Citation Analysis of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine from KoMCI, Web of Science, and Scopus
Article information
Abstract
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine (KJIM) is the international journal published in English by the Korean Association of Internal Medicine. To understand the position of the journal in three different databases, the citation indicators were elucidated. From databases such as Korean Medical Citation Index (KoMCI), Web of Science, and Scopus, citation indicators such as the impact factor, SCImago journal rank (SJR), or Hirsch Index were calculated according to the year and the results were drawn. The KJIM 2010 impact factor increased to 0.623 in Web of Science. That of year 2009 in KoMCI was a 0.149. The 2009 SJR in Scopus was 0.073, with a ranking of 27/72 (37.5%) in the category of internal medicine and 414/1,618 (25.6%) in the category of medicine, miscellaneous. The Hirsch Index from KoMCI, Web of Science and Scopus were 5, 14, and 16, respectively. The KJIM is now cited more by international researchers than Korean researchers, indicating that the content of the journal is now valued at the international level.
INTRODUCTION
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine (KJIM) is an international journal published in English by the Korean Association of Internal Medicine since 1986 [1]. From the launch of the journal to the end of 2010, 1,116 papers have been published. Although there is another official journal in South Korea named The Korean Journal of Medicine (Taehan naegwa hakhoi chi) that has been published since 1949, the journal in English was necessary to circulate the medical information from Korea worldwide. From the first issue of the journal, whole issues have been indexed in Medline and its contents have been accessible through Medline before 1996 and through PubMed since 1996 [2]. Up to the year 2000, it was one of the five Korean medical journals to be indexed in Medline before 2000, indicating its central place in the academic medical literature of Korea. Nowadays, a much larger number of international medical journals from Korea are being published. Therefore, to recruit the best quality manuscripts, the KJIM has to compete not only with journals abroad but also with other local journals. The KJIM is now indexed in many major international databases and some local ones: Medline, PubMed, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, Biosis Previews, Crossref, KoreaMed, KoreaMed Synapse, and Korean Medical Citation Index (KoMCI). This allows for wide exposure and the opportunity for sound and insightful content to be cited by other journals throughout the world. The year 2010 was the KJIM's 25th anniversary, so it is appropriate to take stock of the journal's position among general and internal medicine journals internationally by evaluating its citation indicators. Of the citation indicators, the impact factor, SCImago journal rank (SJR), and Hirsch Index (h-index) were calculated from the KoMCI, Web of Science, and Scopus databases [3-5]. The results of this analysis may suggest directions for ongoing development of the KJIM's quality.
Methods of obtaining citation indicators
Databases
KoMCI is the citation database maintained by the Korean Academy of Medical Science. Journals indexed are KoreaMed journals, of which there were 156 in 2009. The citation information has been included since 2000. Journals are indexed in KoreaMed after an evaluation process by the Korean Association of Medical Journal Editors [6]. Web of Science is the database maintained by Thomson Reuters and currently indexes 8,269 Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) journals. Scopus is the database maintained by Elsevier and contains over 18,000 journals.
Citation indicators
Calculation of the impact factor was based on the KoMCI Web and Journal Citation Ranking provided by Thomson Reuters. It can be calculated as follows:

The three, four, or five year impact factor is calculated in a similar fashion, using publication and citation data from the relevant number of years.
The Impact Index in SCImago Journal & Country Ranking originated from Scopus is calculated in the same way as the impact factor of Journal Citation Reports (JCR) or KoMCI, but instead takes into account the 18,000 + journals of Scopus.
The Z impact factor is an impact factor excluding self citation. It can be obtained from KoMCI Journal Web. For the Web of Science, the Z impact factor is the same as the impact factor since the KJIM is not indexed in Web of Science yet.
The SJR formula is complicated to calculate and to explain [7]. It reflects the prestige of the citing journal. For example, there are two journals with same impact index. If the highly-prestigious journal cites one journal, its SJR becomes higher than the other journal's SJR. It was developed by Elsevier, and it is also a good indicator of the citation position of a journal in a category.
The h-index is defined as the number of papers with a citation number ≥ h. A scientist has index h (the Hirsch number) if h of his or her Np (number of published) papers have at least h citations each and the other (Np - h) papers have ≤ h citations each [8]. The h-index was originally designed for the scientific productivity and quality of individual researchers. However, it can be applied to each journal, department, or institute.
Method of data collection and analysis
For the citation indicator of KoMCI, the KoMCI Journal Web was searched and the impact factor and Z impact factor for KJIM was located. H-index was manually calculated from KoMCI Web. For impact factor from Web of Science, the KJIM was searched through the Cited Reference Search in Web of Science. The impact factor was calculated according to the year and the h-index was also noted. The impact factor calculated from Web of Science was separately analyzed for reviews or original articles and for case reports. For those from Scopus, the data in SCImago Journal & Country Ranking was searched and the SJR and impact index for KJIM was summarized according to the year. However for the h-index, Scopus was searched because the data in the SCImago Journal & Country Ranking included content up to the year 2009.
Impact factor
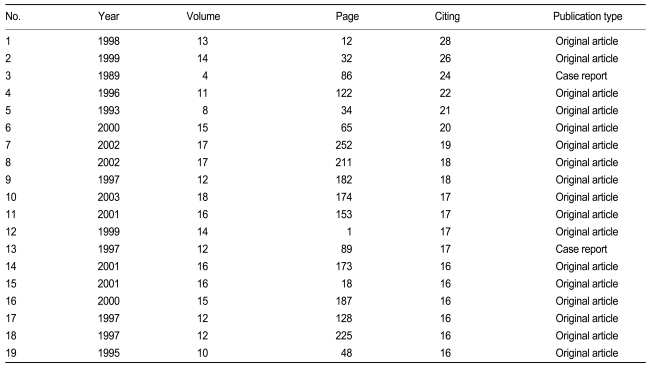
The chronological changes in the impact factor and Z impact factor of KJIM of the KoMCI Journal Web is illustrated in Fig. 1. There was no remarkable difference between the two factors. The average impact factor for 10 years was 0.162 and average Z impact factor was 0.158. Although the ranking of the KJIM impact factor in 2009 was 74 out of 156 Korean medical journals, that of its Z impact factor in 2009 was 26 out of 156.

Impact factor (IF) and Z impact factor (ZIF) of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine from 2000 to 2009 in Korean Medical Citation Index (KoMCI) Journal Web.
The impact factor calculated from the Web of Science is illustrated in Fig. 2. The average impact factor from 2000 to 2010 was 0.36. It soared to 0.62 for 2010 from 0.41 in 2009. If this value is compared with other journals in the category of general and internal medicine in the Web of Science, the ranking in 2009 corresponds to 111th out of 133 journals. Although there is still no impact factor for 2010 in the JCR Web, the journal ranking of KJIM can be estimated as 95th if there is no change in the impact factors of the other SCIE journals of the same category in 2010. Total citations and the number of papers published in each year are presented in Fig. 3. The total citation count jumped to 303 in 2010. Since the total citation count in 2000 was 85, it increased 3.5 times compared to 10 years earlier. As for the source titles, the Journal of Korean Medical Science is the journal that has cited KJIM most frequently. Also the Yonsei Medical Journal is the fifth most frequently citing journal. Those two journals are top quality general medicine journals in Korea. The other top citing journals are all international journals. Out of them, five journals belong to the gastroenterology category (Table 1). The 10 countries of authors that cited the KJIM most frequently from 2000 to 2010 in the Web of Science is shown in Fig. 4. Researchers from the U.S. rank first in the list for citing KJIM.

Impact factor (IF) of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine from 2000 to 2010 manually calculated from Web of Science [cited 2011 Jan 17].
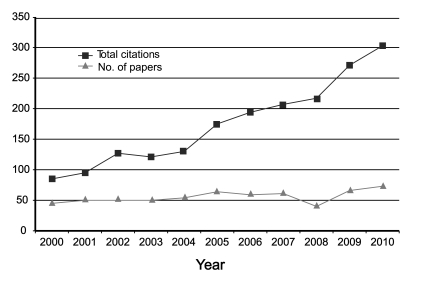
Total citations and number of papers of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine from 2000 to 2010 manually calculated from Web of Science [cited 2011 Jan 17].
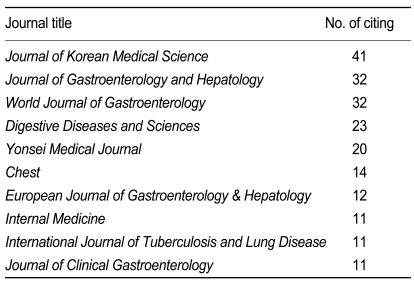
Top 10 journals cited The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine most frequently from 2000 to 2010 in Web of Science
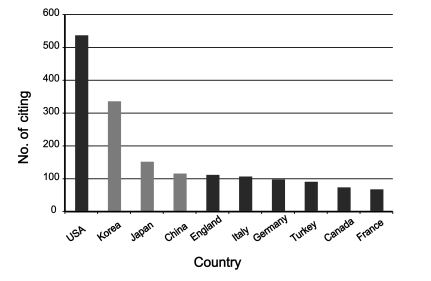
Countries of authors who cited The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine from 2000 to 2010 manually calculated from Web of Science [cited 2011 Jan 17].
As for the impact factor of 2010, there was a notable difference in impact factors for original articles or reviews and for case reports. The impact factor for reviews or original articles was 0.878 and that of case reports was 0.3125.
The chronological impact index and SJR of the KJIM in the SCImago Journal & Country Rank is presented in Fig. 5. The SJR and impact index has been steadily maintained for 10 years. The SJR fluctuated from 0.059 to 0.089. The impact index ranged from 0.38 to 0.56. The value of the impact index was higher than that of the impact factor over the 10 years. Since there is no data for 2010, it is not possible to compare the values for that year. The SJR ranking of KJIM in 2009 is 27th out of 72 journals (37.5%) in the internal medicine category and 414th out of 1,618 journals (25.6%) in the miscellaneous medicine category. When Scopus journals from Korea were compared, this journal's SJR ranking was 13th out 115 journals.
H-index
The h-index in KoMCI Web was 5. Those highly cited papers in KoMCI Web are listed in Table 2. The h-index in Web of Science was 14. The highly cited papers from the Web of Science are listed in Table 3. The h-index in Scopus was 16. Those from Scopus are shown in Table 4. The value of the h-index (16) manually calculated from Scopus was different to h-index (15) in SCImago Journal & Country Ranking since there was the addition of papers to the Scopus database in 2010. All papers in Table 3 were also included in Table 4. The h-index ranking in SCImago Journal & Country Ranking is 23 out of 72 (31.9%) in the internal medicine category, being higher than the SJR ranking (37.5%). Ranking in miscellaneous medicine is 445 out of 1,618 (27.5%), which is similar to the ranking by SJR (25.6%).
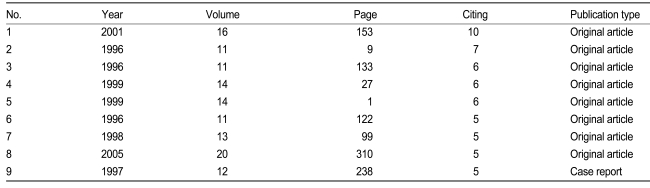
Mostly highly cited papers of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine in KoMCI Web [cited 2011 Feb 14]

Mostly highly cited papers of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine in Web of Science [cited 2011 Feb 14]
Position and directions for ongoing development
After obtaining the results of the citation analysis of the journals, the following questions can be raised: First, how much is the journal cited by local and international researchers? Second, what is the ranking of the journal according to the various citation indicators? Third, what may be a trigger event to increase the citation indicators? Fourth, what may be an editor's strategy to increase the scores of the citation indicators?
The citations from KoMCI Web are presented as the impact factor and Z impact factor. When the impact factors from KoMCI Web and from Web of Science were compared, it can be said that citations from researchers abroad were more frequent than those from local researchers. This is taken for granted, since KJIM is searchable from all over the world via PubMed so that many researchers or physicians can read the papers. Also, out of the top 10 most frequent sources of citation, two journals--the Journal of Korean Medical Science and Yonsei Medical Journal--are from Korea. The others are international titles (Table 1). These two journals have been indexed in the Web of Science since 1999 and 1988, respectively, and have become major sources of citations of many medical journals from Korea.
The relatively high SJR ranking of KJIM in 2009 (37.5%) in the internal medicine category and in the miscellaneous medicine category (15.6%) means that this is one of the influential journals in its category. However, when the impact factor of JCR is concerned, its ranking is 83.5% in the general and internal medicine category. The difference in ranking from two databases might originate from the difference in the algorithm of calculation and the difference in the set journals compared. If the impact factor of 2010 is introduced to JCR 2009, its ranking soars to 95/133 (71.4%). Since impact factors of other journals may also have increased in 2010 JCR, this estimate may be inaccurate.
Although there was a difference between Web of Science and Scopus in the set of journals covered, the h-index was not so different. Every paper ranked as highly cited from Web of Science was included in the highly cited papers in Scopus. The h-index of KJIM will continue to increase year by year if the present citation trends continue. Out of medical journals from Korea, a recent bibliometric analysis of the Korean Journal of Parasitology was publicized in 2009 [9]. In that paper, the h-index from the Web of Science was 17 and that from Scopus was also 17. This value is similar to those of KJIM. Since the Korean Journal of Parasitology had existed for 47 years as of 2009, the h-index of KJIM base on a 25-year history is difficult to be compared. H-index of Yonsei Medical Journal and that of the Journal of Korean Medical Science in 2009 SCImago Journal & Country Ranking were 30 and 26 respectively [7]. Yonsei Medical Journal has been published from 1960 and its number of papers is 2,930 until February 2011. The Journal of Korean Medical Science has been published since 1986 and its total number of papers is 3,308. Therefore, KJIM's h-index is of significance when number of papers is considered.
Why did the impact factor of KJIM increase so dramatically in 2010? Probably the quality of papers increased and the effect of indexing in PMC increased the exposure of the papers to readers. KJIM began to be indexed in PMC from June 17, 2009.
How should an editor try to increase the impact factor of a journal? First, case reports should be more focused to the clinically or diagnostically representative ones since the frequency of citation of case reports is 35% of that of reviews or original articles. Also, out of highly cited articles in Tables 2-4, the case reports constitute 11.6% (5/43). Proportion of case reports out of total number of papers is 37.5% (378/1,009). Proportion of highly cited papers is less in case reports than in other publication types. Other method is to receive high quality papers with clinically important study designs such as cohort studies, double blind randomized trials, multi-institutional studies, nationwide epidemiological surveys, multi-national studies and meta-analyses. Furthermore, if a digital object identifier were assigned to every paper from the first issue, it would help to increase the total citation count.
CONCLUSION
In Korea, out of 23 specialties in medicine, the number of internists is the greatest. Internal medicine is the leading field in specialties in medicine. The Korean Association of Internal Medicine has published two journals, one in English and the other in Korean. The former is for international readers and the latter is for local readers and trainees. From the above data, it can be said that KJIM has become an international journal, cited more frequently by international researchers than those in Korea. If it becomes a SCIE journal, it will be easier to see its bibliometric position in the Web of Science.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Research Grant from the Centers for Diseases Control, Republic of Korea (2010E1100200).
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.