 |
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 30(5); 2015 > Article |
|
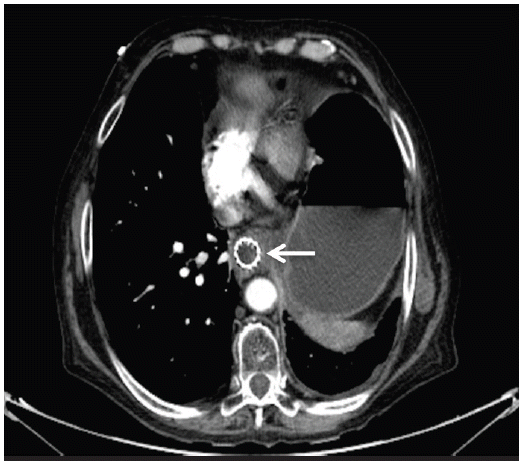
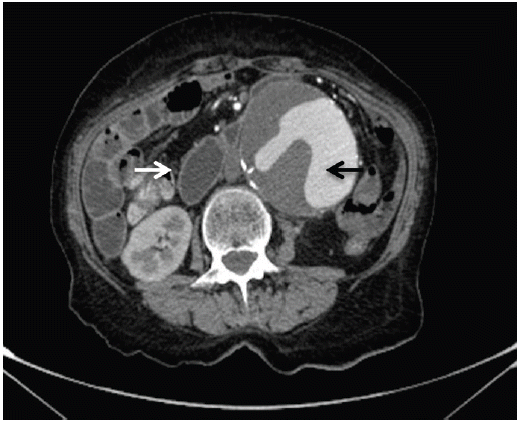
An 85-year-old male with stage IV lung cancer, being treated with palliative chemo-radiotherapy for nine months, presented with nausea, early satiety, bilious vomiting, and abdominal pain for 2 weeks prior to admission. During staging, computed tomography revealed an abdominal aortic aneurysm; however, only surveillance was indicated. A month earlier, a self-expandable metallic stent had been placed in the esophagus at the midlevel to alleviate external compression by mediastinal malignant adenopathy (Fig. 1). On physical exam he was cachexic and dehydrated, and a pulsatile mass in the epigastrium was noted. All distal pulses were present and equal bilaterally. Endoscopy revealed external compression of the third portion of the duodenum. Abdominal computed tomography revealed a 13 ├Ś 8.5 ├Ś 8.5 cm infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm with partial duodenal obstruction and distension of the stomach and proximal duodenum (Fig. 2). After discussion with the patient, a nasojejunal enteral feeding tube was offered, but the patient refused any further treatment and was discharged with prokinetic medication.
Aortoduodenal syndrome is a rare cause of intestinal obstruction, with fewer than 40 cases reported. The most frequent symptoms at presentation are vomiting, pulsatile abdominal mass, abdominal pain, weight loss, and electrolyte disturbances. There is male predominance, and most patients are 60 years of age or older. The syndrome is rare before the age of 40 years. Computed tomography with contrast, followed by either upper gastrointestinal contrast-enhanced imaging or upper endoscopy, establishes the diagnosis and rules out other causes of gastric outlet obstruction. Surgical intervention is indicated in all patients except those who are too debilitated to withstand any intervention. Before the advent of aortic surgery, therapy consisted primarily of palliative gastric bypass. Resection of the aneurysm and graft replacement is the procedure of choice.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



