID-Associated Gastric Ulcer Prevention Study Group. Ulcer prevention in long-term users of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: results of a double-blind, randomized, multicenter, active- and placebo-controlled study of misoprostol vs lansoprazole. Arch Intern Med 2002;162:169ŌĆō175.


9. Abraham NS, El-Serag HB, Johnson ML, et al. National adherence to evidence-based guidelines for the prescription of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Gastroenterology 2005;129:1171ŌĆō1178.


10. Lanas A, Sekar MC, Hirschowitz BI. Objective evidence of aspirin use in both ulcer and nonulcer upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterology 1992;103:862ŌĆō869.


11. Strate LL, Orav EJ, Syngal S. Early predictors of severity in acute lower intestinal tract bleeding. Arch Intern Med 2003;163:838ŌĆō843.


12. Chen WC, Lin KH, Huang YT, et al. The risk of lower gastroin-testinal bleeding in low-dose aspirin users. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017;45:1542ŌĆō1550.



13. Chan FK, Kyaw M, Tanigawa T, et al. Similar efficacy of proton-pump inhibitors vs H2-receptor antagonists in reducing risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers in high-risk users of low-dose aspirin. Gastroenterology 2017;152:105ŌĆō110.e1.

14. Nadatani Y, Watanabe T, Tanigawa TS, et al. Incidence and risk factors of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients on low-dose aspirin therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention in Japan. Scand J Gastroenterol 2013;48:320ŌĆō325.


15. Miyake K, Akimoto T, Hanada Y, et al. Proton pump inhibitors are associated with lower gastrointestinal tract bleeding in low-dose aspirin users with ischaemic heart disease. Dig Liver Dis 2015;47:757ŌĆō762.


16. Lu├® A, Lanas A. Protons pump inhibitor treatment and lower gastrointestinal bleeding: balancing risks and benefits. World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:10477ŌĆō10481.



17. Watanabe T, Sugimori S, Kameda N, et al. Small bowel injury by low-dose enteric-coated aspirin and treatment with misoprostol: a pilot study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;6:1279ŌĆō1282.


18. Bianchi Porro G, Parente F. Side effects of anti-ulcer prostaglandins: an overview of the worldwide clinical experience. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl 1989;164:224ŌĆō229discussion 229ŌĆō231.

19. Chan FK, Chung SC, Suen BY, et al. Preventing recurrent upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection who are taking low-dose aspirin or naproxen. N Engl J Med 2001;344:967ŌĆō973.


20. Taha AS, McCloskey C, Prasad R, Bezlyak V. Famotidine for the prevention of peptic ulcers and oesophagitis in patients taking low-dose aspirin (FAMOUS): a phase III, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2009;374:119ŌĆō125.


21. Kwok CS, Arthur AK, Anibueze CI, Singh S, Cavallazzi R, Loke YK. Risk of Clostridium difficile infection with acid suppressing drugs and antibiotics: meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1011ŌĆō1019.



22. Garc├Ła Rodr├Łguez LA, Ruig├│mez A, Pan├®s J. Use of acid-suppressing drugs and the risk of bacterial gastroenteritis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:1418ŌĆō1423.


23. Khalili H, Huang ES, Jacobson BC, Camargo CA Jr, Feskanich D, Chan AT. Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of hip fracture in relation to dietary and lifestyle factors: a prospective cohort study. BMJ 2012;344:e372.



24. Hoorn EJ, van der Hoek J, de Man RA, Kuipers EJ, Bolwerk C, Zietse R. A case series of proton pump inhibitor-induced hypomagnesemia. Am J Kidney Dis 2010;56:112ŌĆō116.


25. Choi SM, Shin JH, Kang KK, Ahn BO, Yoo M. Gastroprotective effects of DA-6034, a new flavonoid derivative, in various gastric mucosal damage models. Dig Dis Sci 2007;52:3075ŌĆō3080.



26. Huh K, Kwon TH, Shin US, et al. Inhibitory effects of DA-9601 on ethanol-induced gastrohemorrhagic lesions and gastric xanthine oxidase activity in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2003;88:269ŌĆō273.


27. Kim JS, Cha KH, Kang SY, et al. In vivo gastric residence and gastroprotective effect of floating gastroretentive tablet of DA-9601, an extract of Artemisia asiatica, in beagle dogs. Drug Des Devel Ther 2016;10:1917ŌĆō1925.


28. Seol SY, Kim MH, Ryu JS, Choi MG, Shin DW, Ahn BO. DA-9601 for erosive gastritis: results of a double-blind placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial. World J Gastroenterol 2004;10:2379ŌĆō2382.

29. Kim TJ, Kim ER, Hong SN, et al. Effectiveness of acid suppressants and other mucoprotective agents in reducing the risk of occult gastrointestinal bleeding in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug users. Sci Rep 2019;9:11696.




30. Kim SH, Lim YJ, Park J, et al.; Research Group for Capsule Endoscopy/Small Bowel Endoscopy. Changes in performance of small bowel capsule endoscopy based on nationwide data from a Korean Capsule Endoscopy Registry. Korean J Intern Med 2020;35:889ŌĆō896.




31. Lee HS, Nam JH, Oh DJ, Ahn HJ, Lim YJ. Association between eupatilin and reduction in small bowel bleeding in aspirin users and aspirin plus acid suppressant users. Korean J Intern Med 2023;38:484ŌĆō492.




32. Edogawa S, Takeuchi T, Kojima Y, et al. Current topics of strategy of NSAID-induced small intestinal lesions. Digestion 2015;92:99ŌĆō107.



33. Oh TY, Lee JS, Ahn BO, et al. Oxidative damages are critical in pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis: implication of antioxidants in its treatment. Free Radic Biol Med 2001;30:905ŌĆō915.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



