Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on antral gastrin and somatostatin cells and on serum gastrin concentrations
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
Helicobacter pylori infection induces selective reduction of the number of antral D-cells and results in abnormal regulation of serum gastrin secretion. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between H. pylori infection and the numbers of G-cells and D-cells.
Methods
The numbers of antral G-cells and D-cells, the ratio of G-cells to D-cells and fasting serum gastrin concentrations were compared between 37 patients with (29 with duodenal ulcers and 8 with gastric ulcers) and 33 without H. pylori infection (22 with duodenal ulcers and 11 with gastric ulcers). Serum gastrin concentrations were measured using the radioimmunoassay technique. Antral mucosal biopsy specimens were examined using immunohistochemical staining with antibodies specific for gastrin and somatostatin and the numbers of G-cells and D-cells per gastric gland were counted.
Results
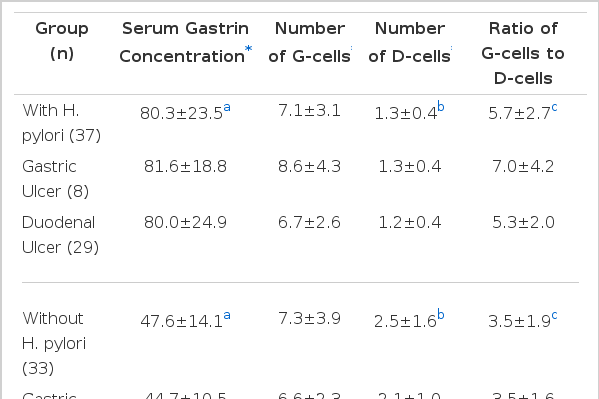
Fasting serum gastrin concentrations were significantly higher in patients with H. pylori infection compared to patients without infection (80.3±23.5 vs 47.6±14.1 pg/ml, p<0.001). The number of G-cells per gastric gland was similar in infected and uninfected patients (7.1±3.1 vs 7.3±3.9, respectively, p>0.5). The number of D-cells was significantly lower in patients with H. pylori infection than in uninfected patients in both duodenal and gastric ulcer patients (1.3±0.4 vs 2.5±1.6, respectively, p<0.001). The ratio of G-cells to D-cells was also significantly higher in infected patients compared with uninfected patients for both gastric and duodenal ulcers (5.7±2.7 vs 3.5±1.9, respectively, p<0.001).
Conclusions
These results strongly suggest that Helicobacter pylori infection induces reduction of the number of antral D-cells. The resulting relative hypofunction of the inhibitory action of D-cells against G-cells may be responsible for increased serum gastrin secretion.
INTRODUCTION
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is now recognized as the cause of type B gastritis, as a critical factor in the development and the recurrence of duodenal ulcer disease, and as an essential co-factor in the development of gastric carcinoma and gastric MALT-lymphoma1–5). Although estimation of the lifetime risk of developing an ulcer in people with H. pylori infection is difficult, it is believed that approximatley 10 – 15 % of individuals with H. pylori infection may develop an ulcer.6, 7) The link between H. pylori and the development of peptic ulcer disease may be related to the inappropriate release of gastrin observed in H. pylori-positive patients. One of the most notable H. pylori-associated changes in gastric secretion is an increased gastrin release after meals and after bombesin stimulation. This abnormality is alleviated following eradication of the infection8–14). It has also been shown that H. pylori infection can induce reversible increased basal and gastrin mediated acid secretion15, 16).
The mechanism by which H. pylori enhances gastrin release is not yet known but there have been increasing numbers of studies which show that changes in the numbers of antral G-cells and D-cells are responsible for the physiologic regulation of gastrin and gastric acid secretion. Many of the studies have suggested that H. pylori infection results in reduction of the number of antral D-cells and in the soamatostatin level resulting in a lack of inhibition of G-cells which leads to an increased amount of gastrin in the antrum and the serum.17–19 The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of H. pylori infection on the behaviour of the G-cell and D-cell populations and on the relationship between the serum gastrin concentration and the G-cell to D-cell ratio.
METHODS
Study Population
The study population consisted of 37 patients with infection and 33 patients without H. pylori infection. All of the 70 patients were either endoscopically and histologically confirmed benign gastric(GU) or duodenal ulcers (DU). Among H. pylori-positive patients, 29 patients had DU and 8 had GU. H. pylori-negative patients were divided as 22 DU and 11 GU patients. None of them had received H2-receptor antagonists, antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors or NSAIDs for at least 30 days prior to biopsy. Patients with any other chronic illness were also excluded.
Methods
Four gastric mucosal specimens were obtained from the antrum within 3 cm proximal to the pylorus. Two of the specimens were examined for identification of H. pylori and the other two were evaluated for the numbers of G-cells and D-cells. Patient selection criteria included subjects with two good histologic specimens which contained the entire section from the surface epithelium to the muscularis mucosae. The presence of H. pylori infection was confirmed by H & E staining, culture, and histologic examination of biopsy specimens. For measurement of the serum gastrin concentration, a blood sample was collected after overnight fast from each patient. Fasting gastrin concentrations were measured by the radioimmunoassay technique using a Gamm Dab[125I] Gastrin RIA kit (INCSTAR Co. UK) which specifically measures both G17 and G34. Results were expressed as ng/ml G17 equivalents. Each examination was duplicated.
Evaluation of Antral G-Cells and D-Cells
Gastric mucosal biopsy specimens were fixed in 10% buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin after routine dehydration and cleansing. Sections 5μm in thickness perpendicular to the surface of the mucosa, including a complete glandular portion and intact muscularis mucosae, were subjected to immunoperoxidase staining.
A complete glandular profile was defined as a gland totally within the microscopic field with a clearly visible lumen. For gastrin immunocytochemistry, the tissues were incubated overnight with rabbit antibiodies against the non-sulfated form of gastrin-17 (DAKO Corp., Copenhagen, Denmark). For somatostatin immunocytochemistry, the tissues were incubated with a polyclonal antibody raised against synthetic somatostatin (DAKO Corp., Copenhagen, Denmark). The secondary system in both cases consisted of an anti-rabbit ABC (avidin-biotin complex) kit (Biomeda Co., Foster). In both cases the reaction was developed with diaminobenzidine as the chromogen. Finally, the tissues were counterstained with H&E, then mounted.
Complete glandular profiles confined in the 7×7 grids of an eyepiece micrometer (Eyepiece Micrometer 20,4 OCM 7/7 SQ, Olympus Co., Japan) were selected and examined under a 40x objective for observation and quantitation of G-cells and D-cells. The total numbers of G-cells and D-cells in an entire grid square, including the nucleus in the plane section, were counted and the mean number of cells per millimeter of muscularis mucosae was calculated. All microscopic examinations were performed blindly by a pathologist unaware of either the individual serum gastrin level or the status of H. pylori infection.
Statistical Analysis
Results were expressed as the means±SD. A two-tailed, unpaired t-test and a Wilcoxon rank sum test were used to determine the significance of difference between means, with differences giving a p value less than 0.05 being considered significant. The number of each peptide-producing cell per gastric gland was calculated by dividing the total number of each cell type by the number of complete gland profiles counted from the same subject. The G-cell to D-cell ratio was calculated by dividing the numbers of G-cells by D-cells from the same subject, then averaging for the group.
RESULTS
Results are summarized in Table 1. There was no significant difference in the number of complete gastric gland profiles per field between patients with and without H. pylori infection. (9.8±2.7 vs 9.0±2.9, respectively, p>0.5).
Serum Gastrin Concentration
The fasting serum gastrin concentration was significantly higher in patients with H. pylori infection compared to patients without infection (80.3±23.5 vs 47.6±14.1 pg/ml, respectively, p<0.001) (Fig. 1). There were no differences in serum gastrin concentration between GU and DU patients within both the H. pylori-infected group (81.6±18.8 vs 80.0±24.9, respectively, p>0.5) and the H. pylori-uninfected group (44.7±10.5 vs 49.1±15.6, respectively, p>0.5).
G Cells
The mean number of G-cells per gastric gland was similar in patients with and without H. pylori infection. (7.1±3.1 vs 7.3±3.9, respectively, p>0.5) (Fig. 2). There were no differences in the number of G-cells between GU and DU patients within both the infected group (8.6±4.3 vs 6.7±2.6, respectively, p>0.5) and the uninfected group (6.6±2.3 vs 7.7±4.5, p>0.5).
D Cells
The mean number of D-cells per gastric gland was significantly lower in both GU and DU patients with H. pylori infection compared to patients without H. pylori infection (1.3±0.4 vs 2.5±1.7, respectively, p<0.001) (Fig. 3). There were no differences in the number of D-cells between GU and DU patients within both the H. pylori-infected group (1.3±0.4 vs 13.±0.4, respectively, p>0.5), and H. pylori-uninfected gruop (2.1±1.0 vs 2.6±2.0, respectively, p>0.5).
The Ratio of G-cells to D-Cells
The ratio of G-cells to D-cells was significantly higher in patients with H. pylori infection compared to patients without H. pylori infection (5.7±2.7 vs 3.5±1.9, p<0.001, respectively) (Fig. 4). There were no differences in the ratio between GU and DU patients within both the H. pylori-infected group (7.0±4.2 vs 5.3±2.0, respectively, p>0.5), and the H. pylori-uninfected group (3.5±1.6 vs 3.5±2.1, respectively, p>0.5).
DISCUSSION
The pathogenetic mechanism of H. pyori-associated peptic ulcer diseases have not been proved yet. However it is well known that a direct cytopathic effect of the organism on either the gastric or the duodenal epithelium is not involved in the development of peptic ulcer diseases because H. pylori is a non-invasive microorganism. One of the most characteristic abnormalities in gastric secretion induced by H. pylori infection is increased gastrin release after meals or after bombesin stimulation; this abnormality restored to its original state following eradication of the organism8–14). It has also been shown that H. pylori infection can induce reversible increased both basal and gastrin-mediated acid secretion15, 16). However, the mechanism by which the microorganism alters gastrin metabolism is still unclear. Since synthesis and secretion of somatostatin, which is a physiologic paracrine inhibitor of antral G-cell function, are directly regulated by the intragastric pH, there is substantial evidence that the increased gastrin secretion of H. pylori-positive patients is related to an interplay between antral G-cells and D-cells. Therefore, we measured the numbers of antral G-cells and D-cells and correlated these numbers with serum gastrin concentrations in both H. pylori-infected and H. pylori-uninfected patients.
Our study showed that the number of complete gastric gland profiles was not different between patients with and without H. pylori infection. The number of G-cells per complete gastric gland was also not different between H. pylori-positive patients and -negative patients. Similar observations were made by Queiroz et al18), Sankey et al20) and Moss et al21), who demonstrated that the number of antral G-cells is apparently not affected by the presence of H. pylori. With regard to the serum gastrin concentration our results are in agreement with earlier studies which show that H. pylori-associated abnormalities in gastrin secretion are reversible with alleviation of the bacterial infection8–, 11, 13, 22–25).
There were also no differences in serum gastrin concentration between GU and DU patients within both the H. pylori-infected group and the H. pylori-uninfected group. In this study, the number of D-cells per complete gastric gland was significantly lower in both GU and DU patients with H. pylori infection compared to patients without infection. Consequently, the ratio of G-cells to D-cells was also significantly higher in H. pylori-positive patients than in H. pylori-negative patients. There were no differences in the ratio between GU and DU patients within both the H. pylori-infected group and H. pylori-uninfected group. Similar results have also been reported17, 18, 26, 27).
The mechanism by which H. pylori decreases the number of antral D-cells should be considered. One possible explanation is an inflammatory change in the region of the D-cells. Recently, Kaneko H. et al17) and Moss et al19) have reported that H. pylori infection is associated with a decrease in somatostatin-mRNA and is associated with the somatostatin-immunoreactive cell density of the antral mucosa. These changes were reversed after eradication of H. pylori. The degree of reversal was correlated with the grade of chronic inflammation. These findings are consistent with the reports of Domschke et al28) and Sumii et al26). Ito et al29) also reported that the number of D-cells decreased in proportion to the extent and degree of chronic atrophic gastritis, and that D-cells disappeared earlier and more diffusely than G-cells. Another possibilty may be a local alkaline environment induced by ammonia which is produced by bacterial urease. This possibility is supported by previous studies30–34). These reports indicate that changes in intragastric acidity exert an influence on the antral D-cell density, on the tissue content of soamtostatin and on both the plasma and the antral gastrin concentration. Recently, there have been new efforts to explain the mechanism of increased gastrin release which is observed in patients with H. pylori infection. Graham et al35) observed that the number of G-cells was significantly lower in patients with DU than in either infected or uninfected controls, and that the ratio of G-cells to D-cells was similar in duodenal ulcer patients and in uninfected controls. They also found that, although eradication of the H. pylori infection results in a dramatic reduction in stimulated gastrin secretion, infection was not associated with a change in the number of either antral G-cells or D-cells in patients with DU. Based on these results they concluded that an H. pylori-associated increase in gastrin secretion appears to be related to local factors which regulate G-cell function. There are several reports regarding the role of cytokines, which are released by the inflammatory cells activated by H. pylori, in the regulation of antral G-cell function. These reports have suggested that interleukins, TNF-α or interferons stimulate gastrin secretion via receptors potentially residing on antral G-cells36–38).
In conclusion, our results strongly suggest that the exaggerated response of gastrin secretion observed in H. pylori-positive patients is due to a reduction of the antral D-cell mass because these cells normally inhibit the synthesis and release of gastrin.